E5 - The human brain
advertisement

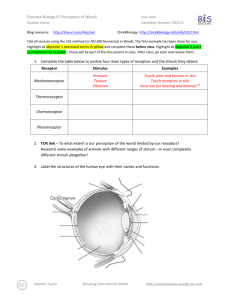
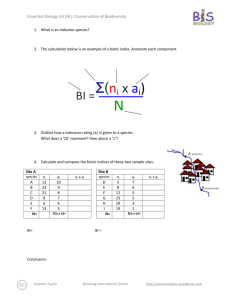
Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- Student Name: Blog resource: http://tinyurl.com/4f64hzw Click4Biology: http://click4biology.info/c4b/E/E5.htm Cite all sources using the CSE method (or ISO 690 Numerical in Word). Highlight all objective 1 command terms in yellow and complete these before class. Highlight all objective 2 and 3 command terms in green – these will be part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Pre-learning: NewScientist Brain section: http://www.newscientist.com/topic/brain 1. Label the regions of the brain, including the function of each: 2. Discovery of the functions of parts of the brain is due to a number of areas of research over the last couple of centuries. Outline each of the methods below and explain what they have told us about the brain. a. fMRI i. Define fMRI. ii. Outline how fMRI works. iii. Outline an experiment that shows how fMRI has been used to determine the function of a brain region. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- b. Brain Lesion studies i. Define lesion. ii. Outline the effects of lesions on brain function. iii. Outline the famous discovery of Broca’s area and its importance in language development. c. Animal experimentation Outline the following examples of animal experiments into brain function: i. Dissection and comparative anatomy ii. Removal of brain regions (causing lesions), e.g. Flouren’s experiments iii. Electrical stimulation of brain regions, e.g. Ferrier’s experiments The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nerves make up the peripheral nervous system, which is divided into the autonomic and somatic systems. 3. Distinguish between the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- Student Name: 4. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric nervous systems. a. Distinguish between the overall functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. b. The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems can regulate heart rate, blood flow to the gut and control of the iris, among other functions. Complete the table below, outlining these functions: Sympathetic Parasympathetic Acetylcholine (Ach) Neurotransmitters Nerve pathways Sympathetic nerves Heart rate Stimulus: Elevated CO2 levels in blood Stimulus: Receptors: Chemoreceptors in medulla oblongata Receptors: Action Stimulates SA node Action Blood flow to gut Stimulus: Stimulus: Receptors: Receptors: Action Iris control Effect Action Relaxes blood vessels to gut Stimulus: Stimulus: Receptors: Receptors: Action Stephen Taylor Effect Increases heart rate Effect Bandung International School Action Effect Effect Increases blood flow to gut, allowing for ‘rest and digest’ Effect http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- 5. Explain the pupil reflex as a response to bright light: Stimulus: Receptor: Sensory neuron: Relay neurons: Motor neurons: Effector muscles: Effect: 6. The pupillary response can be used to determine brain death. a. Distinguish between cardiac and brain death. b. Explain why the pupillary response is a good indicator of brain death, with reference to the functions of the medulla oblongata. c. Discuss the ethical considerations regarding diagnosis of death and of organ donation. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- 7. Pain is an unpleasant or aversive sensation associated with an action which causes the body harm or trauma. a. What is a function of pain in terms of survival? b. Outline the pain pathway: Stimulus: Receptors: Sensory neurons: Function of the brain: c. Endorphins are protein-based molecules that can block pain impulses. i. State why this might be useful in survival. ii. Explain the effect of endorphins on synaptic transmission in the brain. iii. Suggest a method by which pain-related brain regions can be identified. iv. Suggest reasons why morphine is a highly effective painkiller and can be used in cases of serious injury. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- 8. Experimental Research Read this article on research into pain perception in fish: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/04/090430161242.htm a. Outline the prevailing hypothesis with regards to fish pain perception. b. State the different treatments given to the two experimental groups of fish. c. Outline the experimental protocol used to inflict pain upon the fish. d. Outline how the response of the fish was like a reflexive action. e. Explain the researchers’ conclusions, with regard to the behavior of the fish, postexperiment. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology E5 The Human Brain (HL) Due Date: Candidate Number: 002171- Student Name: Works Cited 1. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. 2. Mindorff, D and Allott, A. Biology Course Companion. Oxford : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978099151240. 3. Clegg, CJ. Biology for the IB Diploma. London : Hodder Murray, 2007. 978-0340926529. 4. Campbell N., Reece J., Taylor M., Simon. E. Biology Concepts and Connections. San Fransisco : Pearson Benjamin Cummings, 2006. 0-8053-7160-5. 5. Taylor, Stephen. Science Video Resources. [Online] Wordpress, 2010. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com. 6. Burrell, John. Click4Biology. [Online] 2010. http://click4biology.info/. 7. IBO. Biology Subject Guide. [Online] 2007. http://xmltwo.ibo.org/publications/migrated/productionapp2.ibo.org/publication/7/part/2/chapter/1.html. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Presentation & Organisation Academic Honesty Objective 1 understanding Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research Assessment Complete (2) Partially complete (1) NA Complete and neat. All command terms highlighted, tables and diagrams well presented. Self Sources cited using the CSE (ISO 690 numerical) method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. All answers for the following command terms Most answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Define Draw Label List Measure State Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used most times, with correct NA unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct answers to challenging questions. If any NA questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. NA Total (max 10): Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com MrT