plasma
advertisement

PLASMA!
revised from this site:
http://ww.spacescience.org/ExploringSpace/PlasmaStateOfMatter/1.html
What is a Plasma?
Plasma is one of five states of matter. The other four states of matter are solid, liquid,
gas, and Bose-Einstein condensate. The term "plasma" has nothing to do with blood plasma.
Plasma is actually the most common form of matter in the universe, but it is one of the
least familiar states of matter to us mere mortals.
Plasma makes up 99% of all visible matter in our universe. Although naturally occurring
plasma is rare on Earth, there are many man-made examples. Inventors have used plasma
to conduct electricity in neon signs and fluorescent bulbs. Gift shops sell cool novelties called
Plasma spheres and scientists have made special chambers to experiment with plasma in
laboratories.
Naturally occurring plasma is relatively rare on Earth, occurring only in lightning
discharges and in artificial devices such as fluorescent lights. Plasma is everywhere in our
space environment, however. Examples include:
The aurora, or northern lights, which flicker in the uppermost reaches of Earth's
atmosphere.
The solar wind. It generates an immense sheet of electrical current that spirals like a
ballerina's skirt as the Sun rotates.
The Sun and all the other stars in our galaxy, and colossal exploding jets from distant
galaxies.
Hannes Alfvén (1908-1995), a Swedish physicist, is the father of modern day plasma
science. He believed that the effects of electricity and magnetism played important roles in
many astrophysical areas. He received the Nobel Prize in 1970 for his contributions to basic
plasma physics and for his studies of space plasmas.
How are Plasmas Created?
Plasma, like ordinary matter, is made up of atoms. Atoms are so tiny that more than a
million can fit across the head of a pin. They are composed of one or more negatively charged
electrons that orbit a positively charged nucleus (made up of neutral particles, called neutrons,
and positively charged particles, called protons). Electrically neutral atoms have the same
number of positive and negative electrical charges.
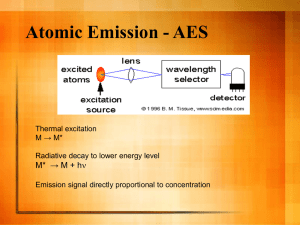
When gases are exposed to lots of heat or radiation the atoms are split into a sea of
positively charged ions and the negatively charged electrons, forming Plasma. Another term
for plasma is "ionized gas", which means it is gas that is electrically charged. {Contrast this to
our atmosphere which is predominantly neutrally charged gaseous nitrogen (~78%) and
oxygen (~21%).} Because plasma consists of electrically charged particles, it acts very
differently from ordinary forms of gas. As electrically charged particles, plasmas are
influenced by electric and magnetic fields.
We are just beginning to understand how plasmas interact with electric and magnetic
fields. Once we figure this out we will have a much better idea of what is happening between
the Sun and Earth and elsewhere in the universe! Even then, many mysteries of the universe
will still remain!