SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.1 Type of Nutrition
No
Marking scheme
Marks
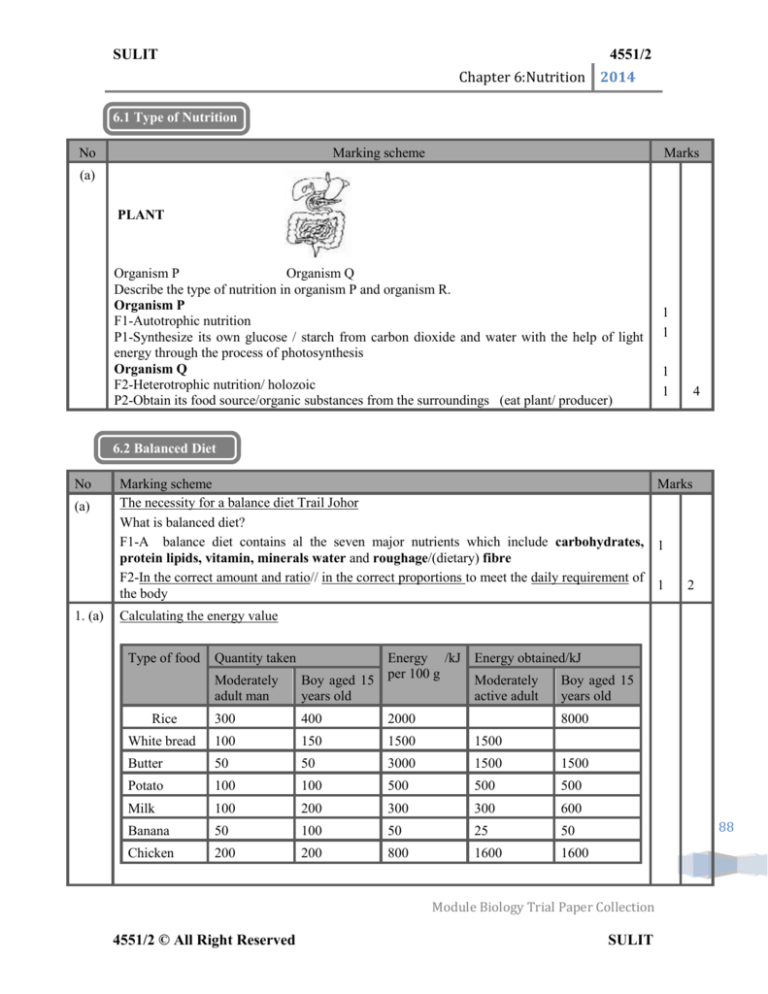
(a)
PLANT
Organism P
Organism Q
Describe the type of nutrition in organism P and organism R.
Organism P
F1-Autotrophic nutrition
P1-Synthesize its own glucose / starch from carbon dioxide and water with the help of light
energy through the process of photosynthesis
Organism Q
F2-Heterotrophic nutrition/ holozoic
P2-Obtain its food source/organic substances from the surroundings (eat plant/ producer)
1
1
1
1
4
6.2 Balanced Diet
No
(a)
1. (a)
Marking scheme
Marks
The necessity for a balance diet Trail Johor
What is balanced diet?
F1-A balance diet contains al the seven major nutrients which include carbohydrates, 1
protein lipids, vitamin, minerals water and roughage/(dietary) fibre
F2-In the correct amount and ratio// in the correct proportions to meet the daily requirement of
1
2
the body
Calculating the energy value
Type of food
Quantity taken
Moderately
adult man
Energy /kJ Energy obtained/kJ
Boy aged 15 per 100 g
Moderately
Boy aged 15
years old
active adult
years old
Rice
300
400
2000
White bread
100
150
1500
1500
Butter
50
50
3000
1500
1500
Potato
100
100
500
500
500
Milk
100
200
300
300
600
Banana
50
100
50
25
50
Chicken
200
200
800
1600
1600
8000
88
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Complete table 5 by calculating the total energy obtained by each individual 2
Moderate active adult man
Rice : 6000
Total energy obtained :11425
Boy aged 15 years old
White bread :2250
Total energy obtained:14500
(b)
1
2.
2
1
1
2
The enrgy requrment for a girl aged 15 is 9000kJ daily
Types of food
Quantity taken (g)
Energy content (kJ/100g)
Rice
350
1500
Chips
150
1000
Roasted chicken
300
800
Grilled mutton
200
1200
Boiled potato
150
500
Chocolate
100
2500
yogurt
200
200
Egg
100
600
Calculate the daily total value taken by the girl2
Total eneygy value is 5250+1500+2400+2400+750+2500+400+600=15800kJ
Working -1m
Answer with units -1m
(c)
1
Is he daily menu a balanced diet?Explain the consequence to her health2
P1-no/the menu is not balnced diet
1
E1-The menu does no contain the 7 calsses of food in the approproate ratio//The menu is 1
highly rich in carbohydarte and fats//no vegetables and lack vitamins//higher eneygy intake
compared to energy requirment for a girl aged 15
Diagram 3 shows an experiment to determine the energy values of a peanut and a Dried
prawn.
2
89
In this experiment, 20 cm3 of distilled water is used and 2.0 g of peanut and 1.8 g of
dried prawn is burnt. The initial and final temperature of water is shown in Table 1below.
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
(a)
Food sample
Mass
Initial temperature of water(oC)
Final temperature
of water(oC)
Peanut
2.0
29
45
Dried prawn
1.8
30
34
Rise
in
temperature
of
the water (oC)
State a hypothesis for this experiment
The peanut contains more energy (value) compared to dried prawns
(b)
(c)
(d)(i)
(ii)
(e)
(f)
1
Record the rise in temperature of the water in the spaces provided in Table 1
Rise in temperature of the water ( 0C ) :
1
Peanut : 16
1
Dried prawn : 4
( Both must be correct)
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 Jg-1 oC -1. Use the following formula to calculate
the energy values of the peanut and the dried prawn. 4
Energy value = ( mass of water X 4.2 X rise in temperature of water ) Jg-1
mass of food
1
Energy value of the peanut = 20 X 4.2 X 16 Jg-1
2.0
1
= 672.0 Jg-1
1
Energy value of the dried prawn = 20 X 4.2 X 4 Jg-1
1
1.8
= 186.7 Jg-1
Which food sample has a higher energy value?
The peanut
Give a reason for your answer in (d)(i).
Peanuts contain more lipids /Lipids have higher energyvalue than proteins
The energy values of the peanut and the dried prawn are much lower than the theoretical
values. State two reasons for your answer.
1. Not all the energy released during the burning of the food is absorbed by the water; some is
lost in the form of heat to the surroundings.
2. Some of the energy is absorbed by the boiling tube.
3. The food may not be completely burnt, especially the centre. ( Any two )
Suggest two ways of obtaining a more accurate result in this experiment.
1. Water in the boiling tube must be stirred to ensure that the heat is distributed evenly.
2. (The food must be oxidized completely by) making sure the flame does not extinguished
too quickly.
3. The distance between the food and the boiling tube must not be too far.
4. Make sure the thermometer does not touch the bottom of the test tube.( Any two )
1
2
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
1
4
90
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Factor affecting daily energy requirement Trail Johor
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
(b)
(c)
Explain the difference on the daily energy requirement between a very active man and
moderately active man 2
F -Very active man need 15100kJ energy , but moderate active man only need 12600 kJ energy 1
E -because very active man need more energy to carry out all the heavy / tough activity
1
2
Pregnant women need more calcium in their diet .Explain why
P1 Calcium need for formation of bone and teeth of the mother
P2 calcium also needed by the fetus to form the bone and teeth
P3 the mother to be need calcium to prepare the mammary gland to produce milk
P4 milk is the food for the baby Any 2
3
Individual group
Daily
energy Carbohydrate/g
requirement/kJ
Protein /g
Fats/g
Sedentary work
10080
390
90
53
Moderate work
11760
455
105
62
Heavy work
16380
635
146
87
Sedentary work
7980
310
70
42
Moderate work
9420
260
85
49
Heavy work
12600
490
115
67
Pregnancy
10500
410
95
56
Up to 2 years
5040
195
45
27
3 to 6 years
6300
245
56
33
1
1
1
1
Man
Women
91
Children
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
7 to 9 years
7560
295
70
40
10 to 12 years
8820
340
80
47
13 to 15 years boy
10500
410
95
56
13 to 15 years girls
9420
360
82
49
16 to 18 years boy
12600
490
115
67
16 to 18 years
9420
360
82
49
adolescent
Based on the table, Explain why different groups of people have different daily energy
requirement 8
F1- Males require more energy input than a female
E1-Bigger body size//higher metabolic rate//thinner layer of insulating fat
F2-A person who a does heavy works need more energy than a person who is moderately
work/sedentary work
E2-Type of occupation determine the rate at which energy from food is utilized
F3-Growing children needs more energy per body weight
E3-The metabolic rate is higher because they require more energy for growth
F4-Adolescent require more energy for growth and physical activities
E4-They have reached maturity/puberty and are very active
F5-Pregant mother needs more energy than non-pregnant women
E5-To cater for the developing foetuses in their wombs/perform respiration , digestion and
excretion for the developing foetus
(d)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
8
Breakfast
A plate of fried rice A cup of fresh milk
Lunch
A bowl of chicken rice A piece of roasted chicken A bowl of chicken soup A glass
of carbonated drink
Does
the menu provide a balanced diet for the pregnant women ,Discuss your opinion
Dinner
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
F1-No
A plate of fried noodle A banana A cup of coffee
P1-Contains too much fat
P2-infired rice/fried noodle
P3-Increase cholesterol; level
E1-cause excess body weight/hypertension/cardiovascular problems
P4 -carbonated drink contain excess sugar
E2-cause diabetes
P5-containing colouring,preservatives/chemicals/acids
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
92
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
E3-cause cancer/gastritis
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
P6-cofee contain caffeine/drugs/chemicals
E4-Acting on nerves
P7-Less/no vegetables
E5-cause constipation
P8-Less vitamin/minerals/ferum//other example
E6-For good health/make blood//other example
OR
F-Yes
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
P1-Rice provides carbohydrates
E1-For energy
P2-Fresh milk provide proteins
E2-For growth of foetus
E3-Calcium for bone formation
P3-Roasted chicken provides proteins
E4--Less fats so less risk of cardiovascular problems
1
1
1
1
1
1
P4-chicken soup provide minerals//examples
E5-for good health//other example
P5-Banana provides fibre
E6-Avoid constipation
(e)
Beside the basic nutrient shown in table 8.1, what other nutrient are also essential to be
inculded in our daily diet 4
1
F1Vitamin e.g. calcium/iron/sodium/potassium/chlorine/magnesium/iodine/sulphur/phosporus/
Flourine/chlorine
F3-(dietary) fibre/roughage,eg cellulose from fruits/vegetables/plants
1
F4- water
1
10
3
93
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Nutrient content in food
No
(a)
(b)
Marking scheme
Marks
Energy content in food Trail Johor
Different fruits have different content of vitamin C and energy value.By using your biiological
knowledge explain briefly how to determine the vitamin C content and the energy value of an
