Carbon Cycle Review Handout
advertisement

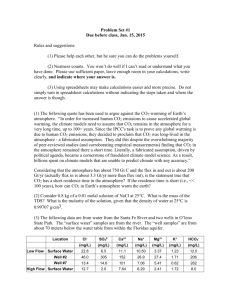
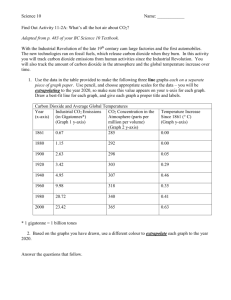
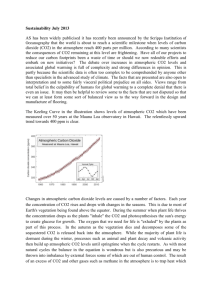
Carbon Cycle LT 1-6 Review Name___________________ Date____________________ LT 1 – I can describe the three primary processes of the biological (short) carbon cycle. 1. What is the Law of Conservation of Matter and how does it apply to the carbon cycle? The Law of Conservation of Matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. The carbon cycle is an example of the Law because the same carbon atoms are being recycled through the carbon cycle. 2. List and explain the three primary processes of the (short) carbon cycle. PHOTOSYNTHESIS – Plants take in CO2, sunlight and water to make their own food. Carbon is used for energy, and some is stored for growth. RESPIRATION – The process of converting food to energy using oxygen and giving off CO2 DECOMPOSITION –When animals die, decomposers (fungi, worms, mushrooms) break down the carbon compounds in the bodies of decaying matter. Decomposers use some Carbon for their own bodies while some is returned to the atm. through respiration as CO2 3. How do animals get the carbon they need? How is the carbon used? By eating plants or animals that eat plants. Some is broken apart releasing energy, some is changed into new compounds to become part of the body, and some is returned to the atmosphere during respiration. 4. How does CO2 get from the atmosphere to into the food web? Through photosynthesis LT 2 – I can identify reservoirs and can explain processes that are part of the delayed cycle. 5. Compare the short (biological) cycle with the delayed cycle. The short carbon cycle deals with the biological processes. Such as breathing, plants producing food, decomposers breaking down the food. In the delayed carbon cycle, this is where carbon is stored for long periods of time. (Nonliving) 5. What is a reservoir? A place where carbon is stored 6. List four places where carbon is stored. Shells, Atmosphere, soil, trees, plants, Deep Ocean, surface ocean rocks. 8. What is another name for places where carbon is stored? Carbon sink LT 3 – I can explain the importance of carbon to living things. 9. What is biosynthesis? The formation of complex compounds from simple molecules. 10. What compound do plants make when they use energy and matter to produce their own food? Glucose which can then recombine to make compounds like carbs, fats, and proteins 11. What do plants need to make their own food? What are the reactants? (Ingredients) Carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water ` 12. What type of energy does a plant need to grow? ___Light__ LT 4 – I can explain the role of plants in the carbon cycle. FYI - BTB is an indicator solution that changes color from blue to yellow in the presence of CO2 13. If a plant is put in a vial with yellow BTB and put in the sunlight, what would be the outcome? Explain Blue…The plants in the vial will absorb the CO2 and take the yellow out and return the color back to blue 14. If a plant is put into a vial that contains green BTB (low CO2) and placed in the dark, what would the color of the vial be after 12 hours? Explain Yellow….Even though there is CO2 present, when placed in the dark, the plant continues to respire and that will cause the color to turn yellow 15. What are the reactants (ingredients) and the product of photosynthesis? Sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water (reactants). (Products) are glucose and oxygen LT 5 – I can identify human impacts on the carbon cycle and can explain possible consequences. 16. What are three examples of fossil fuels? Oil, Gas, and coal 17. How are human activities changing the carbon cycle? Burning of fossil fuels. When we burn fossil fuels, we release carbon atoms that have been locked away inside the earth for millions of years. The extra CO2 acts like a blanket trapping extra heat that usually goes to space. The earth’s high temperature is the result. Cutting down trees…this releases CO2 back into the atmosphere as well as keeping trees from absorbing the CO2 18. What is combustion and how does it impact the atmosphere? The process of burning fossil fuels that returns CO2 to the atmosphere. It impacts the atmosphere by removing gigatons of carbon from fossil fuels into the atmosphere 19. List three human activities that increase CO2 in the atmosphere. By producing electricity, making products from factories, and driving cars. Deforestation, land use changes 20. What is the relationship between temperature and CO2.? Explain the graph. There is a direct correlation between temperature and CO2. When temp goes up so does CO2. The zigzag lines of the CO2 show the change in seasons when there is high vegetation, the CO2 is lower and when the vegetation is low, the CO 2 is higher. 21. What is being illustrated in the simulation? What conclusion can be drawn from the two types of gases? The illustration shows the result of adding CO2 and N2 to the atmosphere. On the left, it shows the deflecting of CO2 back to the earth and warming the earth. There is no reaction with the addition of the N2. The conclusion that is drawn is that CO2 is the greenhouse gas and is responsible for trapping heat in the atmosphere. LT 6 – I can identify and distinguish between carbon sources and carbon sinks and can explain the movement of carbon between these locations. a. CO2 increases in the atmosphere b CO2 decreases in the atmosphere ___A__22. Deforestation ___B__23. Vegetation at its peak during September ___A__24. Vegetation at its peak in March ___B__25. Planting pine trees ___A__26. Releasing fossil fuels through combustion __A___27. Volcanic eruptions ____A_28. When carbon sinks outnumber carbon sources ___B__29. When carbon sources outnumber carbon sinks __A___30. Combustion