Study Guide Test 2 – Answer Key
advertisement
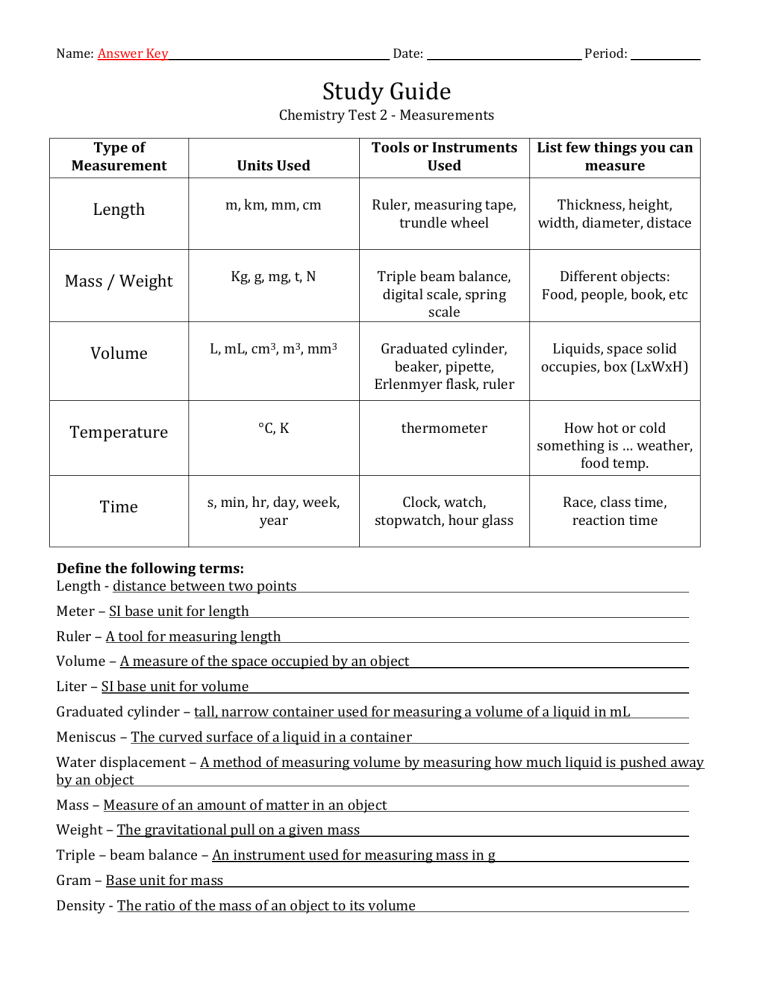
Name: Answer Key Date: Period: Study Guide Chemistry Test 2 - Measurements Type of Measurement Units Used Tools or Instruments Used List few things you can measure Length m, km, mm, cm Ruler, measuring tape, trundle wheel Thickness, height, width, diameter, distace Mass / Weight Kg, g, mg, t, N Triple beam balance, digital scale, spring scale Different objects: Food, people, book, etc Volume L, mL, cm3, m3, mm3 Graduated cylinder, beaker, pipette, Erlenmyer flask, ruler Liquids, space solid occupies, box (LxWxH) Temperature °C, K thermometer How hot or cold something is … weather, food temp. Time s, min, hr, day, week, year Clock, watch, stopwatch, hour glass Race, class time, reaction time Define the following terms: Length - distance between two points Meter – SI base unit for length Ruler – A tool for measuring length Volume – A measure of the space occupied by an object Liter – SI base unit for volume Graduated cylinder – tall, narrow container used for measuring a volume of a liquid in mL Meniscus – The curved surface of a liquid in a container Water displacement – A method of measuring volume by measuring how much liquid is pushed away by an object Mass – Measure of an amount of matter in an object Weight – The gravitational pull on a given mass Triple – beam balance – An instrument used for measuring mass in g Gram – Base unit for mass Density - The ratio of the mass of an object to its volume 10 mm 1. How many millimeters are in one centimeter? (Think about a metric ruler, how many little lines are between each numbered centimeter?) 2. What type of measurement would each group of the following metric units be used for? volume a. mL, L, cm3 length b. m, cm, km mass c. g , kg, mg time d. s, min, hr temperature e. °C, K 3. Record the measurement of the following line in centimeters and then in millimeters. (don’t forget units) 3.1 cm 31 mm 4. What is the volume in mL of the liquid in each of the following graduated cylinders? (don’t forget units) 2.8 mL 44 mL 7 mL 5. Determine the metric volume of the cube below. Remember – a cube is composed of six equal sides. V=LxWxH V = 1.3 cm x 1.3 cm x 1.3 cm = 2.197 cm3 2.2 cm3 V = 38 mL – 24 mL 6. What method for finding volume of an irregular shaped object is depicted in the diagram to the right? 38 mL Water displacemetn 7. Find the volume of the rock. 24 mL 14 mL 8. What do you call the curved, upper surface of water that commonly appears when using a graduated cylinder? meniscus 9. What equation do you use to find the volume of a box? V = Length x Width x Height 10. Find the volume of the boxes (don’t forget the correct units) 40 cm3 305.3 cm3 11. What is the name of the instrument to the right? Triple beam balance 12. What is the instrument to the right used to measure? mass 13 a. What is the name of the instruments to the right? Graduated cylinder / beaker 13 b. What is the instruments to the right used to measure? volume Graduated cylinder beaker 14. What are the three ways you can write the density equation to be able to solve for density, mass or volume? d = m/V m=dxV V = m/d 15. 500 grams of sugar occupies a volume of 0.315 L. What is the density of the sugar in g/mL? 1.6 g/mL d = m/V d = 500g / 315 mL = 1.587 mL 16. The density of a substance is 1.63 g/mL. What is the mass of 0.25 L of the substance in grams? 407.5 g m=dxV m = 1.63 g/mL x 250 mL = 407.5 g 17. The density of pure solid copper is 8.94 g/mL. What volume does 5 kg of copper occupy? 559.3 mL V = m/d V = 5000g / 8.94 g/mL = 559.3 mL 18. What is the mass of a 450 cm³ block of silicon if the density of silicon is 2.336 g/cm³? 1062 g m=dxV m = 2.36 g/cm3 x 450 cm3 = 1062 g 19. What is the mass of a 15 cm cube of iron if the density of iron is 7.87 g/cm³? 26561.3 g m=dxV m = 7.87 g/cm3 x 3375 cm3 m = 26561.25 g 20. What is the mass in grams in the diagram to the right? 317.7 g V=LxWxH V = 3375 cm3