apple
Vitamin C content
1. The ascorbic acid solution is added to DCPIP solution untill the DCPIP decolourised
2. The volume of ascorbic acid used is recorded
3. The procedure is repeated using freshly sqeezed apple to determine the volume of juices
required
4. The percentage and concentration of vitamin C can be calculated using formula.
Energy Value
1. A sliced of apple is weighed
2. It is ignitd and placed under a boiling tube filled with water
3. The final tempearature of water in thr boiling tube is recorded
4. The energy value is calculated using formula
Potato P
Egg Q
Oil R
Based on the diagram suggest a food test to determine the nutrient content in the food P,Qand R
(i) Starch in food P
Iodine test fro starch
P1-Two drop of iodine solution id added to a test tube contaning porato cubes
P2-The iodine soluiton turns dark blue,showing that starch is persent
(ii) Protein in food Q
Millon’s test fro protien
P3- 1ml of million ‘s reagentis added to the egg albumen solution in a test tube.The mixture is
then heat
P4-A white precipitate is forn id for and then changes to a brick red precipitate when boiled,
showing that protien is present
(iii) Lipid in food R
Grease stain test fro lipid
P5-A drop of corn oil fripped onto a piece of filter paper.the paper is then dried gentely
P6-A translucent stain is observed on the filter paper showing that lipid is persent
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
Minerals
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
State the function and symptom of deficiency of these minerals. State one source for each
mineral
Calcium
1 - Needed for the formation of bones and teeth.
2 - deficiency in calcium will cause rickets in children
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
94
1
1
1
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
3 - and osteoporosis most often in women who have gone through menopause
4 - The source of calcium is milk / cheese.
Ferum
5 - Required in the production of haemoglobin.
- Insufficient ferum leads to anemia
7 - Ferum can be found in meat
Iodine
8 - Important component of the hormone (thyroxine) produced by the thyroid gland.
9 - symptom of deficiency is goiter
10 - the source of iodine is sea food/seaweed/ iodine salt
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
No
(b)
Marking scheme
Marks
Roughage or dietary fibre Trail Johor
State the function of food in R (Roughage/dietary fibre)/ State one importance of roughage in
digestion
Aids/stimulates peristalsis//prevent constipation //absorbing and eliminating toxic substances
1
1
Selection of an appropriate balanced diet
No
Marking scheme
(a)
Trial johor 2011
Marks
Name the class of food labeled R and S
R: Roughage/dietary fibre
S:Carbohydrate
Q: protein
1
1
1
Name the classes of food that build the muscle tissue and give two example
F-Protein
P-Fish and meat
1
2
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
3
95
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Explain why ice cream, butter cake are placed at level 4 in the food pyramid6
P1: Food at level 4 should only be taken in smallest amount / ratio.
P2: Ice cream contains a lot of sugar.
P2: Sugar has high energy value.
P3: Excessive sugar in the body will lead to obesity / diabetes.
P4: Butter cake contains a lot of lipid.
P5: Lipid has high energy value.
P6: Excessive lipid will form adipose tissue in the body// increase cholesterol level in body.
P7: (Excessive lipid will) lead to heart attack / cardiovascular disease/ stroke.
(b)
Explain the importance of consuming food from level 2 in our daily diet.4
P1: Food at level 2 contains a lot of water, vitamins, minerals and roughage / fibre.
P2: Water is important in all cell activities / physiological /biochemical processes in our body.
P3 : Body need enough vitamins to preserve / maintain health// Any suitable example of
vitamin and the related function
P4: Body need enough minerals to preserve / maintain health and growth // Any suitable
example of mineral and the related function.
P5: Roughage is necessary in the diet to stimulate peristalsis / to prevent constipation.Any 4 P
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(c)
Explain how to achieved a balanced diet byconsuming food from diverse source.
Sample Answer
P1: Ulam type of salad include fresh leaves/fruits/other plant parts which are eaten raw
P2: rich in mineral ions, vitamins and fibre
P3: other sources of protein rabbit meat/quail meat/ostrich meat/freshwater fish / prawn
P4: rabbit meat is rich in protein but low in fat and cholesterol / the meat has soft texture //
ostrich meat is nutritious // fresh water fish low in cholesterol, the protein is easily digestible
P5: mushrooms have high nutrient content
Any four
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
96
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Choosing an appropriate diet for different target groups
No
(a)
Marking scheme
The photographs in Figure 6.1 show three individuals with different needs for energy.
A lady athlete/
(11 000kJ)
A pregnant lady/
(10 000kJ)
Marks
An old lady/
(6500kJ)
Based on your biological knowledge about balanced diet, explain the factors that
determine the energy requirement for the three individuals in figure 6.1
A lady athlete:
F1: An athlete is a very active person and has high rate of metabolism to produce energy.
E1: The diet should include more carbohydrates to supply enough energy to carry out the
vigorous activity in sports.// She needs to contract and relax her muscles frequently for
her vigorous activities. //Energy is needed to contract the muscles.
E2: The diet should include more protein to build new tissues to replace tissues that are
dead or damaged.
E3: She also needs calcium, sodium and potassium to strengthen the bones and to prevent
muscular cramp.
A pregnant lady:
F2: A pregnant lady has a high rate of metabolism to provide energy for herself and the
baby.
E4: The pregnant lady also needs more iron and calcium to build red blood cells to avoid
anemia.
E5: She needs a high quantity of calcium and phosphate to form strong teeth and bones for
the baby.
An old lady:
F3: An old lady has low rate of metabolism as she does not need energy to grow. (age)
E6: An old lady needs less carbohydrates and fats because she is less active and thus do not
need much energy.
E7: she needs more proteins, vitamins and minerals to replace dead tissues and maintain
her daily activities
E8:She needs calcium and phosphorus to prevent osteoporosis
E9: She should avoid food that contains a lot of fats, sugar and salt because excess fat can
lead to heart diseases, excess sugar can cause diabetes mellitus and excess salt can cause
high blood pressure.
F1, F2 and F3 and any five E:
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
97
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.3 Malnutrition
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
What is malnutrition?
Essay & Structure
F1-Malnutrition result from taking an unbalanced diet
F2-Certain nutrient are excess, lacking or in the wrong proportions
Protein deficiency
1
1
2
Identify the deficiency disease shown in diagram 5.2
Rickets
1
1
State the cause of the disease and possible effect on children 2
Cause: Lack of vitamin/calciuferol
Possible effect in children : bent leg
1
1
2
(b)
(c)
(d)
(f)
Malnutrition caused by the unbalanced diet. Malnutrition of B (protein) for long term will
affects certain health problem
Explain this statement
P1-Malnutrition due to the lacking, the excessive or the wrong proportion of nutrient intake for
a long term
P2-Example of protein :bean/meat/fish
P3-Lack of protein intake cause kwashiorkor
P4-Health problem/symptom: scaly skin/thin muscle /thin hairs
OR
P3-Excessive protein intake cause gout/kidney stone/kidney damage
P4-Health problem/symptom: inflammation of joint/urination trouble
State two effect of malnutrition by giving suitable example 4
F1-Kwashiorkor
E1-Protien deficiency
F2-Marasmus
E2-Protien deficiency combined with a lack of energy-providing nutrient
F3-Scurvy
E3- Deficiency vitamin C
F4-Osteoporosis/oateomalacia
E4-Deficiency in calcium /phosphorus/vitamin D
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
1
SULIT
4
98
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
F5-Obesity
E5-Excess carbohydrate and lipids
F6-diabetes Mellitus
E6-Excess sugar
F7-Cardiovascular disease/high blood pressure
E7-Excess saturated fat/cholesterol
Note: MAX 4
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
(g)
A
B
C
Name and explain the disease in Diagram A, Diagram B and Diagram C related to malnutrition.
Diagram A
1-Kwashiorkor
2-A child does not receive sufficient protein in his diet.
3 -has the characteristic sign of scaly skin, thin muscles , thin hair and a swell of the body
1
1
1
Diagram B
4- Rickets
5 - Vitamin D deficiencies
6 - poor teeth and bone formation in children
7 - leads to softening and weakening of the bones..
