Ch 15 Respiratory and 4th Quarter Assessment Exam Study Guide 1

Ch 15 Respiratory and 4
1. Respiration refers to th
Quarter Assessment Exam Study Guide
a. gas exchange between blood and tissues. b. ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the lungs. c. gas exchange between the air in the lungs and blood. d. gas exchange between the blood and the tissues.
E. All of these are parts of respiration.
2. The nasal cavity is divided into right and left sides by a. the conchae. b. the paranasal sinuses. c. external nares.
D. the nasal septum. e. the hard palate.
3. Which of these functions are accomplished by the nasal cavities? a. Mucus produced by the nasal lining traps debris from the air. b. Cilia on the mucous membrane sweep debris into the pharynx. c. he sense of smell d. Air is humidified and warmed.
E. All of these are functions of the nasal cavities.
4. Given these divisions of the larynx:
1) laryngopharynx
2) nasopharynx
3) oropharynx
From superior to inferior, the correct sequence for the divisions of the pharynx is: a. 1, 2, 3 b. 1, 3, 2
C. 2, 3, 1 d. 2, 1, 3 e. 3, 2, 1
5. The largest and most superior of the cartilages in the larynx is the
A. thyroid cartilage. b. cricoid cartilage. c. arytenoid cartilage. d. cuneiform cartilage. e. corniculate cartilage
6. Which of these problems in the trachea are associated with cigarette smoking? a. Ciliated epithelium is replaced by squamous epithelium. b. Mucus and debris accumulate in the trachea. c. Respiratory infections are likely because of accumulated mucus. d. Irritation and inflammation stimulate the cough reflex.
E. All of these events occur in smokers.
7. Given these respiratory passageways:
1) alveoli
2) bronchi
3) bronchioles
4) respiratory bronchioles
5) terminal bronchioles
From largest to smallest, the correct order for these passageways is: a. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B. 2, 3, 5, 4, 1 c. 3, 1, 2, 5, 4 d. 4, 5, 2, 1, 3 e. 5, 2, 3, 4, 1
8. The pleural cavities a. lie between the visceral and parietal pleura. b. are filled with pleural fluid. c. are found within the mediastinum. d. are lined with mucous membrane.
E. both lie between the visceral and parietal pleura and are filled with pleural fluid.
9. Which of these statements concerning ventilation is NOT correct? a. During inspiration, the pressure in the alveoli is less than atmospheric pressure. b. When the diaphragm contracts, thoracic cavity volume increases.
C. Contraction of the external intercostal muscles decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity. d. During quiet breathing, passive recoil of the lung and thoracic wall cause expiration. e. During labored breathing, the internal intercostal and abdominal muscles assist in expiration.
10. Surfactant a. decreases the surface tension of fluid in the alveoli. b. is lacking in babies with hyaline membrane disease. c. decreases the energy required to keep the lungs inflated. d. helps keep the lungs from collapsing.
E. has all of these characteristics.
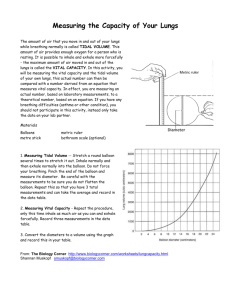
11. In a healthy person, which of these lung volumes should be the largest? a. tidal volume
B. inspiratory reserve volume c. expiratory reserve volume d. residual volume
12. Which of these capacities is NOT correctly defined? a. vital capacity = inspiratory reserve + tidal volume + expiratory reserve b. inspiratory capacity = tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume
C. functional residual capacity = expiratory reserve + residual volume + inspiratory reserve d. total lung capacity = inspiratory reserve + expiratory reserve + tidal volume + residual volume
13. Which of these comparisons concerning respiratory vital capacities is correct? a. Females have larger vital capacities than males.
B. Young adults have larger vital capacities than the elderly. c. Short people have larger vital capacities than tall people. d. Obese people have larger vital capacities than thin people. e. People with silicosis or fibrosis have larger vital capacities than others without the condition.
14. Concerning oxygen transport in the blood, which of these statements is NOT correct? a. Most of the oxygen in plasma combines reversibly with hemoglobin. b. Oxygen combines with the heme group of hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin.
C. A low pH reduces the amount of oxygen released in the tissue capillaries. d. An increase in temperature increases the amount of oxygen released in the tissue capillaries. e. Oxygen bound to hemoglobin does not affect the partial pressure of oxygen in blood.
