MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art
advertisement
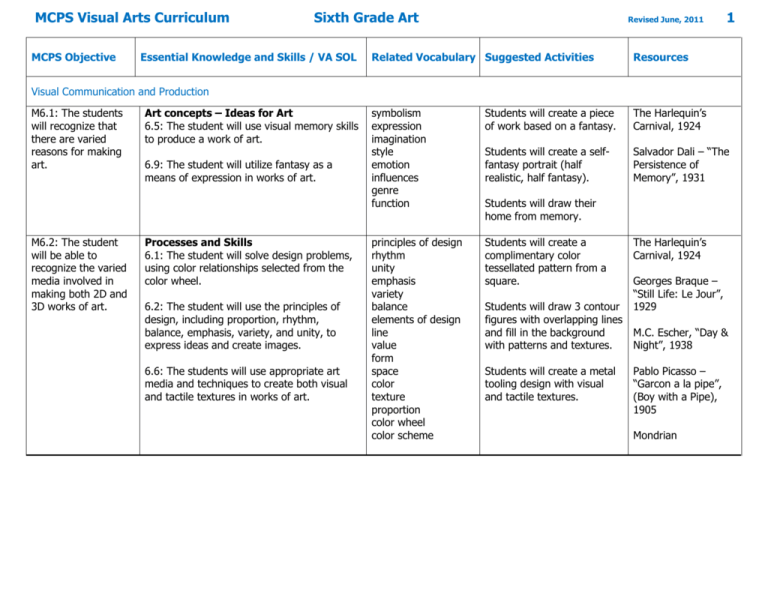
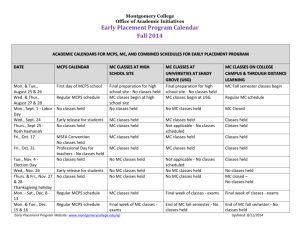
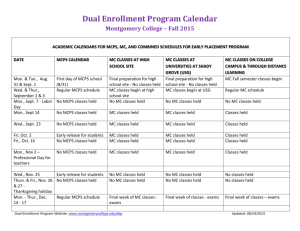
MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum MCPS Objective Sixth Grade Art Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Revised June, 2011 1 Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources symbolism expression imagination style emotion influences genre function Students will create a piece of work based on a fantasy. The Harlequin’s Carnival, 1924 Students will create a selffantasy portrait (half realistic, half fantasy). Salvador Dali – “The Persistence of Memory”, 1931 principles of design rhythm unity emphasis variety balance elements of design line value form space color texture proportion color wheel color scheme Students will create a complimentary color tessellated pattern from a square. Visual Communication and Production M6.1: The students will recognize that there are varied reasons for making art. M6.2: The student will be able to recognize the varied media involved in making both 2D and 3D works of art. Art concepts – Ideas for Art 6.5: The student will use visual memory skills to produce a work of art. 6.9: The student will utilize fantasy as a means of expression in works of art. Processes and Skills 6.1: The student will solve design problems, using color relationships selected from the color wheel. 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. 6.6: The students will use appropriate art media and techniques to create both visual and tactile textures in works of art. Students will draw their home from memory. Students will draw 3 contour figures with overlapping lines and fill in the background with patterns and textures. Students will create a metal tooling design with visual and tactile textures. The Harlequin’s Carnival, 1924 Georges Braque – “Still Life: Le Jour”, 1929 M.C. Escher, “Day & Night”, 1938 Pablo Picasso – “Garcon a la pipe”, (Boy with a Pipe), 1905 Mondrian MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 2 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.3: The student will recognize the use of line in one point perspective drawing. Line 6.3: The student will use one-point perspective to create the illusion of depth in a two-dimensional drawing. contour implied line middle ground directional perspective background vanishing point horizon line texture illusion foreground texture overlapping Students will draw their bedroom from memory in 1 point perspective. Van Gogh – “Bedroom in Arles”, 1888 Students will create simple geometric shapes in 1 point perspective. Raphael – “The School of Athens” geometric organic (free form) foreground middle ground background placement details shapes Students will create a Notan (Japanese for the interaction between dark and light) collage using a simple square from which shapes are cut, and every cut out shape is arranged symmetrically around the central figure. Picasso, “Three Musicians”, 1921 three – dimensional form length x width x height organic geometric space kinetic Students will create a Georgia O’Keeffe style painting of a close up of a flower. Alexander Calder, “The General Sherman”, 1945 M6.4: The student Shape will recognize shape 6.3: The student will use one-point as an element of art. perspective to create the illusion of depth in a two-dimensional drawing. M6.5: The student will recognize form as a means of creating 3-D works of art. Form 6.8: The student will produce a kinetic work of art. Georges Braque, “Fishing Boats”, 1909 Edward Hopper, “Nighthawks”, 1942 Henri Moore, “Reclining Figure”, 1951 Georgia O’Keeffe, “Poppy”, 1927 Claus Oldenburg MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.6: The student will recognize color relationships. Color 6.1: The student will solve design problems, using color relationships selected from the color wheel. monochromatic analogous complementary warm cool hue tint shade primary secondary tertiary intermediate color schemes triadic split complimentary pastel Students will create monochromatic paintings. Claude Monet, “Nympheas”, 1915 Students will create tessellations showing specific color schemes. Picasso three-dimensional form space highlight shadow reflection blending chiaroscuro Student will transfer a circle into a sphere using shading. copper/metal tooling texture implied actual tactile texture visual texture Students will create their own interpretation of van Gogh’s “Starry Night” and apply some of his techniques. M6.7: The student will recognize chiaroscuro as a means of creating the illusion of form. M6.8: The student will recognize media and techniques to create both tactile and visual textures. Value 6.7 The student will use chiaroscuro to create the illusion of form in a work of art. Texture 6.6: The students will use appropriate art media and techniques to create both visual and tactile textures in works of art. Students will create warm and cool landscapes or portraits. 