1
1
1
Diagram C
8 - Obesity
9 - excessive intake of food rich in fat
10 - body weight exceed by 20% of ideal/ normal weight t
1
1
1
10
99
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Effect of excessive intake of nutrient
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Junk food is good that is high in sugar , salt and fat ,.Explain the health problems faced by
individual who continuously taken this food
P1-Overconsumption of salt (sodium) cause high blood pressure leading to heart disease/stroke
P2-Overconsumption of sugar cause overweight/obesity//diabetes //dental caries
P3-Overcomsumption of lipid cause obesity//cardiovascular disease
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
(b)
Content of fast food
Excess of mineral salt
Excess fats
Excess protein
Insufficient fibre
Presence of food preservative,flavouring and food colouring
500 ml of soft drink excess sugar in the soft rink
A teenager frequently consumes the fats food for a long period of time
Explain the effect of consuming the above meal for a long period of time compared to
consuming a balanced diet for the same period of time 10
F1-Excess mineral salts can cause higher osmotic pressure in the blood
P1-Excess fats will be converted into cholesterol
F2-Cholesterol accumulates at the artery wall and cause arteriosclerosis
P2-High blood cholesterol levels are a risk factor for heart attack and stroke.
P3-Excess protein cause excess amino acids which lead to gout. and cause kidney failure.
F4-Low in roughage can cause constipation.
P5-Deficiency in roughage also leads to difficulties in peristalsis process along digestive tract
F5-Food preservatives, food colouring and food flavoring consists of carcinogenic substances.
P6-It may cause cancer
(c)
100
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Explain whether the menu is suitable for the boy
Explain the consequences to his health if the boy continues taking the daily menu for a long
time 5
Criteria
1. Justify
2. Explanaiton
3. Consequences
P1-the menu I not a balanced diet ( not suitable for the boy)
P2-It contains too little food rich in carbohdrte ( it only has banan and carbonated drink ) which
does not dive enough energy value required by the boy to undrgoes his daily activity
P3-It contians too little food rich in carbohdrtes ( it only has banana and carbonated drink)
which does bot give enough vale required by the boy to undergoes his daily activity
P4-It cintains too little water which is required for biocemicel process //anysuitable
processes//any suitable function of water
P5-It does not contain sufficient vitamin for healthly growth
P6-Ir contains food highly rich in fats eaxmple butter and oil which will supply too much
enet\rgy for th boy, if stored will cause obesity /arterioclerosis/heart aatack /high blood perssure
( only abpout one third of body’s energy requirments comes form food rich in fats
But
P7-It has sufficiebt vegetables and frut ( banan ) which are rich in fibre /roughage to prevent
contipation
P8-The banana, vegetable provide miberals needed for the development of bones and
maintianing health(but the different typrs of mieral requirment are not sufficinet Any 2 form
P2 and P3
If the boy keep taking the above menu his total eneygy value is not enough //eneygy needed is
less than energy taken
(i)Bad effect to the boys
(ii)Rickets,lack of vitamin D
(iii)Beri beri, lacking of vitamin B
(iv)Scuvry, lack of vitamin C
(v)Kwashoir, lack of protien
(vi)Cretinism, lack of iodine//any suitable healthy problem
(vii)Diabetes Any one bed effect
(d)
A girl takes food from group P continuously for a long period of time.
Explain the consequences to the health of her heart.
F1 : Food fro group P contains high level of cholesterol
E1 : Cholesterol // fatty deposits tend to accumulate on the inner wall of arteries
E2 : Causes the narrowing of the blood vessels /Coronary arteries are blocked by the build-up
Of fatty tissues.
E3 : Reduces the flow of blood
E4 : The heart muscles become starved of oxygen and dies
E5: The girl might get heart attack.
Any three
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
1
1
1
1
1
1
101
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6. 4 Food digestion
Digestion of carbohydrate, proteins, and lipids
Sites of
digestion
Mouth
Question & Marking scheme
Stomach
Name the secretion found in R
Gastric juice
Name the secretion and the enzyme found in mouth
Secretion : Saliva
Enzyme: Salivary amylase
Write a word equation to show the process of food digestion in liver
(1)
Salivary amylase
(1)
Starch + water
Maltose
Explain how starch is digested in mouth
TIPS:
F1-(Digestive glands) secreted (digestive juice) which contain ( enzyme ) into ( site of
digestion)
E1-Which hydrolysed ……………into ………………
Name a enzyme found in R
Pepsin /Renin
Based on your answer in write a word equation to show the process of food digestion in
(1)
Pepsine
(1)
Protien+ Water
Polypeptide /peptone
(1)
Renin
(1)
Caseinogen + Water
casein
Any one
[2marks]
Explain how he Protien is digested in stomach
TIPS:
F1-(Digestive glands) secreted (digestive juice) which contain ( enzyme ) into ( site of
digestion)
E1-Which hydrolysed ……………into ………………
Duodenum
(liver)
Describe how the hydrochloric acids produce by the gastric gland help in digestion of food
P1-Provide acidic medium
P2-Dor optimal reaction of enzyme pepsin
Name the secretion which passes down tube W and state its function.
Secretion : Bile
Function : Lipids / fats emulsifier / breaking lipids into tiny droplets
State the functions of X.
Functions of Y/liver
P1 - Maintenance of blood glucose level under the influence of insulin and glucagons.
P2 - Synthesis plasma protein such as fibrinogen / prothrombin from amino acids.
P3 - Synthesis bile.
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
102
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
P4 - Storage of nutrients such as fat-soluble vitamins (A & D)/ B12/ ferum/ copper/ potassium.
P5- Detoxification of poisonous substances such as alcohols/drugs/ toxins/pesticides/carcinogens
/poisons.
P6 - Deamination of amino acids.
P7 - Produce heat.
Syarifah eats too many mangoes with vinegar. Explain the effect of eating too much of this kind
of mangoes on the digestion of food in Y.(Duodenum)
1 - Mangoes with vinegar contain much acid, so its reduces the pH value/ increases acidity in the
duodenum
2 - Acid medium is less suitable for the action of enzyme lipase, amylase and trypsin
3 - less/ no lipid is digested/hydrolysed to fatty acid and glycerol by lipase
4 - less/ no starch is digested/hydrolysed to maltose by amylase
5 - less/ no polypeptide is digested/hydrolysed to peptides by trypsin
Duodenum
(Pancreas)
Which organ involves in digestive system and endocrine system
Organ S
State the function of the organ labeled (pancreas)
In digestive system : secretes enzyme lipase, amylase and trypsin
In endocrine system : Secreted insulin and glucagon
Name the secretion found in X
Pancreatic juice
Name a enzyme
Pancreatic amylase/trypsin/lipase
Write a word equation to show the process of food digestion in liver
(1)
Pancreatic amylase (1)
Starch+ Water
Maltose
(1)
Polypeptides + Water
Trypsin
(1)
Peptides
(1)
Lipase
(1)
Lipid droplets + Water
Fatty acids + Glycerol
Any one
Explain how starch is digested in duodenum
F1-The pancrease secreates an amylase into the duodenum
E1-which hydrolysed starch into maltose
TIPS: for tyrpsin/ lipase
F1-(Organ involved) secreted (digestive juice) which contain ( enzyme ) into ( site of
digestion)
E1-Which hydrolysed ……………into ………………
After having a meal containing rice fish vegetable, the glucose level in the body increase3
F-Q/Pancreases secretes insulin
P1-Insulin stimulate the conversion of glucose into glycogen/the rate of respiration is increased
P2-reduced the blood glucose level to normal
(d) As a doctor you have confirmed that a patient is suffering from a disease. Organ S of the
patient has to be removed. (i) What explanation would you give to the patient? In your
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
103
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
explanation, state the effects of the removal of organ S on enzymes and hormones, and how these
affect the digestion and the level of glucose in the blood.
F1-no / less secretion lipase
E1- no / incomplete lipid digestion
F2- no / less secretion amylase
E2- no / less starch digestion
F3 -no / less secretion trypsin
E3- no / less protein digestion
F4- No insulin released
E4 -the blood glucose level high
F4 /F5 F5 : No glucagon released
E5- the blood glucose level low
What advice can you give to the patient to help him handle his health problem that may arise
from the removal of organ S
P1-Avoid / Reduce the intake of oily food
P2-Avoid / Reduce the intake of carbohydrates /sugar
P3-Reduce the intake of protein
P4-injections of insulin
P5-pancreas implantation
Ileum
A man is suffering from cancer, his organ Z need to be removed. What should he do to handle
health problems that may arise from the removal of organ Z?
P1 - Reduce the intake of high carbohydrate food / protein /fatty food.
P2 - Get insulin injection when needed / if glucose level too high.
P3 - Get glucagon’s injection when needed / if glucose level too low.
P4 - Pancreas transplant.
P5 - Eat more vegetables / fruits.
Name the secretion and enzyme found in Y
Secretion : Intestinal juice
Enzyme: Maltase/lastase/sucrase/erepsin
State the final product of protien digestion in T
Amino acids
State one importance of the final product you state in
P1-bulid new cells/growth
P2-Repair/renew damaged cell
P3-Producing enzyme /antibodies / hormones
State the final product of carbohydrate digestion in T
Glucose
Name an enzyme involved in the digestion of carbohydrate in T
Amylase pancreatic amylase
Write a word equation to show the process of food digestion in Ileum [2marks]
(1)
Maltase
(1)
Maltose + Water
glucose
104
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
(1)
lactase
(1)
Lactose +Water
glucose + galactose
(1)
sucrase
(1)
Sucrose + water
glucose +fructose
(1)
Erepsin
(1)
Peptides + Water
amino acids
Explain how the Maltose is digest in Ileum
TIPS:
F1-(Organ involved) secreted (digestive juice) which contain ( enzyme ) into ( site of
digestion)
E1-Which hydrolysed ……………into (Product)
Explain the digestion of food
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Starch is a complex molecule. Digestion of starch is carried out by several enzyme along the
alimentary canal. Describe how glucose is produced form the digestion of starch along the
alimentary canal
1
P1-Saliva is secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth
1
P2-Salivary gland secretes amylase /saliva contain amylase
1
P3-Amlase will hydrolyse starch into maltose
1
P4-Remaining starch and ,maltose enters the stomach
P5-(stomach do not cantina carbohydrase), so no digestion of carbohydrate
1
P6-Will take place in stomach
1
P7-Duodenum received pancreatic amylase from pancreas
1
P8-Pancreatic amylase will hydrolyse the remaining starch into maltose
1
P9-the wall of ileum secretes ,maltase
1
P10-Maltase will hydrolyse maltose into glucose Any 6
1
10
(b)
105
Explain how fried food P is digested in the digestive system
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Criteria
1.
