Text book - جامعة الملك عبدالعزيز
advertisement

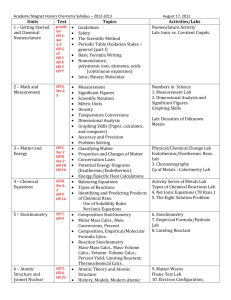
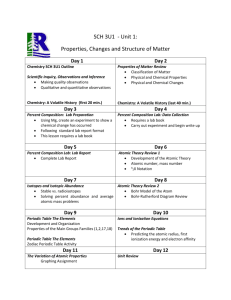
King Abdul Aziz University Faculty of Science and Art Chemistry Department جامعـــة المـلك عبد الـــعزيز كلية العلوم واآلداب بخليص قسم الكيمياء ]txep TpyT[ Chemistry for the path of scientific COURSE ENGLISH CODE TITLE General /NO CREDITS ARABIC CODE/NO. Chem.100 Th. Pr. Tr. TCH 3 0 0 3 Chemistry Pre-requisites ------- Brief contents: Introduction, SI-Units and their prefix, atomic structure, periodic Table, chemical formulae, chemical equations and chemical bonds gas laws, ionic equilibrium and Le Chatelier's Principle, acids and bases, solubility equilibrium, buffer solutions, basic principles of organic and biochemistry. Objectives: The course aims at: 1- Introducing students to the basic knowledge and principles of chemistry branches (physical, inorganic, organic and biochemistry). 2- Writing the electronic configuration for atoms, and their positions in periodic table, chemical equations, as well as reaching ionic equilibrium principle. 3- Applying the fundamental laws of general chemistry for different atoms and gases. Contents: 1- Introduction, SI-Units and their prefix, atomic theory, atomic structure. 2- Periodic Table: naming compounds, chemical formulae and chemical equations. 3- Chemical bonds and Lewis structure, gas laws, ionic equilibrium and Le Chatelier,s Principle, acids and bases, solubility equilibrium, and buffer solutions. 4- Basic principles of both organic, and biochemistry. Course Outcomes: By the end of the course students are expected to acquire: King Abdul Aziz University Faculty of Science and Art Chemistry Department ]txep TpyT[ جامعـــة المـلك عبد الـــعزيز كلية العلوم واآلداب بخليص قسم الكيمياء A- Knowledge: 1- Knowing the information and of concepts of the chemical theories. 2- Knowing the types of formulae as well as many other chemical laws in the chemical equations and their correlation . B- Cognitive Skills: 1-Understanding the concepts of interpretation, investigation and discussion. 2-analysis, scientific evaluation and solving the chemical applications and problems. C- Interpersonal skills and responsibilities : 1-Ability to read, interpret, assimilate, evaluate and remember. 2- how to deal with the chemical issues and applications. D- Analysis and communication skills: 1- Knowing how the information is gathered, analyzed and documented in the field of chemistry. 2- Acquiring the theoretical bases needed for the practical chemical experiments. Text book: (1) Raymond Chang, Chemistry, 10th edition, (2010), Published by McGraw-Hill. Supplementary references: (1) William L. Masterton and Cecile N. Hurley, Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 6th edition, (2008), Published by Brooks, Cole. (2) Charles E. Mortimer, Chemistry, 6th edition, (1986), Published by Wadsworth Inc. Other Information Resources : Time table for distributing Theoretical course contents week 1 2 3 4 5 Experiment Remarks Introduction to the course: Basic Principles SI system of units, derived units, unit conversion, significant figures, scientific notation. Stoichiometry: Atomic symbols, atomic masses, the mole, chemical formulae, mass relations. Stoichiometry: Limiting reagent, theoretical yield, practical yield, percent yield of the reaction, concentration, stoichiometry of reactions in solutions. Atomic structure: Quantum numbers, orbitals, electronic structure of the elements. Periodic Table: types of elements in the periodic King Abdul Aziz University Faculty of Science and Art Chemistry Department 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ]txep TpyT[ جامعـــة المـلك عبد الـــعزيز كلية العلوم واآلداب بخليص قسم الكيمياء table, periodic properties. Chemical bonds: Ionic and covalent bonding, formal charges, Lewis structures, resonance, octet rule and exceptions. Chemical bonds: Lewis structure, resonance, octet rule and exceptions. Mid-Term exam 1 Gases: Introduction, ideal gas laws, general gas constant, kinetic theory of gases and its relation to ideal gas laws. Gases: Molecular energies and speeds, Dalton's law of partial pressures, Graham's law of diffusion, real gases. Ionic Equilibrium: Acids and bases, strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, ionization of water. Ionic Equilibrium: pH, buffer solutions, hydrolysis of salt solutions, solubility product and the common ion effect, applications. Introduction to organic chemistry: Electronic structure and atomic orbital's, types of hybridization. Mid-Term exam 2 Introduction to organic chemistry: Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and nomenclature. Introduction to biochemistry: proteins, and carbohydrates. Final Exam