Physics - Atharva Tutorial
advertisement

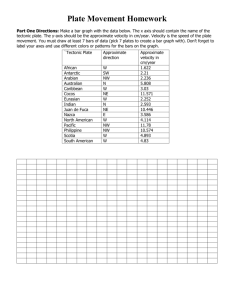
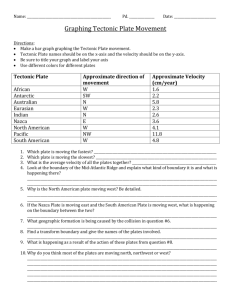
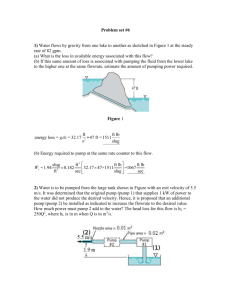
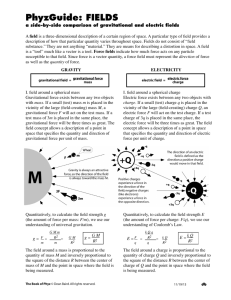
ATHARVA TUTORIALS Unit Test:11 th Chapter Name: Gravitation & Electrostatics Date: 15/07/12 Subject: Phy-I &II Marks:40 Std: XII Time: 2:00hour SECTION I Q. 1 Select the most appropriate option from the given alternatives. [5] 1) Dimensions of gravitational constant G are……. a) [M1L2T–1] b) [M0L1T–2] c) [M–1L3T–2] d) [M1L1T–2] 2) If The distance between the two masses is made half , then the gravitational force of attraction between them is………….. a) Doubled b) increased four times c) reduced to half d) reduced to quarter 3) As we go away from the equator towards poles, the weight of the body…….. a) increases b) decreases c) remains same d) cannot be determined 4) The escape velocity of a body from the earth’s surface is ……… a) 8 km/s b) 11.2 km/s c) 112 km/s d) 9.8 km/s 5) At…….. height above the earth’s surface the gravitational acceleration is 4% of its original value. a) h = R b) h = 2R c) h = 4R d) h = 3R Q.2 Attempt any two from the given questions. [6] 1) Discuss the variation of g with depth. 2) Define critical velocity of a satellite and obtain an expression for it. 3) Define binding energy and obtain an expression for binding energy of a satellite revolving in a circular orbit round the earth. Q.3 Attempt any two from the given questions. 1) State and explain Newton’s law of gravitation. [4] 2) State kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 3) Define escape velocity. Derive an expression for the escape velocity of an object from the surface of the earth. Q.4 Attempt question ‘A’ and ‘B’ [5] 𝟑 A) Density of the earth is 5478 𝒌𝒈/𝒎 . Assuming the earth to be homogeneous sphere. Find the value of g on the surface of the earth. B) Find the escape velocity from the earth for a 1000 kg mass and find the kinetic energy it must have at the surface of the earth in order to escape the Earth’s gravitational field. SECTION II Q.1 Select the most appropriate option from the given alternatives. [5] 1) Which of the following law gives a relation between the electric flux through any closed surface and the charge enclosed by the surface? a) Coulomb’s law b) Charle’s law c) Newton’s law d) Gauss’s law 2) The maximum electric flux can be passed through the surface when electric intensity would by inclined to the surface by an angle of ……. a) 180° b) 90° c) 0° d) 360° 3) The capacity of a parallel-plate condenser is inversely proportional to the a) Dielectric constant of the medium b) area of the plate c) length of the plate d) distance between the two plates 4) To reduce the capacity of a parallel-plate condenser, we shall find that the separation between the plates is ……. a) reduced and area of plates is increased b) decreased and area of plates is decreased c) increased and area of plates is increased d) increased and area of plates is decreased 5) A parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance of 50 μF in air and 110 μF when immersed in an oil. The dielectric constant k of the oil is ….. a) 0.2 b) 1.5 c) 2.2 d) 2.5 Q.2 Attempt any two from the given questions. [6] 1) Explain the effect of dielectrics on capacity of a parallel plate capacitor. 2) Derive an expression for energy stored in charged capacitors Explain its different forms. 3) Obtain an expression for electric field intensity at a point outside infinitely long charged conducting cylinder. Q.3 Attempt any two from the given questions. [4] 1) Whit do you mean by polar molecules and non-polar molecules 2) Define capacity of a conductor. State and define S.I. unit of capacity of condenser. 3) Draw a neat labelled diagram of van de Graaff generator. Q.4 Attempt question ‘A’ and ‘B’ [5] A) A Bakelite cube having each side of length 2 cm is kept in electrostatic field of intensity 300 V/m. Calculate energy contained in Bakelite cube (Dielectric constant of Bakelite = 5) B) A Circular metal plate of radius 2 cm is charged with 10μC situated in air. Calculate mechanical force acting on one side of plate .If the same circular plate carrying same charge were kept in acetone, what would be magnitude of mechanical force? (K acetone = 27 )