Identify the classes of food in fried food P /banana
2.
Peristalsis occurring in the any parts of alimentary canal
3.
Digestion of carbohydrate in month//ileum with correct enzyme
4.
Digestion of fats in duodenum//ileum with correct enzyme
5.
Any correct product of carbohydarate
P1-Fried banana /food P is rich in carbohydrate/starch and fats
(physical digestion takes place in the mount where fried banana are chewed into smaller pieces
of carbohydrate)
P3-In the month Salivary amylase hydrolysed the pieces of carbohydrates/starch
P5 in to maltose
P2-The food is push down the oesophagus through peristalsis
(In stomach ,Food P is not hydrolysed)
P4-Fats is hydrolysed /break down
P5-To fatty acids and glycerol by lipase //
Lipase
Fats + Water
Fatty acids+ glycerol ( in an alkaline medium)
In ileum
P4&P5( fats is hydrolysed /break down into fatty acids and glycerol
P3&P5-Maltose is hydrolysed into glucose//sucrose is hydrolysed ny sucrose to glucose and
fructose//lactose is hydrolysed by lactase to glucose and galactose (in alkaline medium)
(c)
No
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
The main food for baby is milk ,describe th digestion of milk in the stomach 4
P1-(gastric glands in the wall of ) stomach secrete gastric juic
1
P2-Gastric juice ( cintian mucus.HCl),Pepsin nd renin
1
P3-Renin coagulates milk by converting soluble milk protien caseinogen to ythe insoluble 1
casien
P4-Casein ios then hydrolysed( digested) by pepsin to peptones
1
P5-HCl optimises pH in the stomach for action of enzyme
1
Digestion of cellulose in ruminants and rodents
Marking scheme
10
4
Marks
(a)
106
Explain One similarity and four differences between alimentary canal R and S
Similarity:
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
F1-The alimentary canals of both R and S have bacteria/protozoa to hydrolyse cellulose
E1-both and S do not produce cellulose in their food
Differences:
F2-R has 4 stomach chambers but S has One stomach chamber
E2-The stomach of S is not involved in cellulose digestion
F3-The size of caecum for R is small but S has a large caecum
E3-Caecum for S is involved cellulose digestion
F4-the bacteria and protozoa in r are found in the rumen and reticulum While in S they are
found in the caecum
E4-To produce enzyme cellulose
F5-Food passes only once in R but twice in S //regurgitation take Place in R, but does not take
place in S
E5-R-to increase efficiency of cellulose action
S-To complete food absorption
(b)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
Compare the process of cellulose digestion in organism R and S
Similarities
1
1 - Both have alimentary canal which are made up of the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine
and large intestine.
1
2 - Both are unable to produce cellulase to digest cellulose.
1
2
3
4
(c)
1
1
Organism Q
The type of diet is omnivores
Stomach has one chamber
Microorganisms in the digestive tract do
not play an important role in digestion of
cellulose/ do not have enzyme cellulase
to digest cellulose.
The food from the mouth is swallowed to
the stomach without regurgitation.
Organism R
The type of diet is herbivores
Stomach has four chambers
Bacteria and protozoa in rumen and
reticulum secrete the enzyme cellulase to
digest cellulose
The food from the mouth is swallowed to
the rumen and reticulum, then it is
regurgitated into the mouth to be chewed
again before being swallowed into the
omasum.
1
1
1
1
6
The digestive system of rodent and herbivores
107
By giving one example of organism S , explain how the structure involved in the digestion
process
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Example of organism S: Rabbit/other examples of rodents
E1-Stucture T/caecum are enlarge to store the cellulose producing bacteria
E2-Plants eaten contain cellulose
E3-Bacteria in structure T caecum produce cellulose to digest cellulose to digest cellulose
Problem associated with food digestion
No
1
1
1
Marking scheme
3
Marks
(a)
R
S
Explain the effect of malfunction of organ S and organ R to the digestion of food P
Malfunction of liver
P1-Too little /no bile is secreted by the liver
P2-Resulting fats is not / hardly emulsified //medium is not alkaline
Malfunction of pancreas
P3-Too little / no pancreatic juice us secreted
P4- lipid is not / hardly hydrolysed by amylase to maltose
P5-Starch is not /hardly hydrolysed by amylase to maltose Any 4
1
1
1
1
1
4
(b)
X
A paitien has organ X removed
Explian the effect of removal of organ X on enzyme and hormones and these affect the
digestion and level of glucose in the blood
1
F1-no insulin secretion
1
E1-Excess blood glucose cannot be converted to glycogen
1
E2-Blood sugar level increases
1
F2-No glucagons secretions
1
E3-Stored glycoen cannot be converted to glucose
1
E4-Low blood glucose level cannot be increase to normal level
1
F3-No trypsin secretion
1
E5-Protiendigestion not completed
1
F4-No amylase secrerion
1
E6-stach digestion not cimpleted
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
108
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
F5-No lipase secretion
E7- Lipie not digested.No lipid digestion in body
E8-Body donot have enough amino avids and glucose
E9-No fatty acids and glycerol
(c)
1
1
1
1
All 5F+any E
Predict wht will happen to a perosn if fails to function (liver)?
1
1
1
P1-Digestion of lipid /starch/protien is distribed
P2-risk have diabetes mellitus
P3-(because)excess glucose cannot be converted in to glycogen
(d)
10
3
Mr X is an obese person. He undergoes an operation to shorten his small intestine
Explain how that treatment can help Mr.X to reduce his body mass
P1-small intestine is the site/where digestion /absorption of ( digested) food occur
P2-lower rate of hydrolyzing of food ( to simplest food)P3-Iluem /small intestine ( has
intestinal gland to ( produce ( intestinal juice containing digeative enzyme
1
1
P4-Shorter ileum has lesser villi/lower surface area
1
1
1
1
1
P5-As the rate of diffusion of digested food is slower
P6-Less digested food is absorbed into blood capillary from the villus
P7-the body tissue receives less glucose ( to undergoes cellular respiration )
P8-Lack of glucose will cause the adiposed tissues/stored fat to be oxidized/used to produce
energy
1
1
P9-Reducing the amount of fats stored// increasing the amount of fats used
P10-Thus reducing the body mass
(e)
A gall bladder of a patient is removed due to a gall stone. Explain the effects on the health.
P1-Bile cannot be secreted by gall bladder to emulsify excess of lipids into the tiny droplets
P2-Lipase cannot react on lipids effectively / less lipids is digested to fatty acid and glycerol.
P3-Bile cannot neutralize the acidic foods from the stomach
P4-Alkaline medium that is an optimum meduim for the digestion of lipids, carbohydrate and
protein cannot be created.
P5The digestion of lipids, carbohydrate and protein are affected.
P6-More acid in the duodenum, it leads to duodenum gastric.
No
Marking scheme
(f)
Gallstone preventing the flow of bile
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
Marks
A man has his bile duct blocked with gallstones. He is advised to cut down on
his fat intake. Explain why such an advice is given to him?
F1 : ( When the bile duct is blocked) , bile cannot be channeled out to the duodenum
F2 : Fats / lipids cannot be emulsified
F3 : Digestion of fats /lipids will be very slow / digestion of fats /lipids will be incomplete
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
3
109
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.5 Absortion and assimilation of digested food
Adaptive characteristic of the digestive system
No
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain One adaptation/characteristic of the villus for the process in
F1-Thin wall/one cell Thick
E1-Increase rate of diffusion of digested food/nutrients
F2-Large surface area/has microvilli
E2-Increase rate of absorption of digested food /nutrient
F3-Has a network of capillaries/blood vessels
E3-To transport the absorbed nutrients
P4-The villus is moist covered with a thin layer of water
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(a)
2
(b)
By referring to diagram 8(a) and *(b), explain the characteristic/adaptation of structure X and
Y a a major site of nutrient absorption in human digestive system6
Strcuture X
F1-Being almost 6 meter long
1
1
1
E1-For maximum absorption of nutrient
F2-Highly folded
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
110
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
E2- Provides a large surface area for efficient absorption of digested food./To increase the rate 1
of nutrient absorption
1
F3-Having finger like projections called villi over its surface
1
E3-To increase total surface area for efficient absorption
Structure Y
F4-Have microvilli
1
1
1
1
1
E4-To increase the surface area for absorption
F5-Have thin walls : one cell thick
E5-so that digested food can be aborb rapidly
F6-Have rich supply of blood capillary
E6-To transport glucose, amino acids and water soluble vitamin
1
1
1
F7-Have lacteals
E7-To absorb fatty acids and glycerol/water soluble vitamin efficiently F+E=1mark
10
(c)
Based on the figure ,Explain three structural adaptation of the small intstine in effective
absorption of digested food
F1-length of intestine is long (6m)
1
1
1
1
1
E1-Increase time for food absorption increase SA for absorption
F2-Inner surface is (highly) floaded
E2-To increase the SA for absorption
F3-Numerous villi ( on the inner surface if iluem)
E3-to increase the SA for absorption
1
1
F5-Numerous blood ncapillaries and lacteal
111
E5-to transport absorbed nutrient ( away)//to maintian concentration gradient ( form diffusiuon
1
of nutrient) Any 3F+3E
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
6
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Absorption of digested food
No
(a)
Marking scheme
The structure T in Diagram 2 has numerous projections. Draw and label a longitudinal section
of one of these projections in the space below.