15. Most carbon dioxide is transported
A. as bicarbonate ions in the blood. b. dissolved in the plasma. c. in combination with blood proteins. d. by oxygen atoms in the blood. e. in combination with sodium ions in the blood.
16. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood increase, a. pH of the blood increases.
B. the blood becomes more acidic. c. the number of hydrogen ions in the blood decreases. d. both pH of the blood increases and the number of hydrogen ions in the blood decreases. e. All of these events occur.
17. Which of these cause an increase in respiration rate? a. stimulation of pain receptors b. anticipation at the start of exercise c. movements of the limbs d. stress
E. All of these will increase respiratory rate.
18. Patients with diabetes mellitus who are not being treated with insulin therapy rapidly metabolize lipids, and there is an accumulation of acidic byproducts of lipid metabolism in the circulatory system. What effect would this have on respiration?
A. increase in respiratory rate b. decrease in respiratory rate c. decrease in respiratory rate if oxygen is reduced d. no influence on respiratory rate
19. An asthma attack a. almost always has an immune or allergic component. b. is less severe during or after strenuous exercise.
C. is characterized by abnormal increases in bronchoconstriction. d. is characterized by abnormal increases in bronchodilation. e. only occurs where cells are dividing and the proper gene is expressed.
20. Constriction of smooth muscle in bronchioles is seen in a. emphysema.
B. asthma. c. pulmonary edema. d. pneumothorax.
21. The air that can be inspired forcefully above normal tidal volume is the a. tidal volume. b. forced expiratory vital capacity.
C. inspiratory reserve volume. d. residual volume. e. expiratory reserve volume.
22. The _____________ is the volume of air inspired or expired during quiet breathing.
A. tidal volume b. forced expiratory vital capacity c. inspiratory reserve volume d. residual volume e. expiratory reserve volume
23. The volume of air still remaining after maximum expiration is the a. tidal volume. b. forced expiratory vital capacity. c. inspiratory reserve volume.
D. residual volume. e. expiratory reserve volume.
24. The amount of air that can be expired forcefully above or beyond the normal tidal volume is the a. tidal volume. b. forced expiratory vital capacity. c. inspiratory reserve volume. d. residual volume.
E. expiratory reserve volume.
25. All of the following are functions of the respiratory system EXCEPT: a. gas exchange between the blood and air b. regulation of blood pH by changing blood carbon dioxide levels
C. provides acquired immunity that prevents microorganisms from entering the body d. air movement past the vocal cord makes sound and speech possible e. provides innate immunity
26. The right lung has ______ lobes and _______ bronchopulmonary segments. a. 2, 9 b. 2, 10 c. 3, 9
D. 3, 10
27. The primary functions of the respiratory system include all of the following EXCEPT: a. maintain homeostasis by regulating the acid/base balance b. to provide an area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood
C. to increase the diffusion distances of gases d. to protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration and environmental variations e. to provide innate immunity
28. During normal, quiet inhalation a. air is drawn into the lungs because of the contraction of the internal intercostal muscles. b. there is an increase in the atmospheric air pressure. c. the diaphragm relaxes while the rib cage is pulled down.
D. the volume of the thoracic & pleural cavities increases. e. air is introduced into the pleural cavity thus increasing the pressure around the lungs.
29. Gas exchange at the respiratory membrane is efficient because a. the difference in partial pressures is substantial. b. the distances involved in exchange are small. c. the total surface area of the membrane is large. d. blood flow and air flow are coordinated (blood flow is highest around alveoli with highest Po2).
E. All of these are correct.
30. The C-shaped cartilages that form the lateral and anterior sides of the trachea a. are called the thyroid cartilages. b. make up the vocal cords. c. consist of ligamentous membranes and smooth muscle.
D. function to protect the trachea and maintain an open air passage. e. give rise to the structure known as the Adam's apple in men.
31. Which of the following would be appropriate to perform if you swallowed incorrectly and had a piece of food stuck in your trachea? a. the sneeze reflex
B. the Heimlich maneuver c. intubation d. vomiting e. All of these would remove the obstruction.
32. Pleural fluid a. acts as a lubricant allowing the pleurae to slide past each other. b. holds the pleural membranes together. c. increases surface tension. d. is located in the space between the parietal and visceral pleurae.
