Land Forms Power Point Review Interactive Slideshow
advertisement

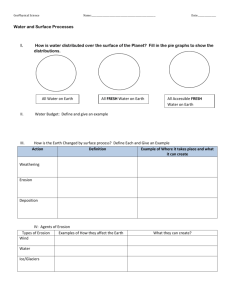
Land Forms Power Point Review Interactive Slideshow So far in this unit, you have learned that there are two forces at work in nature: Constructive (to build, create) and Destructive (to tear down, destroy). Landforms are constantly changing as a result of these forces. What causes the changes involve the three processes of Weathering (to break down), Erosion (to move or transport away) and Deposition (to deposit, lay down, or settle). Weathering and erosion are destructive processes, while deposition is a constructive process. There are two kinds of weathering: Physical Weathering and Chemical Weathering. Agents of physical weathering break down rock and other surfaces into smaller pieces and include temperature change, wind, ice (ice wedging) , glaciers, gravity, wave action, and water (running water). Water (dissolves things) is the main agent of chemical weathering. Acid in rain would be a good example of chemical weathering. In chemical weathering, a reaction takes place and a new substance forms. Many of the same agents of weathering are at work in erosion, as well. Gravity-and with enough speed and energy-water (running water), wind, wave action, and glaciers, all serve to move or transport broken down pieces to a different location. If speed and energy decrease, then deposition (settling down) of the eroded materials takes place. To help you with the upcoming test on W, E, & D, and Landforms, I have provided an interactive power point slideshow to help you practice identifying the forces, processes and agents of W, E, & D. Here’s how to begin: Step 1: Open the powe point/slideshow. Step 2: From the tabs across the top, select slideshow. Step 3: On the top left, click on “From the Beginning” to see the slide containing the title of the show Step 4: To advance to the first question/slide, click the mouse within the title slide. Step 4: Using your power point check off sheet, decide which force(s), process(s), and agent(s) are shown. You may choose as many boxes as you think apply to the situation. Step 5: Click your mouse within the frame to see the answers pop up. Step 6: Click within the frame to advance to the next slide. Landform Review Check Off Sheet Processes: Forces: * Situations #1 A rock heats in the sun & cracks #2 A slowing stream drops its sediment #3 Blown sand piles up along a tree line #4 A limestone cave is dissolved by H20 #5 A beach shrinks #6 A deep hole forms at the base of a waterfall #7 Water seeps into a cracked brick ledge & breaks away part of a brick #8 Blowing sand cuts a hole in a Sandstone cliff #9 The Colo. River flows through the Grand Canyon #10 A strong wind shifts the position of a sand dune #11 A town is covered in mud after a flooded river returns to its banks #12 A moving glacier plows the ground as it slides down the valley #13 A rock freezes and cracks #14 Roots grow into a cracked rock & make the crack bigger Constructive Check all the boxes that apply to each situation Destructive Weathering Erosion Deposition Agents: Agents: Physical Chemical Water Wind Gravity Glaciers Waves Water Acids O2 Processes: Forces: * Situations #15 Soil is blown from one field to another #16 Water eats away at buried limestone #17 A glacier leaves a trail of debris as it slides down a valley #18 Wind blown sand smooths a boulder #19 The backyard of a beach house becomes smaller #20 A delta forms at the mouth of the Miss. River #21 The rain washes loose soil from a flower bed onto the lawn #22 A river removes soil from the outside curve and leaves debris along the inside corner #23 Rocks tumbling downstream are broken into smaller pieces #24 Constructive Destructive Weathering Erosion Deposition Agents: Agents: Physical Chemical Water Wind Gravity Glaciers Waves Water Acids O2 Land Forms Power Point Review Interactive Slideshow So far in this unit, you have learned that there are two forces at work in nature: Constructive (to build, create) and Destructive (to tear down, destroy). Landforms are constantly changing as a result of these forces. What causes the changes involve the three processes of Weathering (to break down), Erosion (to move or transport away) and Deposition (to deposit, lay down, or settle). Weathering and erosion are destructive processes, while deposition is a constructive process. There are two kinds of weathering: Physical Weathering and Chemical Weathering. Agents of physical weathering break down rock and other surfaces into smaller pieces and include temperature change, wind, ice (ice wedging) , glaciers, gravity, wave action, and water (running water). Water (dissolves things) is the main agent of chemical weathering. Acid in rain would be a good example of chemical weathering. In chemical weathering, a reaction takes place and a new substance forms. Many of the same agents of weathering are at work in erosion, as well. Gravity-and with enough speed and energy-water (running water), wind, wave action, and glaciers, all serve to move or transport broken down pieces to a different location. If speed and energy decrease, then deposition (settling down) of the eroded materials takes place. To help you with the upcoming test on W, E, & D, and Landforms, I have provided an interactive power point slideshow to help you practice identifying the forces, processes and agents of W, E, & D. Here’s how to begin: Step 1: Open the powe point/slideshow. Step 2: From the tabs across the top, select slideshow. Step 3: On the top left, click on “From the Beginning” to see the slide containing the title of the show Step 4: To advance to the first question/slide, click the mouse within the title slide. Step 4: Using your power point check off sheet, decide which force(s), process(s), and agent(s) are shown. You may choose as many boxes as you think apply to the situation. Step 5: Click your mouse within the frame to see the answers pop up. Step 6: Click within the frame to advance to the next slide.