Marks
D – Able to draw the following parts
epithelium, lacteal, finger-like projection
1
L – Able to label any two parts
Epithelium
1
2
(b)
Amino acids
Glucose
Glucose
Amino acids
Lipid
Vessel Q
112
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Name process X t the villus
Absorption /simple diffusion/facilitated diffusion
(c)
(d)
Vessels P and Q transport digested food form the villi to the liver and body cells Respectively
Name vessel and Q
P:Hepatic portal vein
Q:Lymphatic/lymph vessel/duct
Figure 6.2 shows human’s digestive system. X is part of the cross section of structure Y.
1
1
2
1
1
2
Y
Figure 6.2
What are the processes that occur in structure Y?
Describe the processes by giving examples
F1: Digestion //
P1-Intestinal glands of the wall of ileum secrete a few enzymes to complete the digestion
process.
P2-Digestion process is completed in ileum to produce simple sugars (glucose, fructose and
1
1
galactose), amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
1
P3-Example: (any correct enzymes/ intestinal juices and substrate reaction)
1. Enzyme erepsin(peptidase) --- peptide to amino acids.
1
1
1
2. Enzyme sucrose -----sucrose to glucose and fructose
F2: Absorption //
P4-The wall of ileum has many projections called villus to absorb the products of
1
digestion.
P5-Blood capillaries in the villus absorb simple sugars, amino acids, minerals, vitamins B and
C…
P6-Lacteal of the villus absorb fatty acids, glycerol, fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K)
1
1
10
Must have F1 and F2 and other 3
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
113
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
(e)
Explain how glucose is transferred form the small intestine to the body cells
1
1
1
1
P1-Glucose in the lumen of small intestine enter the epithelial cells by active transport
P2-Glucose from epithelial cells enter blood capillary by facilitated diffusion
P3-Blood carry the glucose into the hepatic Portal vein
P4-Hapatic portal vein channel the blood containing glucose into the liver
Liver cells will use/assimilate some of the glucose
1
1
P5-Blood then send the glucose to the heart via hepatic vein then vena cava
P6-Heart pump the blood to all body cells
P7-Glucose diffused from the blood capillary into the body cells by facilitated diffusion any 6
1
6
Assimilation of digested food
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Explain what happen to the excessive amino acids in the liver? 2
P1-Deamination //The amino group is removed (from amino acid)/converted to ammonia
P2-(Ammonia) is converted to urea
P3-urea will be excreted through the kidneys
any2P
1
1
1
(b)
(c)
Digested food are used by the body cells for growth , to complex compound or structural
components
State how lipids , amino acids and glucose are used in the cell
Lipids; L1-A major energy reserve in the body//
L2-(phospholipids)are components of the plasma membrane //
L3-Lipids is used as a respiratory substrate/
L4-Excess fats are stored in adipose tissues(under the skin, around internal organs)
Any 1 L
Amino acids:A1-Amino acids are used in protein synthesis//
A2-For repair and production of new protoplasm/growth and repair//
A3-Used in the formation of enzyme /some hormones /protein part of hemoglobin /antibodies
Any 1A
Glucose: G1-Glucose is used as the main respiratory substrate//It is oxidized to realeased
energy
G2-Excessive glucose is converted to glycogen //blood glucose level rise/increase
Any 1 G
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Explain what will happen to a person if his liver receives insufficient insulin from the
pancreas2
P1-Diabetes mellitus blood sugar level increase level increase // hyperglycemia
1
P2-Exces glucose cannot be converted to glycogen
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
2
10
2
114
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(d)
Digested nutrient will be absorbed by ileum and some of ity will be transported to liver .In the
liver , the nutrient arte used form complex Process that take place in the liver
F-Able to state the nutrient that transported to liver
P-Able to describe the process that take place in liver
F1-Glucose
Amino acids
P1-Assimilation
P2-Glucose used as the main respiratory substrate/release energy
P3-Excess glucose is converted to glycogen and stored in the liver
P4-Further excess is converted in to lipids
P5-when the blood glucose level decrease below the normal level , glycogen is converted back
into glucose
P6-Amino acids are used in protein synthesis for the production of new protoplasm , growth
and repair
P7-Amino acids are involved in the formation of enzymes and some hormones
P8-Amino acids are also involved in the formation of the protein part of hemoglobin in the red
blood
P9-Excess amino acids are deaminated to form urea which is excreted in the urine any 7P
Synthesizing Skill :Able to state one of F,P1-and any 3P correctly
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
115
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(e)
Urea
Glucose
Kidney
Amino Acids
Glycogen
Glucose
Lipid
Glucose
Carbohydrate
Amino Acids
Fatty acids& Glycogen
Protein
Ileum
Lipid
Based on Diagram 7, Explain the assimilation of the following
(i)
Glucose
P1-Excess glucose in the blood is converted to glycogen and stored in the liver
P2-when glucose level in the blood is low , glycogen is covert to glucose in the liver
P3-Excess glucose is converted to lipids by the liver
P4-In the body cells , glucose is oxidized to released energy in cellular respiration
(ii)
amino acids
P5-Amino acids is used to synthesise protein in the liver
P6-Excess amino acids undergo deamination to produce urea in the liver
P7-Urea is then eliminated by the kidney
P8-Amino acid is used to synthesise enzymes/antibodies/hormones/new protoplasm/repair
damaged tissues in the body cells
(iii)
Lipids
P9-Excess lipids is stored in adipose tissues
P10-Phospholipids and cholesterol make up the plasma membrane
(f)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Helmie takes fried chicken at lunch. Explain the absorption and assimilation process of lipid
content in the fried chicken
Absorption
P1-Digestion od lipid prouce fatty acid and glucerol
1
P2-Absorbtion of lipid occur at ileum
1
P3-At ileum there are villi which have lacteal
1
P4-Fatty acid and glycerol are absorbed into lacteal
1
P5-In lacteal condensation of fatty acid and glycerol form lipid
1
P6-the lpipids then transported via the subclaviian vein into the blood stream
1
Assimilation
P7-In the cells lipid is use as a ian compomemt of plasmam membrane
1
P8-Lipids also is use as a main component of some hormone and vitamins
1
P9-Excess lipid will be stored underneath the skin as adiposed tissue
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
10
116
8
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
Based on the diagram on diagram ,explain how the ileum and liver in the absorption and
assimilation of the following digestedfood substances
(i)
Glucose
(ii)
Amino acids
(iii)
Fatty acids
F1-iluem has (adaptive features such as having ) many villi/villus /very thin cell wall /villus are
surrouded by dense network of blood capilarry/lacteal
E1-To increase the rate of diffusion of dieated food
E2-glucose diffused from villi into the blood capilary to the liver via the hepatic portal vein
E3-excess glucose is converted to glycogen ( to be kept in the liver)
E4-Glycogen acts as stored food
E5-in body tissueglucose is oxidized during the cellular respiration to produce energy
E6-amino acids from villi diffused into blood capilary to the liver via the hepaic portal vien
E7-Excess amino acid is deaminated/conveted into urea( to be excreated through the kidney)
E8-amino acid will be used to synthesis new protoplasm/repair of damaged tissue//used to
synthesis protien of plasma membrane//produce enzymes antibodoes/hormones
E9-fatty acids dissuse from villi into lacteal
E10-Then reansport to the throracic duct/right lymphatic vessel//lymphatic vessel
E11-To the subclavin veins back to the blood circulatory system
E12-Fatty acids is synthesized to form the plasmamembrane
E13-Stored in the adiposed tissues(beneath the skin as a source of energy) Any 10
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(g)
(h)
Explain the assimilation of digeated food of glucose and amino acids b organ R / liver
Glucose
P1Gucose is used ( by cells ) to produced energy/ carry ( cellular ) respiration
P2Excess of glucose in the blood is converted to glycogen and //Stored as glycogen as
glycogen
P3-When glucose level in the blood is low the glycogen is converted into glucose
P4-Excesss of glycogen is converted into lipids
Amino acids
P1-Synthesis of plasms protien /enzymes /any suitable protien molecule form amino acids
P2-Excess amino acids are converted/ deaminated into area ( to be excreated) Any 4
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
1
10
1
1
1
1
1
1
117
4
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Assimilation in the liver (summary)
Marking scheme
Amino
Acids
P1- Amino acids from villi diffused into blood capilary to the liver via the hepaic portal vien
P2-Amino acids is used to synthesise plasma protein in the liver
P3-Excess amino acids undergo deamination to produce urea in the liver
P4-Urea is then eliminated by the kidney
P5-Amino acid is used to synthesise enzymes/antibodies/hormones/new protoplasm/repair
damaged tissues in the body cells
Glucose
P1-iluem has (adaptive features such as having ) many villi/villus /very thin cell wall /villus are
surrouded by dense network of blood capilarry/lacteal
P2-To increase the rate of diffusion of dieated food
P3-glucose diffused from villi into the blood capilary to the liver vua the hepatic portal vein
