ANSWERS to C1 Vocab packet
advertisement

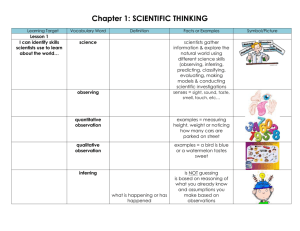
Chapter 1: SCIENTIFIC THINKING Learning Target Lesson 1 I can identify skills scientists use to learn about the world… Vocabulary Word Definition Facts or Examples science a way of learning about the natural world observing using one or more of your senses to gather information scientists gather information & explore the natural world using different science skills (observing, inferring, predicting, classifying, evaluating, making models & conducting scientific investigations senses = sight, sound, taste, smell, touch, etc… quantitative observation observations that deal with numbers, or amounts examples = measuring height, weight or noticing how many cars are parked on street qualitative observation observations that deal with descriptions that cannot be expressed in numbers examples = a bird is blue or a watermelon tastes sweet inferring when you explain or interpret the things you observe is NOT guessing is based on reasoning of what you already know and assumptions you make based on observations what is happening or has happened Symbol/Picture predicting classifying making a statement or a claim about what will happen in the future based on past experiences or evidence what will happen the grouping together of items that are alike in some ways all socks in a drawer all 6th graders in a school all red items in the room making models creating representations of complex items or processes examples = maps, math equations, computer programs help people study things that can’t be observed directly Lesson 2 I can describe the attitudes, or habits of mind for thinking scientifically, ethically, and without bias… skepticism having an attitude of doubt Scientific thinking involves characteristics such as curiosity, creativity, openmindedness, skepticism, awareness of bias, honesty and ethics. prevents scientists from accepting ideas that are presented without enough evidence or that may be untrue I can describe scientific reasoning and explain how it is used… ethics the rules that enable people to know right from wrong personal bias if a person’s likes and dislikes influence how he or she thinks about something cultural bias when the culture in which a person grows up affects the way the person thinks experimental bias a mistake in the design of an experiment that makes a certain results more likely scientists must consider the effects their research will have on people and the environment and make decisions only after considering the risks and benefits to living things & the environment example = if you like the taste of milk you might think everyone also likes the taste of milk, too example = a culture that regards milk as a food just for babies might overlook the nutritional benefits of drinking milk in later life example = comparing health effects of drinking low-fat vs. regular milk. both drink only this milk for a month, but what if one group had been less healthy before the experiment – your results would be biased scientific reasoning requires a logical way of thinking based on gathering and evaluating evidence Lesson 3 I can explain what scientific inquiry is and how it involves posing questions and developing hypotheses… objective when you make decisions and draw conclusions based on available evidence subjective when personal feelings affect how you make a decision or reach a conclusion deductive reasoning a way to explain things by starting with a general idea and then applying the idea to specific observation a process: 1ststate general idea 2nd relate general idea to a specific case working on 3rd reach a conclusion inductive reasoning uses specific observations to make generalizations (opposite of deductive reasoning) scientific inquiry the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on the evidence they gather Begins with a question about an observation. Because others may have asked similar questions, you should do research to find what information is already known about the topic before you go on with your investigation. hypothesis a possible answer to a scientific question a hypothesis is NOT a fact! a hypothesis must be testable – researchers must be able to carry out investigations and gather evidence that will either support or disprove the hypothesis I can explain how to design and conduct an experiment so that it uses sound scientific principles… variables factors that can change in an experiment independent variable a factor that is purposely changed to test a hypothesis dependent variable a factor that may change in response to the independent variable controlled experiment an experiment in which only one variable is changed at a time I can differentiate between a scientific theory and a scientific law… data the facts, figures and other evidence gathered through qualitative and quantitative observations once data has been collected it needs to be interpreted – graphs can reveal patterns and trends in your data scientific theory is a well-tested and widely accepted explanation of observations and experimental results scientific laws a statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions scientists are constantly testing scientific theories. If new observations or experiments do not support a theory, then the theory is changed or thrown out. describe observed patterns in nature without trying to explain those patterns Learning Targets for Chapter 1 Lesson 1 I can identify skills scientists use to learn about the world… Scientists use skills such as observing, inferring, predicting, classifying, evaluating and making models to study the world. Lesson 2 I can describe the attitudes, or habits of mind for thinking scientifically, ethically, and without bias… Scientists posses certain important attitudes including, curiosity, honesty, creativity, open-mindedness, skepticism, good ethics, and awareness of bias. I can describe scientific reasoning and explain how it is used… Scientific reasoning requires a logical way of thinking based on gathering and evaluating evidence. Lesson 3 I can explain what scientific inquiry is and how it involves posing questions and developing hypotheses… Scientific inquiry refers to the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on the evidence they gather. I can explain how to design and conduct an experiment so that it uses sound scientific principles… An experiment must follow sound scientific principles for its results to be valid. I can differentiate between a scientific theory and a scientific law… Unlike a theory, a scientific law describes an observed pattern in nature without attempting to explain it.