5.4.1 Self-perceived physical and mental health status at follow up
advertisement
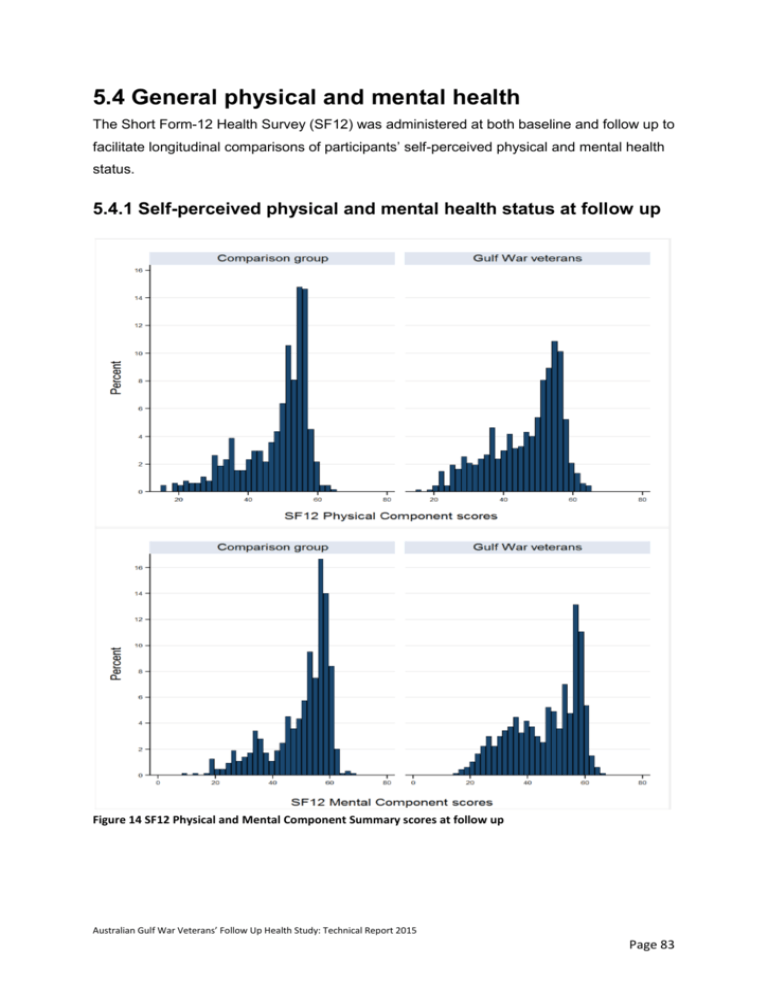
5.4 General physical and mental health The Short Form-12 Health Survey (SF12) was administered at both baseline and follow up to facilitate longitudinal comparisons of participants’ self-perceived physical and mental health status. 5.4.1 Self-perceived physical and mental health status at follow up Figure 14 SF12 Physical and Mental Component Summary scores at follow up Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 83 The charts in Figure 14 show the distribution of the SF12 Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores at follow up for both the Gulf War veterans and the comparison group. Higher scores represent higher perceived health status. The distributions for both the PCS and MCS in both groups were left skewed, with larger numbers of participants reporting high scores than low scores. The distributions were less skewed in the Gulf War veteran group, with these participants more likely than the comparison group participants to report mid-range PCS and MCS scores. Table 19 SF12 Physical and Mental Component Summary scores at follow up SF12 subscale score Gulf War veterans (N=670) mean (sd) Physical Component Summary Mental Component Summary Comparison group (N=642) mean (sd) mean diff Adj mean diff (95% CI) 46.68 (10.30) 48.18 (9.76) -1.50 -1.34 (-2.42, -0.26) 46.12 (11.85) 49.92 (10.67) -3.80 -3.32 (-4.57, -2.06) Comparing the two groups on mean PCS and MCS scores at follow up, Table 19 shows that the Gulf War veterans reported significantly poorer physical health status and mental health status than the comparison group, with a greater difference found for the mental component score. 5.4.2 Association between Gulf War-deployment characteristics and self-perceived physical and mental health in veterans at follow up The associations between Gulf War deployment characteristics and self-perceived physical health at follow up, as measured by the SF12 PCS, are shown in Table 20 for male Gulf War veterans. Significantly poorer self-perceived physical health status at follow up was associated with older age at deployment and with ranks lower than Officer. There were no significant differences in self-perceived physical health across Gulf War veterans from different service branches. The associations between Gulf War deployment characteristics and self-perceived mental health at follow up, as measured by the SF12 MCS, are shown in Table 21 for male Gulf War veterans. None of the differences were statistically significant, however lower self- Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 84 perceived mental health status in ‘other ranks, non-supervisory’ and younger age at deployment approached statistical significance; p = 0.10 and p = 0.08 respectively. Table 20 Association between Gulf War-deployment characteristics and SF12 Physical Component Summary sores at follow up in Gulf War veterans Gulf War deployment characteristic Age at deployment < 20 20-24 25-34 >=35 Service branch Navy Army Air Force Rank category Officer Other rank-supervisory Other rank -non supervisory Mean SF12 PCS score for Gulf War veterans at follow up N mean (sd) diff Adj diff (95% CI) 58 165 351 96 47.28 (9.80) 48.13 (10.49) 46.54 (10.11) 44.34 (10.66) 0.00 0.85 -0.74 -2.94 0.00 -0.47 (-3.65, 2.71) -3.70 (-7.19, -0.21) -7.11 (-11.10, -3.12) 577 44 49 46.73 (10.33) 44.85 (10.20) 47.75 (9.97) 0.00 -1.87 1.02 0.00 -2.01 (-5.20, 1.18) 0.43 (-2.34, 3.21) 142 341 186 49.36 (9.53) 45.83 (10.24) 46.20 (10.69) 0.00 -3.53 -3.16 0.00 -4.55 (-6.46, -2.65) -6.78 (-9.47, -4.08) Table 21 Association between Gulf War-deployment characteristics and SF12 Mental Component Summary sores at follow up in Gulf War veterans Gulf War deployment characteristic Age at deployment < 20 20-24 25-34 >=35 Service branch Navy Army Air Force Rank category Officer Other rank-supervisory Other rank -non supervisory Mean SF12 MCS score for Gulf War veterans at follow up N mean (sd) diff Adj diff (95% CI) 58 165 351 96 41.23 (11.85) 45.71 (12.67) 46.63 (11.40) 47.93 (11.41) 0.00 4.48 5.40 6.70 0.00 3.32 (-0.46, 7.10) 3.05 (-1.05, 7.16) 3.93 (-0.84, 8.69) 577 44 49 45.97 (11.85) 48.46 (11.90) 45.84 (11.84) 0.00 2.49 0.14 0.00 1.78 (-1.98, 5.55) -1.15 (-4.69, 2.38) 142 341 186 47.49 (11.77) 47.03 (11.38) 43.45 (12.42) 0.00 -0.45 -4.04 0.00 -0.27 (-2.66, 2.12) -2.91 (-6.34, 0.51) Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 85 5.4.3 Change in self-perceived physical and mental health status since baseline In both study groups, participants’ self-perception of their physical health, as represented by their PCS scores, and mental health, as represented by their MCS scores, decreased in the period from baseline to follow up. These differences within groups across time were statistically significant. Additional analysis showed that there was no difference between the two groups in regard to change over time on either subscale (PCS: diff -0.67, adj diff -0.67, 95% CI -1.69, 0.35; MCS: diff -0.36; adj diff -0.16, 95% CI (-1.45, 1.13). Table 22 SF12 Physical and Mental Component Summary mean scores at baseline and follow up for participants who completed the SF12 at both time points PCS MCS Baseline mean (sd)* 49.41 (9.07) 48.07 (10.86) Gulf War veterans (N=652 Follow up mean diff (95% CI) mean (sd)* -2.68 (-3.38, -1.97) 46.72 (10.29) -1.80 (-2.69, -0.91) 46.18 (11.85) Baseline mean (sd)* 50.34 (8.71) 51.56 (9.12) Comparison group (N=624) Follow up mean diff (95% CI) mean (sd)* -2.01 (-2.72, -1.29) 48.32 (9.70) -1.64 (-2.55, -0.73) 50.03 (10.61) * Includes only those participants who also completed the SF12 at follow up 5.4.4 Key findings In both study groups, participants completing the SF12 were more likely to report high selfperceived physical and mental health scores than low scores. However, Gulf War veteran participants were more likely than the comparison group participants to report mid-range physical health and mental health scores. Comparing the two groups on SF12 mean PCS and MCS scores, Gulf War veterans reported significantly poorer physical health status and significantly poorer mental health status than the comparison group, with the greater difference being for the mental component scale. Amongst Gulf War veterans, poorer self-perceived physical health status at follow up, but not mental health status, was associated with older age at deployment and with ranks lower than Officer. There were no significant differences in self-perceived physical or mental health at follow up across Gulf War veterans from different service branches. In both study groups, participants’ self-perception of their physical health and mental health declined in the time period from baseline to follow up to a similar degree. Australian Gulf War Veterans’ Follow Up Health Study: Technical Report 2015 Page 86