P4-Gucose is used ( by cells ) to produced energy/ carry ( cellular ) respiration
P5-Excess glucose is converted to glycogen and stored in the liver
P6-when the blood glucose level decrease below the normal level , glycogen is converted back into
glucose
P7-Excesss of glycogen is converted into lipids
P8-In the body cells , glucose is oxidized to released energy in cellular respiration
Lipids
P1-fatty acids dissuse from villi into lacteal
P2-Then reansport to the throracic duct/right lymphatic vessel//lymphatic vessel
P3-To the subclavin veins back to the blood circulatory system
P4-Fatty acids is synthesized to form the plasmamembrane
P5- Excess lipid will be stored underneath the skin as adiposed tissu e (beneath the skin as a
source of energy)
Assimilation in the cells (Summary)
Question & marking scheme
Amino acids
P1-Amino acids are used in protein synthesis//
P2-For repair and production of new protoplasm/growth and repair//
P3-Used in the formation of enzyme /some hormones /protein part of hemoglobin /antibodies
Any 1A
Glucose
P1-Glucose is oxidized during the cellular respiration to produce energy
Lipids
P1-A major energy reserve in the body//
P2-(phospholipids)are components of the plasma membrane //
P3-Lipids is used as a respiratory substrate/
P4-Lipids also is use as a main component of some hormone and
P5- Excess lipid will be stored underneath the skin as adiposed tissu e (beneath the skin as a
source of energy)
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
118
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.7 Evaluating Eating habits
Health problem related to eating habits
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
If she continues to take the menu everyday for a long time , explain the consequence to her
health
F1-Constipation
E1-Her menu lacks fibre/roughage so her faeces moves too slowly through the colon
F2-Scuvry
E2-Lack of vitamin C //any other vitamin deficiency with explanation
F3-Obesity
E3-High intake of roasted chicken/gilled mutton /chocolate/chips increase the amount of fat
stored in the body
F4-diabetes mellitus
E4-Excess of carbohydrate in rice/chips/potatoes/chocolate increase the amount of glucose in
blood when digested
F5-Arteriosclerosis/Arthrosclerosis
E5-Roasted chicken /grilled mutton /chips contain
F6-Heartattack
E6-Roasted chicken /grilled mutton/chips contain cholesterol which are deposited in te
coronary artery//cause blockage in the coronary artery
F7-High blood pressure
E7-Narrowing of artery cause the heart to pump with higher pressure
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
119
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(b)
Content
Mass for 100 g of fried chicken nugget(g)
Carbohydrate
10.5
Protein
20.1
Lipid
25.3
Fibre
2.5
Sodium chloride
0.7
A teenage boy aged 13 eats 500g this snack food for energy week
Is the snack food suitable as a daily diet for the boy? Describe the effect of taking this snack
food over a long period
F-not suitable
1
P1-The snack contains high fat and protein
1
1
P2-the intake of high fat irregularly may lead to obesity
1
P3-saturated fats in the snack may deposited in the wall of artery
1
P4-the narrow lumen of artery leads to arteriosclerosis
1
P5-soon the teenager faces high blood pressures
1
1
P6-If arteriosclerosis occur at coronary artery the teenager may have heart attack
1
P7-Excessive intake of protein may cause kidney problem
1
P8-th snack contain lack of fibre
1
P9-This may lead to constipation
6
(c)
Breakfast
Lunch
Dinner
Full cream mik
Fried egg
Fried chicken rice
Rice with brrf curry
Fried chicken
Ice cream
Carbonated soft drink
Chicken burger
Cheese cake
Teh tarik
Explain the long term effect of comsuming excess of these foods on harith health
F1-Full cream milk,fried egg, fried rice chicken,beef curry
E1-A health problem will be obesity
E2-Excess saturated fats increases the bood cholesterol level
E3-Cholesterol deposits on the walls of the blood vessel narrowing them
E4-This will contribute to cardiovascular disease/arteoriolesis /hypertensiom/heart problem
F2-Fried egg crry,fired chicken ,chicken burger also contain a lot of protien beside fat
E5-Excess protien will,cause very taxing on the kidneys duirng excretion
E6-Might alos lead to gout
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
120
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
F3-Ice cream , cheese,the tarik,carboanted soft drink contain a lot of sugar
E7-lead to obesity /diabetes mellitus
F4-His diet does not cantain fruit and vegetables
E8-That leads to constipation
(d)
Meals
Types of food
Breakfast
Coffee, Nasi lemak
Lunch
Rice, Beef curry,chicken soup,Fresh orange juice
Dinner
Rice,Grilled Fish,Spinach soup,Tea
1
1
1
1
Based on the able ,analysed the food content and justify the preperation food methods toward
ahmad’s health
F1-Imbalanced diet
P1-Excess of lipids
P2-Excess of protien P3-Excess of carbohdrates
P4-Fibres
P5-Vitamin
F2-Good /not good preperation food methods
P6-Frouts anf vegetables should not be cooked because vitamins B ,C soluble in water
//vitamins A,D Eand K soluble in oil
P7-Grill prbvent from more oil added into the food
P8-Fry the food not good becouse more oil added into the food Any 2P
Evaluation
Able to atate F1 and F2- corecly
Able to state any one of P1-P4-and any one P5-P7 correctly
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
8
(e)
Some families often eat fast food because working parent does not have time to
prepared home cooked food. These eating lead to many health problems
You are asked to prepared a talk on good eaing habits for a group of parents
Dicuss the good eating hanits that you may want to educate them
P1-Good eating habits mean taking food in the correct quatity/propotion at the correct time
1
P2-Improper eating habitscan lead health problemssuch a obesity/diabetes mellitus /anorexia 1
nervosa / and bulimia
P3-Always eat a balanced diet that include all /seven /the different classes of food /prtoein , 1
carbohydrate, fat, vitamins , minerals , water and fibre ( follow food pyramids)
P4-Take propermeals a regular times of the days //take in three meals a day ( breakfast,lunch 1
and dinner)
P5-Check the food labels for information regarding the nutrint content s /The total caloroies of
the food]
P6-avoid consuming unhealthly food /junk foods,snack foods,because junck food include food
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
121
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
that is high in Slat/sugar/fats but low in nutritional value
1
P7-Avoidunder eating , it cause food and food rich in sugar
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
P8-Avoid under eaitng , it cause tiredness , amlnutriment
P9-Sufficient amount of fibre form friuts and vegetables
P10-Take time to chew the food to avoid indigestion
P11-Avoid smoking ,drinking too much alcohol ansd coffee
P12-We should refrain form overeating or eatign too little during a mela
P13-Drinking at least 2 to 3 liters of waters a days Any 10
10
6.9The importance of macronutrient and micronutrient in plants
Element required by plant
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Marks
“The uses of organic fertilizers and inorganic fertilizers in the field of agriculture is
hiped farmers ti increase their agriculture yield and as a result helps to increase the
country’s productivity”
Extract from Datuk Seri Abdullah Badawi’s speech
Based on the above extract as well as your biological knowledge, describe how do the element
found in the inorganic and organic fertilizers, aid in plant growth
F1-The element found in the fertilizers consists of macronutrient and micronutrient elements
F2-Macronutrient are element needed by the plant in large quantities
Element
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Potassium
Calcium
Sulphur
Function
For the formation of protein /nucleic acid chlorophyll/photosynthetic
enzyme/respiratory enzyme
For the formation of nucleic acids/ ATP/ Phospholipids/ coenzymes/
/important for the synthesis of protein/plasma membrane
For the protein/carbohydrate metabolism
For the formation of lamella //Formation of spindle fibres
For the formation of protein//coenzyme in respiration
Function
Boron
For carbohydrate transport
1
1
1
1
122
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
1
1
F3-Micronutrient are elements required by the plant in minute quantities
Element
1
1
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Molybdenum
For nitrogen fixation
Zinc
For the synthesis of hormone//growth of shoot/root
Manganese
To active respiratory enzymes
Copper
For the formation of enzyme //Important for photosynthesis
Iron
For synthesis of chlorophyll
1
1
1
1
1
10
6.10Photosynthesis
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
State the meaning of photosynthesis based on the schematic diagram in diagram
F1-(Photosynthesis is the )process where by a green plant synthesizes glucose form carbon
dioxide and water
F2-In the presences of chlorophyll and sunlight
(b)
1
1
2
The process of photosynthesis contributes to the balance of nature
State one importance of photosynthesis to the balance nature
(c)
E1-Provide food to human beings/animals//
1
E2-Provides /replaces oxygen in the atmosphere//
1
E3-Help maintaining percentage of CO2/O2 in the atmosphere Any 1
1
1
Explain how the problem of air pollution can affect the rate of photosynthesis
F1-Particles accumulate on the leaf surface
1
E1-covers the stomata//reduces O2 and CO2 gas exchange
1
E2-Cuts/reduces light intensity (that reached the leaves)
1
E4-Less CO2 is absorbed from atmosphere and less O2 is released Any 2
1
3
123
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Leaf structure and function
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
U
T
Name the structures labeled P, Q, R and S.
