The Nervous System 64 new vocab
advertisement

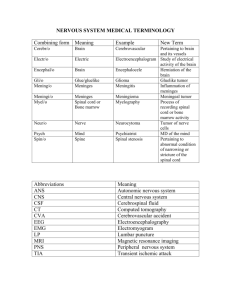
The nervous system : Anatomy and Physiology afferent neurons (afferent means toward) Alzheimer's disease disorder associated with degenerative changes in the brain structure that lead to progressive memory loss, impaired cognition, and personality changes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) a degenerative disease in which patients become progressively weaker until they are completely paralyzed; also known as Lou Gehrig's disease anesthesia the absence of normal sensation, especially sensitivity to pain, that is induced by the administration of an anesthetic anesthetic the medication used to induce anesthesia anticonvulsant administered to prevent seizures such as those associated with epilepsy antidepressant a medication administered to prevent or relieve depression antipsychotic drug a medication administered to treat symptoms of severe disorders of thinking and mood that are associated with neurological and psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia, mania, and delusional disorders anxiolytic drug a medication administered to temporarily relieve anxiety and to reduce tension; also known as an antianxiety drug or tranquilizer aphasia the loss of the ability to speak, write, and/or comprehend the written or spoken word attention deficit disorder characterized by a short attention span and impulsive behavior that is inappropriate for the child's developmental age autism describes a group of conditions in which a young child cannot develop normal social relationships 1 autonomic nervous system controls the involuntary actions of the body axon a process that extends away from the cell body and conducts impulses away from the nerve cell barbiturates a class of drugs whose major action is a calming or depressed effect on the central nervous system Bell's palsy temporary paralysis of the seventh cranial nerve that causes drooping only on the affected side of the face brainstem the stalk-like portion of the brain that connects the cerebral hemispheres with the spinal cord; made up of three parts: the midbrain, pons, and medulla carotid ultrasonography an ultrasound study of the carotid artery to detect plaque buildup in the artery to predict or diagnose an ischemic stroke centrall nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord cerebellum the second-largest part of the brain, located at the back of the head below the posterior portion of the cerebrum cerebral pertaining to the cerebrum or to the brain cerebral hemispheres the cerebrum is divided into these two parts cerebral lobes each cerebral hemisphere is subdivided to create pairs of lobes; each lobe is named for the bone of the cranium that covers it cerebral palsy a congenital condition characterized by poor muscle control, spasticity, speech defects, and other neurologic deficiencies cerebrospinal fluid a clear, colorless, and watery fluid that flows throughout the brain and around the spinal cord cerebrovascular accident damage to the brain that occurs when the blood flow to the brain is disrupted; also known as a stroke 2 cerebrum the largest and uppermost portion of the brain, consisting of four lobes complex regional pain syndrome pain that occurs after an injury to an arm or a leg, a heart attack, stroke, or other medical problem Concussion a violent shaking up or jarring of the brain that may result in a temporary loss of awareness and function connecting neurons associative neurons which link sensory and motor neurons conversion disorder characterized by serious temporary or ongoing changes in function, such as paralysis or blindness, that are triggered by psychological factors rather than by any physical cause cranial hematoma a collection of blood trapped in the tissues of the brain cranial nerves 12 pairs of nerves that originate from the undersurface of the brain dementia a slowly progressive decline in mental abilities, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes dendrites the root-like processes that receive impulses and conduct them to the cell body dyslexia a learning disability characterized by substandard reading achievement due to the inability of the brain to process symbols; also known as a developmental reading disorder echoencephalography the use of ultrasound imaging to diagnose a shift in the midline structures of the brain efferent neurons (efferent means away from) motor neurons which carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord and toward the muscles and glands electroencephalography the process of recording the electrical activity of the brain through the use of electrodes attached to the scalp 3 encephalitis an inflammation of the brain epidural anesthesia regional anesthesia produced by injecting a local anesthetic into the epidural space of the lumbar or sacral region of the spine epilepsya chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent episodes of seizures of varying severity factitious disorder a condition in which an individual acts as if he or she has a physical or mental illness when he or she is not really sick; previously known as Munchausen ganglion a nerve center made up of a cluster of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system glial cells provide support and protection for neurons Gullain-Barre syndrome an inflammation of the myelin sheath of peripheral nerves, characterized by rapidly worsening muscle weakness that may lead to temporary paralysis; also known as infectious polyneuritis hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures; also known as a bleed hydrocephalus a condition in which there is an abnormally increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid within the ventricles of the brain hyperesthesia a condition of excessive sensitivity to stimuli hypnotherapy the use of hypnosis to produce a relaxed state of focused attention in which the patient may be more willing to believe and act on suggestions hypnotic depresses the central nervous system and usually produces sleep hypothalamus located below the thalamus, controls vital bodily functions impulse-control disorders a group of psychiatric disorders characterized