Stanford-Binet SB5 Test Evaluation Outline
advertisement
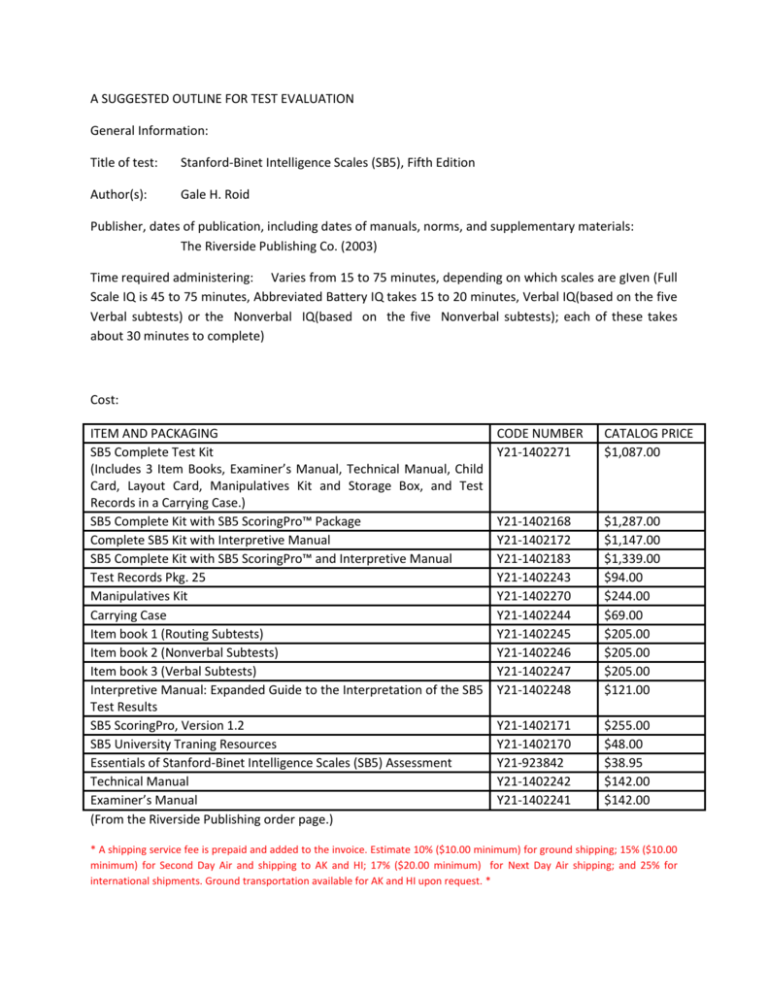
A SUGGESTED OUTLINE FOR TEST EVALUATION General Information: Title of test: Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (SB5), Fifth Edition Author(s): Gale H. Roid Publisher, dates of publication, including dates of manuals, norms, and supplementary materials: The Riverside Publishing Co. (2003) Time required administering: Varies from 15 to 75 minutes, depending on which scales are gIven (Full Scale IQ is 45 to 75 minutes, Abbreviated Battery IQ takes 15 to 20 minutes, Verbal IQ(based on the five Verbal subtests) or the Nonverbal IQ(based on the five Nonverbal subtests); each of these takes about 30 minutes to complete) Cost: ITEM AND PACKAGING SB5 Complete Test Kit (Includes 3 Item Books, Examiner’s Manual, Technical Manual, Child Card, Layout Card, Manipulatives Kit and Storage Box, and Test Records in a Carrying Case.) SB5 Complete Kit with SB5 ScoringPro™ Package Complete SB5 Kit with Interpretive Manual SB5 Complete Kit with SB5 ScoringPro™ and Interpretive Manual Test Records Pkg. 25 Manipulatives Kit Carrying Case Item book 1 (Routing Subtests) Item book 2 (Nonverbal Subtests) Item book 3 (Verbal Subtests) Interpretive Manual: Expanded Guide to the Interpretation of the SB5 Test Results SB5 ScoringPro, Version 1.2 SB5 University Traning Resources Essentials of Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (SB5) Assessment Technical Manual Examiner’s Manual (From the Riverside Publishing order page.) CODE NUMBER Y21-1402271 CATALOG PRICE $1,087.00 Y21-1402168 Y21-1402172 Y21-1402183 Y21-1402243 Y21-1402270 Y21-1402244 Y21-1402245 Y21-1402246 Y21-1402247 Y21-1402248 $1,287.00 $1,147.00 $1,339.00 $94.00 $244.00 $69.00 $205.00 $205.00 $205.00 $121.00 Y21-1402171 Y21-1402170 Y21-923842 Y21-1402242 Y21-1402241 $255.00 $48.00 $38.95 $142.00 $142.00 * A shipping service fee is prepaid and added to the invoice. Estimate 10% ($10.00 minimum) for ground shipping; 15% ($10.00 minimum) for Second Day Air and shipping to AK and HI; 17% ($20.00 minimum) for Next Day Air shipping; and 25% for international shipments. Ground transportation available for AK and HI upon request. * Brief Description of Purpose and Nature of Test General type of test: Intelligence Test, Individually administered Population for which designed: 2 to 85+ years Nature of Content: Working Memory Fluid Reasoning, Knowledge, Quantitative Reasoning, Visual-Spatial Processing, Subtests and separate scores: Item types: FACTORS NONVERBAL (NV) Fluid Reasoning (FR) Verbal Fluid Reasoning Nonverbal Fluid Reasoning Activities: Early Reasoning (2-3), Activities: Object Series/Matrices Verbal Absurdities (4), Verbal (Routing) Analogies (5-6) Knowledge (KN) Nonverbal Knowledge Verbal Knowledge Activities: Procedural Knowledge Activities: Vocabulary (Routing) (2-3), Picture Absurdities (4-6) Nonverbal Quantitative Quantitative Reasoning Reasoning Activities: Quantitative (QR) Reasoning (2-6) VERBAL (V) Verbal Quantitative Reasoning Activities: Quantitative Reasoning (26) Visual-Spatial Processing (VS) Nonverbal Visual-Spatial Processing Activities: Form Board (1-2), Form Patterns (3-6) Working Memory (WM) Nonverbal Working Memory Verbal Working Memory Activities: Delayed Response (1), Activities: Memory for Sentences (2Block Span (2-6) 3), Last Word (4-6) Verbal Visual-Spatial Processing Activities: Position and Direction (26) Practical Evaluation Qualitative features of test materials: Wide variety of items requiring nonverbal performance by examinee - ideal for assessing subjects with limited English, deafness, or communication disorders Ability to compare verbal and nonverbal performance - useful in evaluating learning disabilities Greater diagnostic and clinical relevance of tasks, such as verbal and nonverbal assessment of working memory Includes Full Scale IQ, Verbal and Nonverbal IQ, and Composite Indices spanning 5 dimensions with a standard score mean of 100, SD 15 Includes subtest scores with a mean of 10, SD 3 Extensive high-end items, many adapted from previous Stanford-Binet editions and designed to measure the highest level of gifted performance Improved low-end items for better measurement of young children, low functioning older children, or adults with Mental Retardation Enhanced memory tasks provide a comprehensive assessment for adults and the elderly Co-normed with measures of visual-motor perception and test-taking behaviour Scoreable by hand or with computer software Enhanced artwork and manipulatives that are both colourful and child-friendly The SB5 Complete Kit includes