Ren Fest Work
advertisement

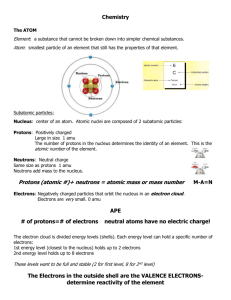
Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work Enter the appropriate word(s) to complete the statement. 1. A rule that describes the behavior of something in nature is a scientific ____________________. 2. Hydrogen peroxide _______________ and forms water and oxygen gas. 3. Newton's first law of motion states that an object stays in constant motion unless a(n) ____________________ force acts on it. 4. A distance-time graph shows a horizontal line. This means that the velocity is ____________________. 5. When a substance combines with O2 and releases energy, a _______________ reaction has occurred. 6. All matter is made up of particles called ____________________. 7. Each nitrogen atom can share three valence electrons forming a _______________ covalent bond. 8. There are _______________ hydrogen atoms in the chemical formula CH4. 9. Speeding up, slowing down, and going around curves are examples of ____________________. 10. The attraction between positive and negative _______________ forms an ionic bond. 11. _______________ shows information about the element such as chemical symbol and atomic mass. 12. Speeding up, slowing down, and going around curves are examples of ____________________. 13. A rocket launching is an example of Newton's ____________________ law. 14. The likely location of the negatively charged particles in an atom is called a(n) ____________________. 15. Atoms that are unstable are more likely to be ____________________ than atoms that are stable. 16. The _______________ ratio provides a measure of a structure’s safety. 17. Geoff observed an experiment in which one compound underwent a chemical reaction that produced two compounds. He classified this as a _______________ reaction. 18. Elements on the left side of the periodic table are classified as ____________________. 19. Atoms of the same element containing different numbers of neutrons are called ____________________. 20. Metal atoms bond together to form a _______________ bond. 21. Kalina conducted an experiment in which she started with one element and one compound and ended up with a different element and a different compound. She classified this as a _______________ reaction. 22. A(n) ____________________ is a push or a pull. Powered by Cognero Page 1 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 23. Mike has a mass of 60 kg. He pulls on a wagon of mass 30 kg with a force of 20 N. The wagon remains motionless. The wagon exerts a force of ____________________ on Mike. 24. The progression of the atomic theory is as follows: Democritus, Aristotle, _______________, Thomson, _______________, Chadwick, _______________ 25. Qualitative data use _______________ to describe what is observed in an experiment. 26. To calculate ____________________ you divide distance traveled by the time it takes to travel that distance. 27. _______________, not velocity, is used to calculate the average acceleration. 28. Most of the mass of an atom is located in its ____________________. 29. Different factors that can change in an experiment are ____________________. 30. Of the three main subatomic particles, the ____________________ has the least mass. 31. Sugar is an example of a _______________ molecule due to the unequal sharing of electrons. 32. Elements that have properties halfway between those of metals and nonmetals, are classified as ____________________. 33. Rutherford's contribution to atomic models was the discovery of the ____________________. 34. The speed you read from your speedometer is your ____________________. 35. An explanation for the law of conservation of matter is that the same _______________ is present before and after the reaction. 36. If you are riding on a skateboard and it stops suddenly, your body keeps moving forward. This is because of ____________________. 37. Organizing elements in a table enables scientists to relate the _______________ of the elements. 38. If you triple the net force on an object, the acceleration will ____________________. 39. A(n) ____________________ is a push or pull that one object exerts on another. 40. Comparing what you already know about something with new information and then making a decision about whether you agree with the new information is called _______________ thinking. 41. Elements that have properties halfway between those of metals and nonmetals, are classified as ____________________. 42. Analysis of the Minneapolis bridge collapse and _______________ eventually showed that the bridge was not overloaded. 43. Friction always acts in a direction ____________________ to the direction of motion. 44. According to modern atomic theory, electrons are usually found _______________ the nucleus. Powered by Cognero Page 2 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 45. Marie Curie discovered that the radiation released by uranium was made of _______________ and _______________. 46. A spacecraft orbits the Earth at a constant speed. The forces acting on it must be ____________________. 47. Quantitative data use _______________ to describe what is observed in an experiment. 48. Jaunita watched as two compounds reacted and changed into two different compounds. She determined the reaction that she observed was a _______________ reaction. 49. The _______________ switch places in a double-replacement reaction. 50. ____________________ is the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. 51. A car going around a corner, hits an icy path, and skids off the road. This represents a change from rolling friction to ____________________ friction. 52. If two or more substances combine to produce one substance, a _______________ reaction has occurred. 53. The French chemist, _______________, conducted experiments that led to the law of conservation of mass. 54. A(n) ____________________ group is used to study how a change in the independent variable changes the dependent variable. 55. Reinforcement rods on a truss bridge are sometimes called _______________. 