Ch 7 Notes
advertisement

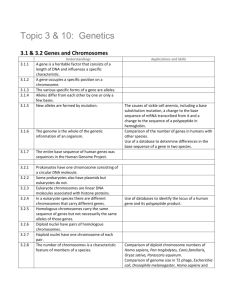
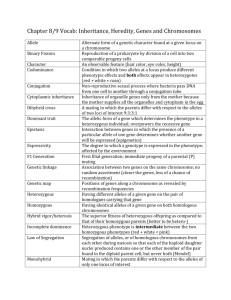
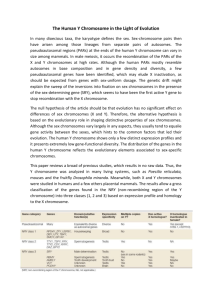
Honors Bio Ch 7 Notes Vocabulary Heterozygous – Has two different alleles for a trait. Ex: Ss Homozygous – Has two of the same alleles for a trait. Ex: SS or ss Genotype – the combination of alleles that an individual has for a trait. Ex: Ss Phenotype – the physical trait that results from a genotype. Ex: Sickle cell anemia Sex-linked gene – located on the X or Y chromosome. Expressed more frequently in males than females. Carrier – heterozygous for a recessive allele for a disorder (ex: Cc for Cystic Fibrosis or XHYh for Hemophilia). They carry the defective allele so they can pass it on to their offspring, but they do not express the phenotype. X chromosome inactivation - female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly turned off in each cell Polygenic trait – traits controlled by multiple genes. Results in a wide range of phenotypes (ex: eye color) Epistatic gene – a gene that interferes with the expression of other genes Codominance – both alleles for a trait are completely expressed. Ex: AB Blood type Incomplete dominance – the heterozygous genotype is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. Ex: Japanese 4 ‘0 clock flowers RR = red, WW = white, RW = pink. Karyotype – picture of all the chromosomes in someone’s cells. Can show some chromosomal disorders. Autosomes are the 1st 22 pairs of chromosomes, sex chromosomes are the last pair (#23) Pedigree – Diagram that traces a particular trait in a family. Can show genotype and/or phenotype. Chapter Notes 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotypes Autosomal genes – genes located on any autosomal chromosome two copies are present (one on each homologous chromosome both copies affect phenotype Recessive Genetic Disorders An individual must have 2 recessive alleles to have the disorder (cc) Carriers are heterozygous (Cc) so they don’t have the disorder but can pass it on to their offspring. This allows the allele to “hide out” in a population. Cystic fibrosis affects sweat and mucus glands. Dominant Genetic Disorders Less common. An individual can be homozygous dominant (HH) or heterozygous (Hh) to have the disorder. Ex: Huntington’s disease – affects the nervous system and appears in adulthood Sex–linked Genes – genes located on sex chromosomes Males: XY Females XX Genes on the X chromosome are expressed more frequently than in females. Why? When will a sex-linked trait be expressed in females? X chromosome inactivation – one of two X chromosomes is randomly “turned off”. Ex: Fur color in cats is a sex-linked trait resulting from several genes. Tortoiseshell and Calico cats are females that express different genes in different cells across their bodies. 7.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Incomplete Dominance Heterozygous phenotype is between the two homozygous phenotypes. Ex: Japanese 4 ‘0 clock flowers RR = red, WW = white, RW = pink. Codominance Both alleles are completely expressed so both phenotypes show up. Ex: ABO blood types Phenotypes: Type A, Type B, Type AB, Type O Polygenic traits Traits produced by 2 or more genes that influence the phenotypes Produces a continuous range of phenotypes Ex: Human skin color Epistatic gene – a gene that interferes with the expression of other genes. Ex: fur color in mice is controlled by many genes, but one gene (epistatitic gene) overshadows all the others and results in albinism. Environment and gene expression Environmental conditions influences the expression of some genes Ex: Sea turtles – eggs that mature in warmer temperatures develop into females and eggs that mature in cooler temperatures develop into male turtles. 7.4 Human Genetics and Pedigrees Pedigree – Chart for tracing genes in a family See Figure 7.14 You should be able to look at a pedigree and identify genotype and phenotype for given individuals. You must first determine if the trait is a result of an autosomal or sex-linked gene. Karyotype – a picture of the chromosomes in a cell Can help diagnose chromosomal disorders Loss of part of a chromosome (deletion) Down syndrome (trisomy 21)– extra copy of 21st chromosome. This is a result of nondisjunction (chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis. How might this result in gametes with missing or extra chromosomes?