The story of the cell shortened
advertisement

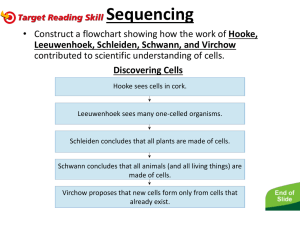
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: _______ The Story of the Cell What is a cell you ask? Cells are the building blocks of all living things. But, scientists didn’t always know that cells existed. Most cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye. As a result, cells remained undiscovered until fairly recently in history. Scientists didn’t observe cells until the seventeenth century, when microscopes were invented. With your lab group, read the introduction about each scientist. Then observe and sketch the necessary slide(s). Robert Hooke—1665 The English scientist, Robert Hooke, was one of the first scientists to use a microscope a great deal. One day, he decided to look at thin slice of cork (which comes from the bark of a cork tree). He noticed that the cork bark was filled with tiny room-like structures. He named these structures cells. But the cells that Hooke saw in the slice of cork were not alive. What Hooke saw were actually the outer walls of dead plant cells. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek—1673 At about the same time, Anton van Leeuwenhoek (pronounced Lay-van-hoke), a Dutch fabric merchant and amateur scientist, used a microscope to examine materials such as blood, rainwater, and scrapings from his teeth. In each material,he found tiny living things. He called these things “animalcules” but they were really living cells! The smallest animalcules observed by van Leeuwenhoek are today known as bacteria which are single-celled organisms. Matthais Schleiden-1837 During the next two hundred years, new and better microscopes were developed. Such microscopes made it possible for the German botanist Matthias Schleiden to view different types of plant parts. In 1837, Schleiden discovered that all the plant parts he observed were made of cells. He came to the conclusion that all plants and their parts must be made of cells, not just some special types. Theodor Schwann—1839 One year later, the German zoologist Theodor Schwann made similar observations using animal parts, including tadpoles. He noticed that all the animal tissues he looked at had cells. He discovered that not only are plants made of cells, but animals are too! Rudolph Virchow—1855 With all of these discoveries, scientists still didn’t know how cells reproduce. How do our bodies, plants, and other animals get new replacement cells? In 1855, another German scientist named Rudolph Virchow answered this question. He observed cells dividing into two parts and discovered that all cells come from previously living cells. The Cell Theory of Life The work and discoveries these and many other scientists permanently changed the way that we think of life. With all of this new information, scientists developed a theory of how life actually works. This theory is called the cell theory of life. Cell theory basically states what cells are and how they are essential to life (see your cells notes for more information). Object on slide:Stagnant Water (which contains single-celled organisms) Observations and impressions: Scientist who observed single-celled organisms: Major Discovery of this scientist: _____________________________________________________________ Object on slides (must observe and draw 2): Animal Slide 1, specifically: _____________________ Observations and impressions of first slide: Animal Slide 2, specifically: ________________________ Observations and impressions of second slide: Scientist who observed animal parts: Major Discovery of this scientist: _____________________________________________________________ Object on slide: ________Cork__________ Observations and impressions: Scientist who observed cork: Major Discovery of this scientist: Object on slide: _Onion Root (which shows cells dividing)___________ Observations and impressions: Scientist who observed cells dividing: Major Discovery of this scientist: _____________________________________________________________ Object on slides (must observe and draw 2): Plant Slide 1, specifically: _____________________ Observations and impressions of first slide: Plant Slide 2, specifically: ________________________ Observations and impressions of second slide Scientist who observed plant parts: Major Discovery of this scientist: _____________________________________________________________ Questions: 1. If cells are everywhere, why didn’t scientists discover them until 1665? 2. What are the three main ideas of the cell theory of life? 3. What does it mean to say that cells are the basic units of living things? Match the following scientists with their contribution to the cell theory. 4. _______ Matthias Schleiden 5. _______ Robert Hooke 6. _______ Theodor Schwann 7. _______ Rudolph Virchow 8. _______ Anton van Leeuwonhoek A. B. C. D. E. Was the first to see cells while observing cork bark. Discovered that all plants have cells. Discovered that cells reproduce by dividing. Was the first to see living cells in many substances. Discovered that all animals have cells. 9. Compare and contrast the nucleus of a cell to that of an atom. Similarities: Differences: 10. Explain in your own words why the discovery of cells was a critical event in the history of science. 11. Using at least two complete sentences, summarize what you have learned about the history of cells today.