ÁTADÁS- ÁTVÉTELI JEGYZ*KÖNYV
advertisement

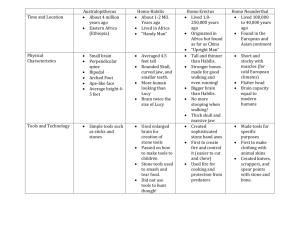
Szakkör megnevezése: Angol szakkör Szakköri foglalkozás címe: Canadian Culture Szakköri foglalkozás sorszáma: 1-2. Foglalkozás vezetője: Fekete Ilona Dóra Időpont: 2011. október 13. Időkeret: 90 perc A kompetencia fejlesztés fókuszai: - az információ rendszerezése, információ feldolgozás - társas kompetenciák: kommunikációs készség, együttműködés, feladatvállalás - language skills: listening, reading, speaking, writing Topic: Canadian Culture Materials used: • books: Evans, Virginia and Jenny Dooley. Enterprise 4. Newbury: Express Publishing, 2002. Harris, Michael, David Mower and Anna Sikorzynska. Opportunities Intermediates. Harlow: Longman, 2002. • maps • information cards • video cassette (The Last of the Mohicans) TÁMOP- 3.2.3/08/2-2009-0022 REKÉP Kulturális innováció az Észak-magyarországi régióban Eszterházy Károly Főiskola Andragógiai és Közművelődési Tanszék 3300 Eger, Eszterházy tér 1. www.ektf.hu/andragogia Stages I. Warm-up Aims - To create a relaxed atmosphere - To raise the topic: Canadian culture To collect basic information about Canada To raise interest Procedure Time “I am travelling somewhere, 10 I can take one person with min. me.” – they have to find out where we are travelling by asking questions from their classmate (using a map) II. Lead-in Directed brainstorming 10 (different aspects are given min. by the T) III. Pre-reading Ss should collect things they 10 know, they do not know min. and things they are not sure about in connection with Canada IV. First reading To look for - T tells the Ss they are 10 information going to read about min. Canada in more details - Ss have to find the answers to their questions (if possible) V. Second To look for specific - Ss are given true-or10 reading information false sentences min. - If they answer all of them correctly, they will get an answer to the question raised at the beginning of the V. part 6 min. VI. Lead-in to - To lead in - T shows a scene of a follow-up another aspect in film about Natives activity connection with (without sound) Canada – Natives - Ss have to predict what - To develop Ss’ is going to happen speaking skill 30 VII. Follow-up - To give further - in groups, Ss have to activity information read a text on Natives min. about Canadian (given on cards) culture - Ss have to introduce - To develop “their” tribe speaking skills - Ss have to argue: which - To encourage tribe should represent creativity Canada on the “Conference for Foreigners on Canada?” TÁMOP- 3.2.3/08/2-2009-0022 REKÉP Kulturális innováció az Észak-magyarországi régióban Eszterházy Károly Főiskola Andragógiai és Közművelődési Tanszék 3300 Eger, Eszterházy tér 1. www.ektf.hu/andragogia Interaction T – Ss Ss – Ss T – Ss Pair work T – Ss Individual work Pair work Individual work T – Ss Individual work T – Ss Ss – T Group work Ss – T VIII. Homework To improve writing assignment skills Ss have to give an oral presentation on what they learnt about Canada 4 min. Individual work at home Mellékletek The text I. (Harris, Michael, David Mower and Anna Sikorzynska. Opportunities Intermediates. Harlow: Longman, 2002, pp. 31.). CANADA – A LAND OF DIVERSITY A Multicultural Identity Although many Canadians’ first language is English or French, many other languages are spoken: Italian, Chinese, German, Polish, Ukrainian, Dutch and Greek. There are many native languages such as Algonquian. The French-speaking province of Canada is very different culturally. Since the 1960s there has been a strong “separatist” movement. There are many different native peoples throughout Canada like the Crees, Mohawks, Iroquois and Sioux. In the north of the country, the Inuit (Eskimos) now have a selfgoverning homeland called Nunavut (meaning “Our Land”). It is over two million sq km and is inhabited by 17,500 Inuits. Canada is one of the most tolerant societies in the world. For example, only 13% of Canadians say that they would object to their children marrying somebody of a different race (compared with 32% in the USA). TÁMOP- 3.2.3/08/2-2009-0022 REKÉP Kulturális innováció az Észak-magyarországi régióban Eszterházy Károly Főiskola Andragógiai és Közművelődési Tanszék 3300 Eger, Eszterházy tér 1. www.ektf.hu/andragogia CANADA FACTFILE • Area: 9,976,169 sq km • Population: 29,000,000 • Capital: Ottawa • Main cities: Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver (75% of the population lives within 300 km of the USA border) • Official languages: English and French • National symbol: the maple leaf • Political structure: Independent constitutional monarchy (Head of State: Elizabeth II) • History: 1608 – Frenchman Champlain established New France in Quebec 1759 – Canada became part of the British Empire 1867 – The Confederation of Canada was set up 1931 – Independence from Britain • Quality of life: Very high standard of living. Ranked number one on the UN “Human Development Index.” The country is particularly advanced in the areas of health, education, social protection and human rights. The text II. (Evans, Virginia and Jenny Dooley. Enterprise 4.Newbury: Express Publishing, 2002, pp. 187). TÁMOP- 3.2.3/08/2-2009-0022 REKÉP Kulturális innováció az Észak-magyarországi régióban Eszterházy Károly Főiskola Andragógiai és Közművelődési Tanszék 3300 Eger, Eszterházy tér 1. www.ektf.hu/andragogia CANADIAN INDIANS A.) The Inuit people lived in the Arctic region. They lived in small groups that moved around to search for food. Their houses were tents made of sealskin in the summer, and snowhouses (called igloos) in the winter. As well as catching fish, they hunted seals, caribou and whales for food, which were usually eaten raw because there wasn’t any firewood for cooking. Sealskin and fur were used for clothing. Skins were also used for making canoes. B.) The tribes of the Subarctic area lived near lakes or in forests. The Chippewa, one of the largest of these tribes, lived around the shores of Lake Superior. They hunted deer in the forests, fished in the lake and gathered wild rice and berries. They lived in bark lodges in winter and in bark tepees in summer. They also used bark to make canoes and baskets. They hunted with bows and arrows. C.) The Iroquois, a large group in the Northeast, lived in permanent villages with tall fences around them. The men hunted and fished, while the women grew corn and beans and collected nuts and berries. They lived in long houses made of a frame of poles covered with bark. They used deerskin to make their clothes, and strings of shells as money. TÁMOP- 3.2.3/08/2-2009-0022 REKÉP Kulturális innováció az Észak-magyarországi régióban Eszterházy Károly Főiskola Andragógiai és Közművelődési Tanszék 3300 Eger, Eszterházy tér 1. www.ektf.hu/andragogia