3 Munch – “The Scream”, 1893 Students will create a composition of a still life in a color scheme. Students will divide a simple drawing with intersecting lines, and shade in the resulting spaces with alternation gradation of values. Students will create masks. Students will create works using weaving techniques. Michelangelo Merisi da Caravagio, “St. Jerome”, 1605-1606 Durer Henry Ossawa Tanner, “The Banjo Lesson”, 1893 van Gogh, “Starry Night”, 1889 Butterfield Faith Ringgold Jackson Pollock MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 4 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.9: The student will recognize the use of proportion to express ideas and create images. Proportion 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. siting Albrecht Durer, ”Selfportrait”, 1500 Students will create a selfportrait showing understanding of facial proportions. Alice Neal 6.4: The student will depict the proportional relationships among the parts of the human body or among other objects. M6.10: The student will create a kinetic work of art. Rhythm/Movement 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. da Vinci repetition alternation wire contours optical illusions Students will create a freestanding mobile/stabile based on natural or abstract forms using the principles of balance. Alexander Calder, “Myxomatose”, 1953 symmetrical asymmetrical radial formal informal Students will create 2D or 3D compositions using types of balance – symmetrical and/or asymmetrical. Paul Cezanne, “Mont Sainte-Victoire”, 1882-1885 M. C. Escher 6.8: The student will produce a kinetic work of art. M6.11: The student will recognize balance as a principle of art. M6.12: The student will recognize emphasis as a principle of art. Balance 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. Emphasis 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. focal point dominant center of interest Students will create a radial mandala using colored pencils. Rose Window, Notre Dame Cathedral Mandalas Students will create a digital self-portrait in Pop Art style. Rene Magritte, “The Portrait”, 1935 Students will create a composition with a definite focal point. Andy Warhol, “Campbell Soup”, 1968 Students will create a collage. Litchenstien O’Keeffe Rembrandt MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum MCPS Objective Sixth Grade Art Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities M6.13: The student Variety will recognize variety 6.2: The student will use the principles of as a principle of art. design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. M6.14: The student will recognize unity as a principle of art. Unity 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. Revised June, 2011 Students will create a work using water color, glue, and markers – Kandinsky style. 5 Resources Klimt Kandinsky Students will create an abstract image from a series of realistically drawn objects. harmony oneness order Students will create a composition (2D or 3D) of unifying shapes, color, etc. Students will create a Japanese style scroll of their own land in which they will rule as emperor or empress. Hokusai, “Mt. Fuji Off Kanagawa”, 1829-32 Nevelson Rodin Jasper Johns Michelangelo M6.15: The student will recognize how to create original works of art using computer graphics and text. Technology 6.10: The student will use computer graphics and computer-generated text to create original works of art. gradient software insert graphics select save rotate delete menu bar cursor tools edit Students create tessellated patterns from a square using computer paint programs. Andy Warhol, “Cars art work”, 1986 Microsoft Paint Photo Shop Google Sketch Up F. Lloyd Wright MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities M6.16: The student will recognize that critical thinking and meaningful writing are part of the artistic process. Artistic Development 6.1: The student will solve design problems, using color relationships selected from the color wheel. observation description steps=procedure critique – evaluate success/failure 6.2: The student will use the principles of design, including proportion, rhythm, balance, emphasis, variety, and unity, to express ideas and create images. 6 Resources Students will describe their Rubrics project on a 3 x 5 card which will include a sequence of steps, describe the process, and explain the overall outcome. Students will create a shading chart and tinting chart of the 3 primary colors. Cultural Context and Art History M6.17: The student will recognize an artist’s style media, method, and subject matter. Artists/Works 6.12: The student will identify the components of an artist’s style, including materials, design, technique, and subject matter. art movements Students will analyze various artistic styles by describing subject, colors, techniques, and shapes. Monet – “Poplars”, 1891 M6.18: The student will recognize the relationship between art movements and changes in science and technology (from 1877present). Historical 6.13: The student will identify major art movements in American culture from 1877 to the present, with emphasis on relating these movements to changes in science and technology. Arts and Crafts Movement Renaissance Commercial Art Nouveau Tribal Futurism Pop Art Ethnic Modernism Religious The student will select a painting by an artist and discuss how culture, society, science, and technology influenced the artist. Sargent – “Paul Helleu Sketching with his Wife”, 1889 The student will discuss the “Pop Art” movement using Andy Warhol’s “Campbell Soup”. O’Keeffe – “Red Canna”, 1923 A. Wyeth – “Christina’s World”, 1948 A. Neel – “Katharine Murray Millett”, 1970 Warhol – “Campbell’s Soup I”, 1968 MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 7 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.19: The student will recognize artists’ contributions to society. Community/Culture 6.14: The student will identify how artists contribute to society. movement politics culture functional art decorative Study art movements that show artists reactions to what is going on in their time periods Students will brainstorm ways in which artists contribute to society. Pablo Picasso “Guernica” M620: The student will recognize the various art careers available. Careers 6.11: The student will describe and discuss art careers (e.g., architect, motion picture producer, animator, web page designer, interior designer). architect conservator jeweler animator graphic artist photographer potter designer historian fashion designer landscape designer cinematographer illustrator gallery director commission Students will research different careers for artists. self-assessment peer assessment aesthetics aesthetic view objective nonobjective Students will describe works of art on index cards and divide into teams. Each team will try to correctly identify the most number of works based on index card descriptions. NBC.com Art Colleges Technical Schools Visit businesses in areas of interest Visit working artists in their studios Judgment and Criticism M6.21: The student will use questioning skills (describing, responding to, interpreting, and evaluating) to critique a work of art. Evaluation and Assessment 6.17: The student will demonstrate inquiry skills and appropriate art vocabulary for 1. describing works of art; 2. responding to works of art; 3. interpreting works of art; and 4. evaluating works of art. William Kurelek “Manitoba Party” Charles Russell – “The Medicine Man” MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 8 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities M6.22: The student will recognize the relationship between exploration of ideas and the final outcome. Commitment and Accomplishment 6.19: The student will identify the relationship between art processes and final solutions. generating editing altering implementing Students will record the steps they took to produce a final work of art. M6.23: The student will recognize ideas and emotions expressed in art using appropriate terms and language. Assessment Criteria 6.18: The student will interpret the ideas and emotions expressed in works of art, using appropriate art vocabulary. happy universal controversial sad specific issue impression valid bold personal persuasion depressing Students will discuss and describe a painting. M6.24: The student will recognize persuasive qualities of art. Visual Literacy 6.15: The student will discuss the ways that art can be persuasive. Propaganda art Students will describe how WWII posters were used to persuade the public. J. Howard Miller – “Rosie the Riveter”, 1942 M6.25: The student will recognize how the elements of art, principles of design, technique and media can effect meaning in both 2Dand 3D works of art. Analytical Skills 6.16: The student will explain how the elements of art, the principles of design, art techniques, and art media influence meaning in works of two-dimensional and threedimensional art. interpretation planning production environment composition communication substance form medium function Students will explain and interpret how the elements of art and the principles of design help tell a story and convey a mood in N.C. Wyeth’s painting “I Said good-bye to Mother and the cove”. N.C. Wyeth - “I said good-bye to Mother and the cove”, 1911 6.19: The student will identify the relationship between art processes and final solutions. Students will decide if they think a work is successful. Resources Paul Brach – “Shocking Pink Polka Dot”, 2001 MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 9 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.26: The student will recognize the importance of ethical standards in the use of print and digital images, materials protected by copyright, and information technology. Ethics 6.20: The student will identify and examine ethical standards in the use of 1. print and digital images; 2. materials protected by copyright; and 3. information technology. ethics copyright trademark Students will participate in a poster contest, understanding that their posters will be disqualified if they use or copy any copyrighted words or images. Purpose and Meaning 6.21: The student will respond to works of art and analyze those responses in terms of cultural and visual meaning. aesthetics value culture meaning beauty factors experience value system knowledge beliefs Students will describe the aesthetics and purposes in Navajo Sand paintings. “Southwest Navajo Indian and Horse Pot” Students will explain the cultural functions, construction, and design of African tribal masks. Choose African Tribe and research style of masks Aesthetics M6.27: The student will recognize the cultural and visual meaning in works of art. MCPS Visual Arts Curriculum Sixth Grade Art Revised June, 2011 MCPS Objective Essential Knowledge and Skills / VA SOL Related Vocabulary Suggested Activities Resources M6.28: The student will recognize the importance of the viewer’s belief system in thinking about a work of art. Sensory and emotional responses will be in both oral and written form. Personal Response 6.23: The student will describe the manner in which the belief systems of a viewer may influence contemplation of works of art. religious influences prejudice cultural generation preference values honor customs historical heritage expression classic ethnic Students will write a personal response to Grant Wood’s painting, “American Gothic”. Grant Wood “American Gothic”, 1930 M6.29: The student will ask questions about the nature and philosophical meanings of art. Life Long Appreciation 6.22: The student will generate philosophical questions regarding meanings in works of art. subject message interpretation emotion Students will discuss a painting and the message and/or meaning they feel it portrays. 6.24: The student will explain orally and in writing the means by which visual art evokes sensory and emotional responses. Students will discuss why they think the artist used certain images in a work of art. 10