by the inability to resist an impulse despite potential negative consequences 4 innervations the supply of nerves to a specific body part intracranial pressure the amount of pressure inside the skull ischemic stroke a type of stroke that occurs when the flow of blood to the brain is blocked lobectomy surgical removal of a portion of the brain to treat brain cancer or seizure disorders that cannot be controlled with medication lumbar puncture the process of obtaining a sample of cerebrospinal fluid by inserting a needle into the subarachnoid space of the lumbar region to withdraw fluid lumbar radiculopathy nerve pain in the lower back caused by muscle spasms or by nerve root irritation from the compression of vertebral disks such as a herniated disk magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computer tomography (CT) important neuroimaging tools because they facilitate the examination of the soft tissue structures of the brain and spinal cord medulla located at the lowest part of the brainstem, connected to the spinal cord meninges the system of membranes that enclose the brain and spinal cord of the CNS meningitis an inflammation of the meninges of the brain or spinal cord meningocele the congenital herniation of the meninges that surround the brain or spinal cord through a defect in the skull or spinal column midbrain and pons provides conduction pathways to and from the higher and lower centers in the brain multiple sclerosis a progressive autoimmune disorder characterized by scattered patches of demyelination of nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord myelin sheath the protective covering made up of glial cells 5 myelitis an inflammation of the spinal cord; also inflammation of bone marrow myelography a radiographic study of the spinal cord after the injection of a contrast medium through a lumbar puncture. The resulting record is called a myelogram. myelosis a tumor of the spinal cord narcolepsy a sleep disorder consisting of recurring episodes of falling asleep during the day nerve one or more bundles of neurons that connect the brain and the spinal cord with other parts of the body neurons the basic cells of the nervous system that allow different parts of the body to communicate with each other neuroplasty the surgical repair of a nerve or nerves neurorrhaphy surgically suturing together the ends of a severed nerve neurotomy a surgical incision or the dissection of a nerve neurotransmitters chemical substances that make it possible for messages to cross from the synapse of a neuron to the target receptor; examples include acetylcholine, dopamine, endorphins, norepinephrine, and serotonin obsessive-compulsive disorder an anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent, unwanted thoughts or impulses panic attack a group of intense emotional feelings that include apprehension, fearfulness, and terror panic disorder an anxiety disorder characterized by unexpected and repeated episodes known as panic attacks parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to normal after a response to stress 6 paresthesia refers to a burning or prickling sensation that is usually felt in the hands, arms, legs, or feet, but can also occur in other parts of the body Parkinson's disease (PD) a chronic, degenerative central nervous disorder in which there is a progressive loss of control over movement, resulting in tremors and a shuffling gait peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the 12 pairs of cranial nerves extending from the brain and the 31 pairs of peripheral spinal nerves extending outward from the spinal cord peripheral neuropathy a painful condition of the nerves of the hands and feet due to damage to the peripheral nerves; also known as peripheral neuritis peripheralspinal nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves that are grouped together and named based on the region of the body they innervate phenobarbital a barbiturate used as a sedative and as an anticonvulsant poliomyelitis a highly contagious viral disease; also known as polio psychotropic drug acts primarily on the central nervous system, where it produces temporary changes affecting the mind, emotions, and behavior radiculitis an inflammation of the root of a spinal nerve that causes pain and numbness radiating down the affected limb; also known as a pinched nerve receptors sites in the sensory organs that receive external stimulation restless legs syndrome (RLS) a neurological disorder characterized by uncomfortable feelings in the legs, producing a strong urge to move them Reye's syndrome (RS) a potentially fatal condition that has been linked to giving aspirin to children suffering from viral infections SAM neuron functions: Sensory neurons (afferent); Associative neurons (connecting); Motor neurons (efferent) sciatica inflammation of the sciatic nerve 7 sedative depresses the central nervous system to produce calm and diminished responsiveness without producing sleep seizure a sudden surge of electrical activity in the brain that affects how a person feels or acts for a short time somatoform disorder characterized by physical complaints or concerns about one's body that are out of proportion to any physical findings or disease somnambulism the condition of walking or performing some other activity without awakening; also known as sleepwalking spinal cord a long, fragile tube-like structure that begins at the end of the brain stem and continues down almost to the bottom of the spinal column sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for emergencies and stress by increasing the breathing rate, heart rate, and blood flow to muscles synapse the space between two neurons or between a neuron and a receptor organ syncope the brief loss of consciousness caused by the decreased flow of blood to the brain; also known as fainting tetanusan acute and potentially fatal infection of the central nervous system caused by a toxin produced by the tetanus bacteria thalamuslocated below the cerebrum, produces sensations by relaying impulses to and from the cerebrum and the sense organs of the body transient ischemic attack (TIA) the temporary interruption in the blood supply to the brain 8