Health_Fact_Sheets_files/Hand Foot & Mouth Disease Fact Sheet
advertisement

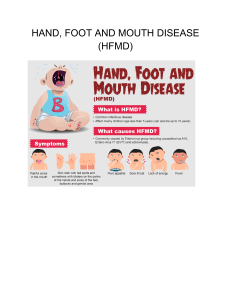
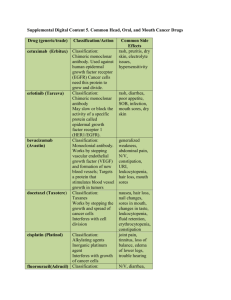
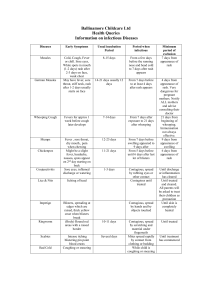
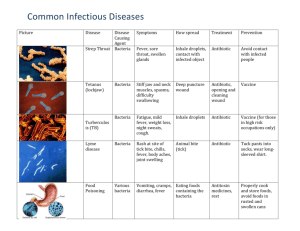
Hand, Foot, & Mouth Disease - Fact Sheet Hand, foot & mouth disease is a common viral illness that can occur in children and adults. Initial symptoms start with a fever, poor appetite, feeling “sick” and a sore throat. Painful sores usually develop in the back of the mouth 1 or 2 days after the fever starts. These begin as small red blisters and may develop into ulcers. A skin rash develops over 1 to 2 days usually on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash may also appear on the knees, elbows and genital area. This rash may be flat or raised red spots which may develop into blisters. Not every persons infected with the virus will exhibit all of these symptoms. Health complications are not common however dehydration may develop from difficulty swallowing due to the presence of mouth sores. The virus is contained in nose & throat secretions, fluid from the blisters, and feces. The virus is spread through close personal contact, sneezing & coughing, contact with contaminated feces, and/or contact with contaminated objects and surfaces. Infected persons are most contagious during the first week of illness but some may be contagious for days or weeks after symptoms disappear. Infected persons should stay home while sick and experiencing symptoms. There is no vaccine to protect against hand, food & mouth disease. Good hand washing, cleaning & disinfecting frequently touched surfaces, & avoiding close contact with persons infected with the virus are effective in preventing the spread of this virus. There is no treatment for this disease but symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever and/or using mouthwashes/sprays to numb mouth pain.