Complex radiologic diagnostics of diseases of respiratory organs
advertisement

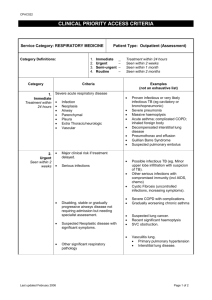
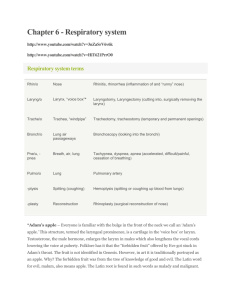
Technological card of lecture № 3 Theme: Complex radiologic diagnostics of diseases of respiratory organs School hours: 2 hours Structure/plan of lecture 1. A role radiological, ultrasonic, CT, МRI and radionuclide researches in studying of respiratory organs. 2. Methods of radiologic research of respiratory organs. 3. Radiologic anatomy of respiratory organs. 4. Radiologic semiotics of diseases of respiratory system. 5. Radiologic diagnostics of inflammatory, purulent and tumoral diseases of lungs. 6. Beam diagnostics of a tuberculosis of lungs and pleurisies. 7. Urgent radiodiagnosis of alien bodies of a trachea and bronchial tubes. The purpose: To acquaint students with radiological, ultrasonic, CT, МRI and radionuclide researches of respiratory organs, features of their carrying out at children, and also radiodiagnosis of often meeting diseases of respiratory system. Problems: Results of educational activity: 1. To familiarize students with radiologic Students list the radiological anatomy of respiratory organs. methods of research applied at 2. To familiarize students with the basic beam diseases of respiratory organs; methods of research of respiratory organs. Give the developed characteristic to 3. To familiarize students with beam semiotics diseases of respiratory organs; of diseases of lungs. Name radiological, symptoms of 4. To familiarize students with in a complex diseases of respiratory organs; diagnostic attributes of acute and chronic Consistently open algorithm of pneumonia. beam diagnostics at the given 5. To familiarize students with in a complex pathology; diagnostic attributes of accumulation of a liquid Solve tests. in a pleural cavity. 6. To familiarize students with in a complex diagnostic attributes of an abscess of lungs. 7. To familiarize students with in a complex diagnostic attributes of multiply bronchoectasis. 8. To familiarize students with in a complex diagnostic attributes of a lung tuberculosis. 9. To familiarize students with in a complex diagnostic attributes of an alien body in respiratory ways. Method of training: The form of the organization of educational activity Means of training Ways and means of a feedback 1. Lecture 2. Discussion and analysis 3. Demonstration of a clinical case 4. Blitz-interrogation Face-to-face-collective • schedules and tables, standard diagnosis • visual materials • multimedia • videofilm The blitz-interrogation, test tasks before - and after lecture. Modern radiological research as the major method of studying of a morphological and functional condition of respiratory organs in norm and a pathology has received a general recognition. There are some methods of research united in following groups: 1. The basic method – X-ray. 2. Additional methods - radioscopy, tomography, lateroscopy, laterography, thoracoscopy, a technique of the superexhibited roentgenograms, photoroentgenography, electroroentgenography. 3. Special methods - bronchography, angiopulmonography, mediastinography, diagnostic pneumothorax, fistulography. Radiosemiotics of lungs diseases Develops of 9 syndromes: 1. Extensive blackout of a pulmonary field; 2. The limited blackout of a pulmonary field; 3. Round shade in a pulmonary field; 4. Ring-shape shade in a pulmonary field; 5. The focuses and limited dissiminations; 6. Spread dissiminations of focuses in pulmonary fields; 7. Pathological changes of a root of a lung; 8. Pathological changes of pulmonary drawing; 9. Extensive enlightenment of a pulmonary field. Radiodiagnosis of inflammatory, purulent and tumoral diseases of lungs Pneumonia Local pneumonia The local bronchopneumonias are characterised by catarrhal inflammation of a pulmonary tissue with formation exudate in a gleam of alveoluses. The centres of infiltration 0,5-1 sm can be located by the size in one or several segments of a lung, is more rare – bilaterally. One of variants of local pneumonia - the localconfluent form. At this form separate sites of infiltartion merge, forming the big, non-uniform centre on the density, occupying quite often whole share and tending to destruction. The lung root is expanded. Segmentary bronchopneumonia (mono- and polysegmentary) are characterised by an inflammation of the whole segment which lightness is