1
P : Palisade mesophyll(tissue)
1
1
1
1
Q : Sponge mesophyll
R : Xylem
S : Phloem
T :stomata
(b)
(c)
U :upper epidermis
1
6
Name the structure where photosynthesis take place
chloroplast
1
1
State the role of oraganelle P in photosynthesis
Choloroplast/organelle P (contains chlorophyll) to trap/absorb/capture light energy
1
1
(d)
Describe the sructure of chloroplst
1
P1 Bounded by double layer of membrane
P2 Fill with stroma (the jelly like matrix)
P3 Contain grana (ie stacks of membranous structure)
P4 Grana contain chlorophyll MAX 2
1
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
124
2
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
How are cells within the tissue of a leaf adapted for photosynthesis? Essay /Structure
TIPS: If question asked (State) just answers F: for 1 marks
e.g.: Explain the adaption of the leaf to optimal/ increase efficiency photosynthesis
Structure
Adaptation (Marking scheme)
Cuticle
F1 : Outer surface of a leaf / cuticle which is waxy/ waterproof
P1 : prevent water loss
Upper epidermis
F1-Epidermis with water proof layer of cuticle / coated with a wax
P1-Prevent excess transpiration /loss of water
OR
F2-//Epidermis are transparent
P2-Allow light easily penetrate the leaf (and reach the chloroplast)
Palisade mesophyll
F1-Palisade mesophyll cells are packed tightly
F2-contain high density of chloroplasts
P1-to receive maximum amount of sunlight
Spongy mesophyll
F1 : Spongy mesophyll loosely arranged/ contain air spaces
P2 : maximize /Easy diffusion of water and carbon dioxide
F1: Irregular shapes of mesophyll
P2 : To increase the internal surface area for gaseous exchange.
Lower epidermis
F1: Lower surface contain abundant of stomata
P2 : To prevent water loss to surrounding //to allow exchange of gases between the leaf
and its surrounding
Stomata
F1-Stoma is flanked by two guard cells
P1-Which regulate the size of stoma
P2-Stoma allow the exchange of gases/ carbon dioxide from atmosphere diffuses into the
leaf/water vapour/oxygen diffuses out of the air
Explain how the light intensity affect the opening of structure R (Stoma)3
F1-High light intensity simulate photosynthesis in guard cells/Cell Q
E1-Guard cells producing glucose //Potassium ions (K+) Diffuse/moves into guard cells
by active transport
E2-The guard cell become hypetonic compare to neighbouring cell
E3-Water moves into/diffuses by osmosis
E4-Guard cells/Cell Q become turgid (stoma open)
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
125
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Xylem
F1- consists of xylem vessels joined together end to an end
P1- Cell P does not have any cytoplasm
P2- The cell walls are thickened with lignin
F1-consists of sieve tubes arranged end to end
F2-Sieve tubes have sieve plates to allow continuous flow of organic compound.
Phloem
Vascular bundle
F1-Vascular bundle/veins contains xylem and poem
F2-Xylem transport water minerals salt // give mechanical support
F3-Ploem transport organic products of photosynthesis/ glucose(away from the leaf) Any
Physical structure
Lamina
F2 : Thin lamina
P3 : allow diffusion of gases to occur efficiently (for photosynthesis)
F3 : Flattened shape of lamina
P2 : Large surface area for maximum absorption of sunlight
// allow light to penetrate and reach the cell
F1-Arrangement of leaf mosaic pattern
P1 : to receive maximum amount of light
6.11 The mechanism of photosynthesis
Light reaction
No
(a)
(b)
Marking scheme
4H2O
Marks
4H++4(OH-)
Name the process that has taken place based on the equation above
Photolysis of wtaer
1
1
Where does the reaction take place?
Granum of chloroplast
1
1
(c)
Describe the photosynthesis /Photosynthetic reaction which occur in Structure P and Q 4
Structure P
P1-In P (granum), light energy is absorbed/captured by chlorophyll to produce chemical
eneygy/ATP
P2-Water molecules are split in to ions H+ and OH-/Photolysis occurs
1
1
(d)
Name an organ in a plant whwre Y is found abundantly
Name of the organ: leaf
Reason :the leaf has aplenty of palisade mesophyll cells (containing plenty of chroloplast)//the
site for photosynthesis
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
2
126
1
1
2
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(e)
During photosynthesis ,P (grana) is the site where light reaction occurs whereas R (stroma) is the
site where dark reaction occurs
Explain how light reaction occurs at P
F-P (granum ) contains plenty of chrophyll absorb//capture light energy
P1-To produce chemical energy//ATP
P2-to split/break donthe water molecule//photolysis os water
P3-To realeased oxygen and hydrogen atom
1
1
1
1
(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
Explain the mchanism of light reaction
P1-Chrolophyll absorbed light reaction
P2-Energy is used to split water molecule in to hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ion loses electron to
form hyfroxyl
P3-Electron is erecieved by hydrogen ion to form a hydrogen atom
P4-Hydroxyl ion loseelectron to form hydroxyl
P5-Produce waterand oxygen
Explain the importance of this reaction
F-Split water molecule into hydroxl ions (OH_) and hydrogen ion(H+)
P1-Each hydrogen ion receive an electron from the chlorophyll
P2-nuetralised to form a hydrogen atom that is used in the dark reaction
P3-to reduce carbon dioxide
Any 2
Explain how gas N(oxygen) is produced in reaction A(light reaction)
F1-Photolysis/light energy is used to split/breakdown water molecule
E1-into hydrogen ion/H+ and hydroxyl ion/OHLight
//24H2O
24H++OHChlorphyll
E2-Hydroxyl ions loses an electron to form hydroxyl group
//24OH24OH+2e
E3-Hydroxyl groups combine to form oxygen and water
//24OH
12 H2O +24 e
3
1
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
1
1
Write down the full equation /overall eqautionfor photosynthesis
Light
Water + carbon dioxide
Glucose+oxygen
Chlorophyll
2
1
127
Light
//6H2O +6CO2
C6H12O6 + 6O2
1
Chlorophyll
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Dark Reaction
No
(a)
(b)
Marking scheme
Describe the photosynthesis /Photosynthetic reaction which occur in Structure P and Q
StructureQ
P1-In Q (stroma),dark reaction occurs
P2-Hydrogen atoms combine carbon dioxide to form glucose
Marks
1
1
Explian the effect to the process of dark reaction in Q if light reaction at P does not occur
F-Photolysis/spliting if water molecule does not occur
P1-No hydrogen atom ( is released to combine with carbon dioxide( during reduciton
process)
P2-No glucose is produced
1
1
1
3
Explain the light reaction and dark reaction
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Photosynthesis is a pocess whereby a green plnt produces organic food substances rom carbon
dioxide and water in the presunce of chlorophyll and sunlight
// Describe the process that occur in the leaves as shown in diagram
// Explain the machanism that makes place on organelle m that involvced in the formation of
starch in the green plant10
Based onyour understanding of th above statement ,describe how a molecule of carbon dioxide in
the air and water absorbd form the roots becomes part od a carbohydrate molecule stored in a leaf
of a plant
1
1
P1-Light raction occur in grane
P2- chrolophyll absorbs light energy to produce ATP/electrons
P3- Light energy split the water molecules into hydroxyl ion and hydrogen ion // photolysis of
water
1
P4-The hydrogen ions (H+) imbine with electron to form hydrogen atoms
1
1
1
1
1
P5-The hydrogen atoms ATP will b used in dark reaction
P6-The datk raction takes place in absence oflight
P7-It occur in stroma
P8-Carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen to form glucose and water
P9-Glucose undergoes condensation and is converted to starch for storage in the leaf
P8-It occur in a series of chemical reaction which require ATP
P10Gucose may also be transformed into sucrose to be transport to other part of the plant Any 8P
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
1
1
1
128
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
The different between light reaction and dark reaction
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(b)
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages are the light reaction and dark reaction.
Describe the differences between the light reaction and dark reaction 4 Prefer in structure Q
Light reaction
Dark reaction
D1-Occurs in granum
Occurs in stroma
D2-Requires light
Does not require light
D3-Involved photolysis of water
Involved
dioxide
D4-Materail required is water /Chlorophyll
Materials
required
is
dioxide/hydrogen atoms/ATP
D5-Produces oxygen and water
Produces glucose
Need chlorophyll
Do not need chrophyll
Light required
Light is not required
Produced ATP and hydrogen
Use ATP and hydrogen
Oxygen produced
No oxygen produced
No reduction of carbon dioxide
Reduction of carbon dioxide
No glucose produced
Glucose produced
reduction/fixation
1
1
of
carbon
carbon
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
ANY 4 Must answer in complete sentences
6.12Factors affecting photosynthesis
The factor a effecting the rate of photosynthesis
No
Marking scheme
Marks
State four factors which affect the rate of photosynthesis
i.
Light intensity
ii.
Carbon dioxide concentration
iii.
Water/humidity
iv.