E. All of these are correct.
33. Which of the following statements is FALSE ? a. Phagocytic cells within the lungs phagocytize carbon particles from inspired air.
B. The walls of the alveoli have a rich supply of lymphatic vessels. c. The superficial and deep lymphatic vessels exit the lungs at the main bronchi. d. The superficial lymphatic vessel drains lymph fluid from the superficial lung tissue and visceral pleura. e. In older smokers, lung tissue can appear gray or black due to the accumulation of debris particles.
34. During which of the following times is the alveolar pressure higher than the atmospheric pressure? a. at the end of expiration
B. at the beginning of expiration c. at the end of inhalation d. at the beginning of inhalation e. Alveolar pressure is never higher than the atmospheric pressure.
35. The air pressure in the lungs can be increased by a. increasing the volume of the lungs.
B. decreasing the volume of the lungs. c. relaxing the diaphragm. d. contracting the internal intercostals muscles. e. Both relaxing the diaphragm and by decreasing the volume of the lungs.
36. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
A. increases calcium level in the blood. b. inhibits the formation of active vitamin D in the kidneys. c. decreases the rate of bone breakdown. d. has an effect similar to that of calcitonin. e. has all of these characteristics.
37. The adrenal medulla a. is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. b. produces epinephrine and norepinephrine. c. is stimulated when a person is physically excited. d. produces the "fight-or-flight" response.
E. has all of these properties.
38. Insulin is secreted in response to
A. increased blood glucose levels. b. decreased parasympathetic stimulation. c. decreased blood levels of amino acids. d. All of these stimulate insulin secretion.
39. Insulin is secreted by the a. anterior pituitary gland. b. posterior pituitary gland. c. adrenal cortex. d. adrenal medulla.
E. beta cells of the pancreatic islets.
40. Glucocorticoids are secreted by the a. anterior pituitary gland. b. posterior pituitary gland.
C. adrenal cortex. d. adrenal medulla. e. beta cells of the pancreatic islets.
41. Growth hormone is secreted by the
A. anterior pituitary gland. b. posterior pituitary gland. c. adrenal cortex. d. adrenal medulla. e. beta cells of the pancreatic islets.
Difficulty: Easy
Seeley - 010 Endocrine... #48
Type: Knowledge
42. Red blood cells a. are biconvex disks. b. have several nuclei in each cell. c. divide frequently.
D. contain large quantities of hemoglobin. e. have all of these properties.
43. Erythropoietin a. requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor. b. is produced in the intestines.
C. stimulates red bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. d. is produced when high blood oxygen levels occur. e. has all of these properties.
44. Platelets a. are also called lymphocytes. b. have no cell membrane. c. are produced in the spleen.
D. play an important role in hemostasis. e. have all of these characteristics.
45. The heart is within the a. thoracic cavity. b. mediastinum. c. abdominal cavity.
D. mediastinum and thoracic cavity. e. mediastinum and abdominal cavity.
Difficulty: Moderate
Seeley - 012 Heart... #2
Type: Knowledge
46. The bicuspid (mitral) valve a. is the location of the pacemaker cells of a normal heart. b. prevents blood flow from the right ventricle to the right atrium.
C. prevents blood flow from the left ventricle to the left atrium. d. prevents blood flow from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle. e. prevents blood flow from the aorta to the left ventricle.
47. Blood flow through capillaries is regulated by a. one-way valves in the veins.
B. precapillary sphincters. c. skeletal muscle contraction. d. elastic valves. e. the tunica intima.
48. Lymph a. is excess interstitial tissue fluid that passes into lymph capillaries. b. is very similar in composition to blood plasma. c. would produce edema and tissue damage if not removed. d. is called chyle where fats are absorbed in intestinal lacteals.
E. has all of these properties.
49. Which of these is NOT a function of the lymphatic system? a. helps to maintain tissue fluid balance b. is part of the body's defense system c. transports fat and other substances absorbed by the digestive tract
D. produces red blood cells e. All of these are normal functions of the lymphatic system.
50. Which of these processes assist in the transport of lymph from the lower limbs? a. gravity b. contraction of facial muscles
C. contraction of skeletal muscles surrounding lymph vessels d. contraction of smooth muscles in blood vessel walls e. None of these assist transport of lymph through lymph vessels.