all 3 Item Books, Examiner's Manual, Technical Manual, 25 Test Records, child card, layout card, a carrying case, and all manipulatives (form board, 10 form board pieces, 9 green blocks, 12 counting rods, 30 sorting chips, spoon, pencil, 3 plastic cups, and toys including cat, bird, duck, ball, car, and shoe) in a plastic storage case. The manipulatives used engaged the attention of young children. It is administered through an easy-to-learn easel format of three books. Each Easel Book has illustrations on one side, and detailed examiner directions on the other. Ease of administration, including facilities for computer administration: For ease of administration, the SB5 is organized into three item books printed on an easel format that includes all administration directions. The easel format allows examinees to easily view test materials, but also allows the examiner to easily record and score responses behind the easel. The first item book includes the two routing subtests, whereas the second item book contains Levels 1-6 of the Nonverbal subtests. The third Item book contains Levels 2-6 of the Verbal subtests. Item Book 1 includes the Matrices and Vocabulary subtests, used as the initial assessment, or Abbreviated Battery IQ. Item Book 2 has the Nonverbal subtests, arranged according to level of difficulty (Levels 1-6). Different levels allow the test to be tailored to the examinee’s ability, saving time and making the assessment accurate and reliable. Item Book 3 has the Verbal subtests, arranged by level of difficulty Clarity of directions: Early SB5, like SB5, has ten subtests. Two subtests – Nonverbal Fluid Reasoning (Matrices) and Verbal Knowledge (Vocabulary) – cover the age range 2-0 through 7-3 and provide initial scores for tailoring the remaining test administration to the ability level of the child. Toys, manipulatives and brightly colored illustrations help engage young children. The remaining eight subtests offer scores in the preschool range, from 2-0 through 5-11 to measure Quantitative, Visual-Spatial, and Working Memory abilities. Testing begins in Item Book 1 with the two initial subtests, which are retained in their entirety and used to calculate an Abbreviated Battery IQ. All remaining subtests are contained in Item Book 2. This provides a streamlined administration compared to the 3 Item Book format of the full SB5. Each Item Book is designed as an "easel" with illustrations and stimuli facing the child and directions (including all examiner prompts, materials layout, and scoring directions) conveniently facing the examiner, as compared to other IQ measures that require a separate test manual of directions. The Record Form guides the examiner through the administration and provides familiar, easy-to-use scoring directions. In the Early SB5, only the most difficult levels of items have been dropped from the subtests in Item Book 2. Dropping these more difficult items generally has no impact on the scores of the young children typically assessed with Early SB5. Scoring procedures, including computer-scoring services and available software Points are summed for each of the subtests & converted to a “scaled score” -- Scaled subtest scores have a mean of 10 & a standard deviation of 3 Scores can also be computed for nonverbal IQ, verbal IQ, full-scale IQ and each of the five factors (fluid reasoning, knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual-spatial processing, working memory) -- These “standard scores” have a mean of 100 & a standard deviation of 15 Scoring Software The SB5 Scoring Pro is a Windows-based software program that replicates the process of handscoring - users enter background information, age, and raw scores. This program provides consistency in raw score conversion, an extended score report, a graphical report, and a brief, narrative summary report with guidelines and suggestions based on well-established principles of assessment. The report can be exported and then imported to a word processing file for editing as necessary. Minimum System Requirements: Windows 98 / NT4.0 / ME / 2000 / XP, Pentium 200 MHz processor, 64 MB RAM (96 MB recommended), CD-ROM or DVD drive, SVGA monitor (.NETcompatible video card), 100 MB free hard disk space. Examiner qualifications and training required High Master’s degree and/or doctorate in education, psychology, or related field. Graduate level training in one or more of the following: Intelligence/cognitive assessment Neuropsychology Technical Evaluation: The SB5 is based on the Cattell-Born-Carroll (CHC) theory of cognitive functioning that has been investigated