Temperature
1
1
1
1
4
129
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Light intensity
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Explain how an increase in light intensity effects the production of Y in stage 1
P1-an increase in light intensity can increase the production of Y
P2-At a higher light intensity, more molecules are split into hydrogen ions hydroxyl ions (
photolysis of water)
1
1
2
(b)
High light intensity
Moderate light intensity
Low light intensity
In the diagram Draw two curve to show the rate of photosynthesis at
(i) a low light intensity
(ii)a high light intensity
1
1
2
130
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Temperature
Diagram show a graph of the effect on the rate of photosynthesis
Rate of photosynthesis
10
20
30
40
Temperature /oC
No
Marking scheme
(a)
Explain the graph shown above
F-Temperature affect the enzyme activity
P1-The rate of photosynthesis/activity of enzyme increase with the increase in temperature
P2-Too high temperature/more than 45 oC enzyme are denature/photosynthesis decrease stops
P3-Low temperatures decrease the reactivity of enzyme/photosynthesis in the leaf /rate of
photosynthesis Any 3
Concentration of carbon dioxide
(b)
Marks
Explain how an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide affects the production of Z in stage 2
P1-When the amount of carbon dioxide is increased, more Z (glucose) is produced
P2-A higher amount of carbon dioxide I reduced by the hydrogen atoms produced in stage I
,and results in more (glucose)
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
2
(c)
Based on the diagram , Explain the changes of the concentration of carbon dioxide occurs at the
places where the density of plants is high such as at the tropical rainforest
F1-At night ,percentage of CO2 is high/increase
131
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
P1-Low/decrease of light intensity leads to photosynthesis does not occur
P2- CO2 does not absorb from environment
P3- CO2 releases to environment as the product of plants respiration (F1and any 1P)
1
1
1
1
1
F2-At morning ,percentage CO2 is reducing
P4-Photosynthesis happen at low rate early morning because of extremity low light
P5-Some CO2
produced form the respiration process which was being used in the
photosynthesis process/carbon dioxide was less released to the environment
1
P6-when the extremity light increase, the photosynthesis rate increased until the
photosynthesize was more that the respiration rate
1
P7- CO2 will be absorbed form environment caused the reducing of percentage(F2and any 3P)
F3-At noon , percentage CO2 is very low
P8-The extremity of light raise higher and photosynthesis arte at maximum level
P9-The absorption of CO2
(3Fand any 1P)
from environment is very high which caused very low percent
1
1
1
1
10
The difference in the rate of photosynthesis in plant throughout the day Trail Johor
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Graph shows the changes in the rate nof photosynthesis throughout the day in a tropical country
Based on the graph, explain the changes in the rate of photosynthesis in the plant throughout
the day 10
F1-From 0000 to 0600 , the rate of photosynthesis is very low
P1-The light intensity/temperature is (very) low
P2-(at low temperature), photosynthetic enzyme are inactive
F2-From 0600 to 1200 , the rate of photosynthesis increase (rapidly)
P3-Light intensity/temperature also increase
1
1
1
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
132
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
1
1
1
P4-Enzyme for photosynthesis become more active
P5-Stomata open wider to allow absorption of more carbon dioxide
F3-From 1200 to 1800 , the rate of photosynthesis decrease
P8-Light intensity /temperature decrease
1
1
1
1
1
P9-Photosynthetic enzyme are less active
P10Stomata opening/pores become smaller
P11-less carbon dioxide id absorbed
F5-From 1800 to 2300, the rate of photosynthesis become very low //stopped/ceased
P12-Light intensity very low/temperature is very low / no light
1
1
1
P14-Stomata closed
P15-Very little / no carbon dioxide is absorbed
ANY 10
Increasing productivity of crops based on the factor affecting the rate of photosynthesis
No
(a)
Marking scheme
10
Marks
In countries with four seasons, plant are grown in green houses
Based on the statement , explain why this method is carried out to ensure the production of
crops throughout the year 6
F-In temperature countries light intensity/temperature changes throughout the year
1
1
1
1
1
1
P1-In winter, temperature is very low
P2-In autumn, the plants shed their leaves //light intensity/temperature is low
P3-Rate of photosynthesis is very low
P4-In spring and summer, the light intensity/temperature are optimum for photosynthesis
P5-So the rate of photosynthesis is maximum/highest
(b)
P6-In the green house , light intensity/concentration of carbon dioxide/ temperature are
maintained at optimum level (for photosynthesis) throughout the year
1
P7-So the rate of photosynthesis is maintain at maximum level throughout the year(regardless
of changes in light intensity or temperature)
1
P8-The plants are able to increase yields /increase the crops production throughout the years
1
8
Explain why the rate of photosynthesis of plant in green is higher than plant outside
1
1
P1-Factors affecting can be be controlled at high level all the time
P2-Artificial lighting can be used when light intensity is low
P3-concentration of cerbon dioxide nof carbon dioxide can be increased by burning paraffin
P4-Temperature can be controlled by using temperature controller
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
133
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.14 Technology used in food production
Hydroponics Kedah 2012
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Diagram shows amethod of plant cultivation without use of soil
Describe the method used
P1-Hydroponic (name the technique)
P2-grow plants in culture solution
P3-The root of the plants are immersed in solution
P4-Which contains all the macronutrient //and micronutrient in the correct proportion
P5-The culture solution is aerated
P6-To provide sufficient oxygen for respiration
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
Genetic engineering Kedah 2012
No
(bn)
Marking scheme
Marks
Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)are organism which carry the genetic
information or beneficial genes from other organism
Nowadays , the crops such as heat, soya bean, paddy and tomatoes are widely to be
cultivated commercially as genetically modified plant
Based on the information above, discuss the advantages and disadvantage of producing
genetically modified organisms in food production 6
Advantages:
P1-Used to produce disease resistance /pest resistant plants
P2-Less pesticides are used
P3-Les pollution to the environment //better health for consumers
P4-increase yields of cops/ profitability
P5-help to solve problem of insufficient
P6-Increase resistance in plant to herbicide eg. Soya bean plantation
P7-Higher vitamin A / Beta carotene content in rice /tomato/accept suitable example of crops
P8-Help to solve problem of malnutrition
P9-Produce crop with longer shelf lifes
P10-Prevent food wastage
Any 4P
Disadvantage:
P11-Pest resistant genes may be transferred to weeds cause difficult to control growth of weeds
P12-Some genetic modified crops may have animal genes
P13-genetic modified crops may have affect the survival of other organism in the ecosystem
P14-Cause the imbalance o nature
Any 2P
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
134
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
6.15Tecnological development in food processing
The necessity fro food processing
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Marks
Food preservation involves methods of preparing food to extend the
lifespan and to avoid wastage of food.
Based on the above statement, explain the necessity for food processing.
P1 – prevent food spoilage
P2 – (food spoilage) causes by the action of microorganism
P3 – decomposing bacteria/fungi on carbohydrate/protein
P4 – produced carbon dioxide, water, ammonia hydrogen
P5 – make food become toxic
P6 – Oxidation of food when cut/expose to air
P7 – oxygen react with enzymes/chemicals released by cell
P8 – Increase it commercial value
P9 – food additives is added in preserving the freshness of
food
P10 – Improve the taste/appearance/texture
P11 – Intention of diversifying the uses of food
P12 – increased the variety of products
(b)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
Diagram 9.2 show a few examples of fresh food and processed food.
Discuss the good effects and bad effects of processed food in our daily life
Good Effect : By producing processed food
G1:Food can be preserved / kept longer.
1
G2 : to prevent wasting of food./food spoilage/can be stored for (further use)
1
G3:Crops can be planted / livestock / poultry can be reared in big scale.
1
G4 :to prevent food shortage.
G5:(food are packaged) to increase the commercial value / to diversify the uses of food 1
substances
G6: more types / varieties of food can be produced.
1
Bad Effect : By regular consuming of processed food
B1 : Loss a lot of nutrition value (under high temperature during the
1
process).
B2: (Contain) preservative / colouring / dye / flavor which is carcinogenic.
1
B3: lead to mutation / cancer / health problem / suitable example.
1
B4: Contain excessive salt / sugar.
1
B5: lead to high blood pressure / diabetes / obesity. Any 10
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
135
10
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
Relating the food processing methods with factors causing food spoilage
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(a)
Fermentation and UHT treatment are food processing methods
Explain how the methods above extend the lifespan of the foods
Method
Explanation/Biological concept
1
M1-Fermentation
Food substances are added with yeast
M2-Fermentation yields ethanol, which at
high concentration, will stop the activity of
bacteria, that cause food spoilage
2
UHT treatment
The high temperature kills microorganism/
o
and
Fresh milk is heated to 132 C for 1-5 bacteria/fungus
microorganisms/bacteria/fungus
spore
seconds(under high pressure )
2
2
4
(b)
Type of food
Food preservation method
Milk
Pasteurisation
Fruits
Cannin
Meat and fish
Refrigeration
Pasteurisation
1
1 - milk is treated to 63oC for 30 minutes//72oC for 15 seconds
1
2 - followed by rapid cooling to below 10oC
1
1
1
1
3 - destroy bacteria but not the spores
4-
retains the natural flavour of milk//nutrients//vitamin B
5 - must refrigerated to avoid the growth of sperms
Canning
6 - use heat sterilization
1
1
1
1
1
7 - kill microorganisms and spores
8 - steamed at high temperature and pressure to drive out air
9 - sealed while the food is being cooled
10 - vacuum in the can prevent growth of microorganism
Refrigeration
11 - stored at temperature below 0oC
1
1
12 - prevent the growth of microorganisms/the germination of spores
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
136
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 6:Nutrition 2014
No
Marking scheme
Marks
(c)
Explain the food processing methods which is related to the factors that cause food spoilage.
Concept : Food can be preserved by destroying the microorganism present in the food //by
stopping the activities of the microorganism
F1: Cooking-.high temperature kill the microorganisms
1
P1: denature the enzyme that cause the breadown of food
1
F2: Treating food with sugar/salt
1
P2: causes the microorganism to lose water due to osmosis
1
F3: Adding vinegar will reduced the pH
1
P3 that prevent microorganism from growing
1
F4: Fermentation of fruit juices and other food by adding east
1
P4: high concentration of alcohol prevent the microorganism from growing
1
F5: Dry under hot sun (meat/fish/fruits)
1
P5: removes water from food – dehydrated
1
F6: Ultravoilets rays
1
P6: kills microorganism
1
F7: Pasteurisation – destroy bacteria which cause tuberculosis and typhoid
1
P7: (technique) -Food is heated to 630C for 30 minutes /
1
720C for 15 seconds followed by rapid cooling to -10 0C
P7.1: (Pasteurisation) retains the natural flavour and nutrients
1
F8: Canning – uses heat sterilization to kill microorganisms and their spores
1
P8 (technique) -.Food is packed in cans, steamed at high temperature and pressure to drive out air
1
P8.1: the vaccum created within the cans prevent growth of microorganism
1
F9: Refrigeration
1
P9: food stored at temperature below 00C prevent growth/germination of microorganism
1
P9.1: food remain fresh for a long period of time Any ten : F + P correctly
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
4551/2 © All Right Reserved
SULIT
10 137









