Finding the loci of human genes
advertisement

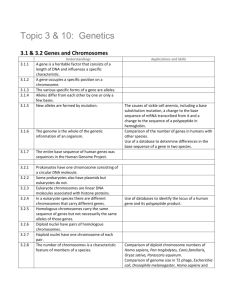
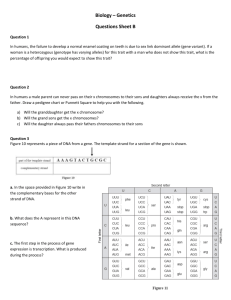
Finding the loci of human genes Last name: First name: Use of online databases to identify the locus of a human gene and its protein product Online databases can be used to find the locus of human genes. There is an example of such a database in the “Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man” website (www.omim.org), maintained by Johns Hopkins University. But before you go there you need to look up the names of some genes at the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (www.genenames.org). 1. Go the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee website. 2. In the search option at the top, type in the name of a characteristic, OR, mouse-over “Gene Families” and select “Full Listing” to see a list of group of genes. 3. Write down the names of three genes to look up: ____________________ 4. Go to the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man website. 5. In the search bar, type in the name of your first gene and fill out the information in the table below. 6. 7. Once you are done with the first three genes, go back to the home page of OMIM. 8. Next to “Advanced Search” choose “Gene Map”. 9. Select a chromosome number between 1 and 22 or one of the sex chromosomes, X or Y. 10. A complete sequence of gene loci will be displayed. Pick three genes from this chromosome (_________________________), go back to the OMIM home page and fill out the information for each gene in the last three rows of the table below. Gene name Locus Protein that is encoded Function of protein The figure below shows all of the types of chromosomes in mice and in humans. Numbers and colours are used to indicate sections of mouse chromosomes that are homologous to sections of human chromosomes. 1. Deduce the number of types of chromosomes in mice and in humans. 2. Identify two human chromosome types that are most similar to mouse chromosomes. 3. Identify mouse chromosomes which contain sections that are not homologous to human chromosomes. 4. Suggest reasons for the many similarities between the mouse and human genomes. 5. Deduce how chromosomes have mutated during the evolution of animals such as mice and humans.