empirically over several decades (D'Amato, Fletcher-Janzen, &- Reynolds, in press). Several other recent intelligence tests have also been based on elements of CHC theory, and studies on earlier versions of the Binet scales revealed distinguishable CHC factors. The SB5 is composed of ~.factors (out of 10) of theCHC model including (CHC factors in parentheses): Fluid Reasoning (Fluid Intelligence or Gf), Knowledge (Crystallized Knowledge or Gc), Quantitative Reasoning (Quantitative Knowledge or Gq), Visual-Spatial Processing (Visual Processing or Gv), and Working Memory (Short Term Memory or Gsm). Norm The Stanford-Binet is a standardized test, meaning that norms were established during the design phase of the test by administering the test to a large, representative sample of the test population. The test has a mean, or average, standard score of 100 and a standard deviation of 16 (subtests have a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 8). The standard deviation indicates how far above or below the norm the subject's score is. For example, an eight-year-old is assessed with the Stanford-Binet scale and achieves a standard age score of 116. The mean score of 100 is the average level at which all eight-year-olds in the representative sample performed. This child's score would be one standard deviation above that norm. While standard age scores provide a reference point for evaluation, they represent an average of a variety of skill areas. A trained psychologist will evaluate and interpret an individual's performance on the scale's subtests to discover strengths and weaknesses and offer recommendations based upon these findings. Standardization sample: nature, size, representatives, procedures followed in obtaining sample, availability of subgroup norms: The norming of the SB5 is one of the most impressive aspects of the instrument. A sample of 4,800 participants, ranging from age 2 to over 85 were closely matched to variables in 2001 U.S. Census Bureau documents. The stratification variabIes included sex, age, race/ethnicity, socioeconomic level, and geographic region. The sample included young children (ages 2-5), 1,000 children (ages 6-10), 1,322 adolescents/young adults (11-20), and 1,onf adults (21-80+). The geographic regions in the Census (Midwest, South, Northeast, and West) were used in stratifying the sample for the SB5. Additionally, the SB-5 was co-normed with the Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, 2nd Edition, and linked to the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement Reliability Reliabilities for the SB-5 are very high. For the Full Scale IQ, Nonverbal IQ and Verbal IQ, reliabilities range from .95 to .98 (average internal consistency composite reliability across all age groups). Reliabilities for the Factor Indexes range from .90 to .92. For the ten subtests, reliabilities range from .84 to.89. Extensive validity studies were conducted, including clinical-group differences, correlations with other tests, age trends, factor structure, and consequential validity. Many of these studies are presented in the Technical Manual and others in the Supplemental Interpretive Manual. Long term stability when available The ideal time period before retesting with the same test is one year or more. Published research has not pinpointed an exact time; however, the main principal is to allow enough time so that examinees will not easily recall specific tasks and items. Perhaps a nine-month interval could be tolerated in cases where students have passed into another grade level. A nine-month interval for elderly might also be possible in cases of memory loss. Validity Concurrent and criterion validity data were obtained using the SB-IV,SB-LM, WJ III®, UNIT, Bender-Gestalt II, WPPSI-R®,WAIS®-III, WIAT®-II, and WISC-III®. Construct validity was obtained from the analyses of age trends for each of the five factor scores, which included both growth and decline, intercorrelations of tests, factors, IQs, and evidence for general ability. Preliminary evidence content:-related, criterion-related, concurrent, and construct-related validity is presented in the SB5 technical manual. Of course, validity of the SB5 will also be gathered after publication as it is used in the field and in research studies. The test development of the SB5 which was a 7-year process, underwent extensive expert review of items and subtests, numerous pilot studies and reviews of the tryout0 edition. Additionally, the SB5 was found to be highly correlated with major cognitive tests such as the Wechsler scales and previous editions of the Stanford-Binet.