56. According to Newton's second law of motion, a larger force acting on an object causes a greater ____________________ of that object. 57. Forces that change an object's motion by touching the object are ____________________ forces. 58. Elements on the left side of the periodic table are classified as ____________________. 59. Nuclear decay produces radiation. _______________ decay causes Americium-241 to decay to Neptunium-237. There are two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons. 60. To keep a sled accelerating downhill, the force of gravity must be greater than the ____________________ force. 61. How does the atomic model developed by John Dalton differ from the atomic model developed by Niels Bohr? Describe each model. 62. Identify a physical property that might be used to tell whether a compound is ionic or covalent. Explain why this physical property is a good indicator. 63. Scientists working in a laboratory wanted a particular chemical reaction to occur as quickly as possible. Identify and describe four ways that the scientists could increase the rate at which the reaction occurs. 64. Describe some of the trends in the periodic table. What is a row called? What is a column called? What properties increase or decrease and in which directions? Powered by Cognero Page 3 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 65. Explain why a molecule formed by two identical atoms is nonpolar. 66. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How does each of these forces change the ball’s motion? Classify the forces acting on the ball as balanced or unbalanced. 67. Use the graph provided to explain the speed of this object. Provide an example of how this graph could happen in real life. How could you change the graph to show an objects’ speed decreasing over time? Provide an example of the new graph. 68. Explain the conclusions of the investigators, scientists, and engineers in the Minneapolis bridge collapse. 69. Lithium's atomic number is 3. Fluorine's is 9. Explain how an atom of lithium and an atom of fluorine combine by ionic bonding. 70. Your friend stated that action and reaction force pairs do not change motion because they cancel one another out. Explain why your friend is incorrect, using an everyday example to clarify your explanation. In your response, identify which of Newton’s laws of motion applies to action and reaction forces. Contrast action and reaction force pairs and balanced forces. Powered by Cognero Page 4 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work Answer Key 1. law 2. decomposes 3. unbalanced 4. zero 5. combustion 6. atoms 7. triple 8. four 9. acceleration 10. ions 11. The element key 12. acceleration 13. third 14. electron cloud 15. radioactive 16. demand-to-capacity 17. decomposition 18. metals 19. isotopes 20. metallic 21. single-replacement 22. force 23. 20 N 24. Dalton, Rutherford, Bohr 25. words Powered by Cognero Page 5 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 26. average speed 27. Speed 28. nucleus 29. variables 30. electron 31. polar 32. metalloids 33. nucleus 34. instantaneous speed 35. number of atoms 36. inertia 37. properties 38. triple 39. force 40. critical 41. metalloids 42. computer modeling 43. opposite 44. orbiting 45. energy, particles particles, energy 46. balanced 47. numbers 48. double-replacement 49. negative ions 50. Inertia Powered by Cognero Page 6 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 51. sliding 52. synthesis 53. Antoine Lavoisier 54. experimental 55. rebar 56. acceleration 57. contact 58. metals 59. Alpha 60. normal friction 61. Dalton’s model of the atom stated that during a chemical reaction, atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of one element are identical to each other, but different from atoms of another element. Dalton also said that atoms combine in specific ratios. Niels Bohr’s atomic model proposed that electrons move in circular orbits, or energy levels, around the nucleus. Electrons have varying energy levels depending on which orbit they are in. Dalton did not realize that atoms can be divided into even smaller particles, such as protons, neutrons, and electrons. Dalton did not know that atomic weight is a product of the structure of the atoms. Bohr was able to observe the light released when an electron’s energy level changed. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student’s response includes the following: description of Dalton’s atomic model description of Bohr’s atomic model similarities between the models differences between the models Student’s response includes three of the following: description of Dalton’s atomic model description of Bohr’s atomic model similarities between the models differences between the models Student’s response includes two of the following: description of Dalton’s atomic model description of Bohr’s atomic model similarities between the models differences between the models Student’s response includes one of the following: description of Dalton’s atomic model description of Bohr’s atomic model similarities between the models differences between the models Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. Powered by Cognero Page 7 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 62. The state of matter at room temperature can be used to classify most ionic and covalent compounds. Most covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature. Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids with high melting points. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student provides a physical property that can be used to tell whether a compound is ionic or covalent and clearly explains his or her reasoning. Student provides a physical property that can be used to tell whether a compound is ionic or covalent, but does not clearly explain his or her reasoning. Student provides an incorrect physical property that can be used to tell whether a compound is ionic or covalent, but does explain his or her reasoning. Student provides an incorrect physical property that can be used to tell whether a compound is ionic or covalent and does not explain his or her reasoning. Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 63. Scientists could first add a catalyst to the reaction. A catalyst speeds up the reaction without changing other aspects of the reaction. The scientists could also increase the temperature at which the reaction occurs, because an increased temperature speeds most types of reactions. The scientists should also make sure the reactants are present in the highest concentration possible, as increased concentration of reactants speeds up reactions. The scientists could also be sure that the reactants had the most possible surface area. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student identifies and describes the following four factors that influence reaction rate: presence of a catalyst temperature concentration surface area Student identifies and describes three of the following four factors that influence reaction rate: presence of a catalyst temperature concentration surface area Student identifies and describes two of the following four factors that influence reaction rate: presence of a catalyst temperature concentration surface area Student identifies and describes one of the following four factors that influence reaction rate: presence of a catalyst temperature concentration surface area Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 64. The periodic table is named such because there are periodic, or repeating, trends that occur throughout the table. The atomic mass increases from left to right as you advance through the table. A row of elements is called a period. A column of elements is called a group. Metallic properties increase as you move to the left and down on the periodic table. Other properties increase as you go left to right. Powered by Cognero Page 8 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work Score Description Student’s response includes four of the listed trends: increase of atomic number label for rows label for columns example of one trend and the direction for increase Student’s response includes three of the listed trends: increase of atomic number label for rows label for columns example of one trend and the direction for increase Student’s response includes two of the listed trends: increase of atomic number label for rows label for columns example of one trend and the direction for increase Student’s response includes one of the listed trends: increase of atomic number label for rows label for columns example of one trend and the direction for increase Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 4 3 2 1 0 Blank 65. Two identical atoms attract the shared electrons equally. Neither end of the molecule becomes positively or negatively charged, so the molecule is nonpolar. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student clearly explains that two identical atoms share electrons equally and that neither end has a charge thus becoming nonpolar. Student explains that two identical atoms share electrons equally, but incorrectly explains the end charges. OR Student explains the atoms become neither positively or negatively charged, but incorrectly explains that the two identical atoms share electrons equally. Student explains that two identical atoms share electrons equally, but does not explain the end charges. OR Student explains the atoms become neither positively or negatively charged, but does not explain that the two identical atoms share electrons equally. Student does not correctly explain the sharing of electrons or the end charges. Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 66. Two forces that act on the ball as it moves through the air are gravity and friction. Gravity causes the ball to move downward toward Earth. Friction causes the ball’s motion to get slower the farther it moves through the air. Because the ball’s velocity is changing as it moves, it can be determined that the forces acting on the ball are unbalanced. Score Description 4 Student’s response includes the following four elements: identification of friction and gravity as forces acting on the ball; explanation that gravity causes the ball to move toward Earth; explanation that friction slows the ball’s motion; classification of the forces acting on the ball as unbalanced Powered by Cognero Page 9 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 3 2 1 0 Blank Student’s response includes three of the following four elements: identification of friction and gravity as forces acting on the ball; explanation that gravity causes the ball to move toward Earth; explanation that friction slows the ball’s motion; classification of the forces acting on the ball as unbalanced Student’s response includes two of the following four elements: identification of friction and gravity as forces acting on the ball; explanation that gravity causes the ball to move toward Earth; explanation that friction slows the ball’s motion; classification of the forces acting on the ball as unbalanced Student’s response includes one of the following four elements: identification of friction and gravity as forces acting on the ball; explanation that gravity causes the ball to move toward Earth; explanation that friction slows the ball’s motion; classification of the forces acting on the ball as unbalanced Student’s response it totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 67. An object at rest is not moving, so its speed is always zero. As a result, the speed-time graph for an object at rest is a horizontal line at y = 0. Any object at rest is an example of this graph. A vase of flowers sitting on a table or a nonmoving car sitting in a parking lot are both examples of this graph. To change the graph to show an objects’ speed is decreasing over time, move the line to begin at a higher point on the y-axis and slope it down and towards the right. Once the line touches the x-axis, the speed is zero and the object has stopped. A car traveling at a rate of 35 miles per hour and slowing to stop at a red light is an example of this new graph. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student’s response should include all four elements of the question: an explanation of the original graph with an example and an explanation of the new graph with an example. Student’s response includes three of the following four elements: an explanation of the original graph with an example and an explanation of the new graph with an example. Student’s response includes two of the following four elements: an explanation of the original graph with an example and an explanation of the new graph with an example. Student’s response includes one of the following four elements: an explanation of the original graph with an example and an explanation of the new graph with an example. Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 68. The U10 node-gusset plates were not thick enough to support the loads they were supposed to handle. They were about half the thickness they should have been. When the investigators examined the original documents for the bridge, they were unable to find any detailed gusset plate calculations. They could not determine whether undersized plates were used because of mistaken calculations, a drafting error, or some other error in the design process. Score 4 3 Powered by Cognero Description Student’s response includes the reason for the bridge failure, the possible errors made in the original design, and two possible reasons for the undersized plates being used. Student’s response includes three of the following: the reason for the bridge failure, the possible errors made in the original design, and two possible reasons for the undersized plates being used. Page 10 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work Student’s response includes two of the following the reason for the bridge failure, the possible errors made in the original design, and two possible reasons for the undersized plates being used. Student’s response includes one of the following the reason for the bridge failure, the possible errors made in the original design, and two possible reasons for the undersized plates being used. Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 2 1 0 Blank 69. Lithium's atomic number of 3 indicates that a lithium atom has three electrons. Two of these electrons fill an inner energy level; the third electron is in an almost empty outer energy level. A fluorine atom has nine electrons. Two of fluorine's electrons fill the inner energy level, and seven are in the outer energy level. Lithium gives an electron to fluorine. Lithium becomes positive, and fluorine becomes negative. Both lithium and fluorine then have full and therefore relatively stable outer energy levels. Score 4 3 2 1 0 Blank Description Student clearly explains how lithium and fluorine atoms combine by ionic bonding by discussing filling of energy levels by giving and taking electrons. Student identifies that lithium becomes positive and fluorine becomes negative and discusses the stability of their outer energy levels. Student explains how lithium and fluorine atoms combine by ionic bonding by discussing filling of energy levels by giving and taking electrons, the resulting charge for the atoms, and their outer energy levels with one or two minor errors. Student explains how lithium and fluorine atoms combine by ionic bonding by discussing filling of energy levels by giving and taking electrons, the resulting charge for the atoms, and their outer energy levels with multiple errors. Student explains how lithium and fluorine atoms combine by ionic bonding by discussing filling of energy levels by giving and taking electrons, the resulting charge for the atoms, and their outer energy levels with major errors. Student’s response it totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. 70. My friend is incorrect. Although it may seem that equal and opposite forces should cancel one another out, action and reaction forces do not, because they act on different objects. For example, if a swimmer pushes against the water with her hand, the reaction force is exerted against the swimmer (not the water), resulting in the swimmer moving forward. In order for equal and opposite forces to cancel one another (or to be balanced forces), they would need to act on the same object, which is not the case. Newton’s third law describes action and reaction force pairs. Score 4 3 Powered by Cognero Description The student correctly explains that action and reaction forces do not cancel one another because they do not act on the same object; uses an everyday example of action and reaction forces; identifies Newton’s third law as the law that describes action and reaction forces; explains that action and reaction forces are not balanced forces (forces that are equal and opposite on the same object) The student’s response includes three of the following: action and reaction forces do not cancel one another because they do not act on the same object; uses an everyday example of action and reaction forces; identifies Newton’s third law as the law that describes action and reaction forces; explains that action and reaction forces are not balanced forces (forces that are equal and opposite on the same object) Page 11 Name: Class: Date: Ren Fest Work 2 1 0 Blank Powered by Cognero The student’s response includes two of the following: action and reaction forces do not cancel because they do not act on the same object; uses an everyday example of action and reaction forces; identifies Newton’s third law as the law that describes action and reaction forces; explains that action and reaction forces are not balanced forces (forces that are equal and opposite on the same object) The student’s response includes one of the following: action and reaction forces do not cancel one another because they do not act on the same object; uses an everyday example of action and reaction forces; identifies Newton’s third law as the law that describes action and reaction forces; explains that action and reaction forces are not balanced forces (forces that are equal and opposite on the same object) Student’s response is totally incorrect or irrelevant. No student response. Page 12