lowered because of expressed atelectatic component. Such pneumonia quite often has propensity to a long current. An outcome of a long pneumonia can be fibrosing pulmonary tissue and deformation of bronchial tubes. Croupous pneumonia (usually pneumococcal) differs hyperergic croupous inflammation having a cyclic current with phases of inflow, red, then white hepatization and permissions. The inflammation has lobar or sublobar distribution with involving in pleura process. A radiological picture: the illness beginning strengthening of pulmonary drawing in the amazed share, expansion of a corresponding root of a lung. Progressing of inflammatory process: the focuses of blackout of the different size, indistinctly outlined, gradually becoming more intensive, quickly increasing and merging among themselves. In a stage of the expressed changes: intensive blackout big lung parts, with the rough greased contour on a course of distribution of process, and on the contrary, with sharply outlined edge according to an interlobar fissure. Pleura consolidation. Resolution stage: reduction of intensity of blackout which becomes non-uniform. Further, on an extent 2-3 weeks blackout slowly resolves. Interstitial acute pneumonia is characterised by development mononuclear or plasmatic cellular infiltration and proliferation of interstitial tissues of lungs, local or widespread character. Such pneumonia more often is caused by certain activators (viruses, pneumocysts, fungus etc.). Chronic pneumonia. Radiological signs: sharp strengthening and deformation of pulmonary drawing, presence of the cellular enlightenments reminding "cellular" drawing; local blackouts separate, indistinctly outlined; pleura consolidation, it adhesion. Deformation of a bronchial tree with occurrence of bronchoectases. Thorax deformation. Narrowing of intercostal intervals, reduction of volume of a pulmonary field, displacement of mediastinal organs. Abscess of a lung. A radiological picture: the illness beginning - typical symptoms is not present. It is observed more or less intensive blackout with rough, places indistinct contours. Illness progressing - a site rather more intensive shade, having the wrong spherical form. Typical radiological signs of an abscess come to light after its break contained in a bronchial tube. There is a limited enlightenment of the semicircular or oval form - a cavity. The cavity part is blacked intensively out at the expense of the liquid contents forming horizontal level. Level remains at any change of position of the patient. Cavity walls in the beginning rough, then become more smooth and accurately outlined. Tromboembolism of pulmonary artery - unilateral pauperization of vascular drawing, zones of avascularization and «stump» artery breakage are defined. II. Exudative pleurisy - radiological signs: definition of homogeneous intensive blackout in the field of pulmonary sine and slanting level of a liquid, displacement of mediastinal organs in the healthy party. Pneumothorax - definition of a site of an enlightenment in the field of sine III. Tumours of lungs: Primary cancer of a lung 1. The central form. The radiological picture depends on character of growth of a tumour. At peribronchial growth - expansion of a shade of a root. Intensive blackout in a radical zone, its external contour is well delimited or rough and indistinct. Endobronchial growth - hypoventilation, and then atelectasis of segment, a lobe or even all lung. Displacement of a median shade in the amazed party. High standing of a cupula of diaphragm. 2. The peripheral form of a cancer. A radiological picture: intensive blackout more or less roundish form with rough, more often polycyclic contours; shade localization - peripheral parts of a lung. Stripe-like "path" connecting a pathological shade with a root of a lung. IV. Cysts of lung - cyst filled with air, it is defined in the form of thin ring-shape shades in which there is no pulmonary drawing. Filled with liquid contents, cysts causes intensive roundish or oval blackout with accurate equal contours. Lecture equipment: 1. Tables: -Norm; -Radiologic semiotics of diseases of respiratory system; -Radiologic diagnostics of traumatic damages, inflammatory, is degeneratedystrophic, tumoral defeats of lungs; 2. Resume on a theme; 3. The multimedia program; 4. Negatoscope; 5. Roentgenograms, echograms, CT-grams, MR-tomograms on the given theme.