Global and local realities in the Arab classroom
advertisement

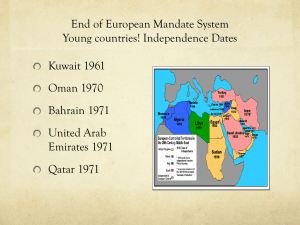
GLOBAL AND LOCAL REALITIES IN THE ARAB CLASSROOM Some reflections. DEVELOPING LEADERSHIP . . WITHOUT DISCUSSING POLITICS Developing critical thinking . . Without being critical of local political systems or leaders. OBSERVATIONS FROM MY TIME IN THE REGION Look at the realities of tackling leadership issues to undergraduate and MBA business students in the Gulf region. Based on a year in the UAE and 5 years in Oman. Leadership is integrated into OB. Increasingly, it is a stand alone course at under/ graduate MBA levels. AMERICAN HEGEMONY IN BUSINESS EDUCATION IN THE GULF Hegemon =leader/ Hegemonia = leadership Gramsci on cultural hegemony. Particularly problematic in Gulf business schools. Teaching of business and of leadership dominated by US materials. Textbooks. PPT slides. Language: English Cases and examples: Primarily western. Research: Leadership Quarterly (US) Institutional dominance: Association for the Advancement of Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB). PROBLEMS WITH HEGEMONY Mismatch between what Gulf Arab students learn, and their work experience. Why? Western business materials/ ideas implicitly assume an idealized Western context: authenticity/ transformational leadership; straight talking; freedom of expression; Challenging the status quo – often highly political (Lincoln, Mandela, Ghandi). Political process, and representation. Models taught are problematic in the Arab workplace. IN THE GULF STATES THERE ARE CERTAIN KEY FACTORS THAT ANY LEADER MUST DEAL WITH. Enormous wealth in the hands of key families in each country. Wasta networks. Absence of political dissent/ critical political discourse. No free press/ investigative journalism. Unions. Industrial democracy. Dominance of state bureaucracies. Qarar culture. Lack of transparency (recent Dubai bailout). IMPLICATIONS FOR LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT “Think critically . . But without publicly criticising the State, the political system, powerful business leaders, or politicians”. Leadership development and education is thus characterized by a tension . . . between Western discourse, theories and research, and local realities, which are often glossed or avoided. That is what why . . when discussing leadership for the common good, we avoid challenging, or even mentioning, the political structures. Global and local realities in the Gulf Arab classroom Developing leadership . . Without discussing politics. Developing critical thinking, without being critical of local political systems or leaders. THE WAY FORWARD? Address these tensions . . and use them to enhance learning and development . . Tensions: Global – Local/ Universal-particular Problem based learning techniques . . Politics: Tightrope . . “Leadership for the common good?” We walk the same tightrope!