Keystone Quia Quiz—Cell Physiology Unit Question Source and
advertisement
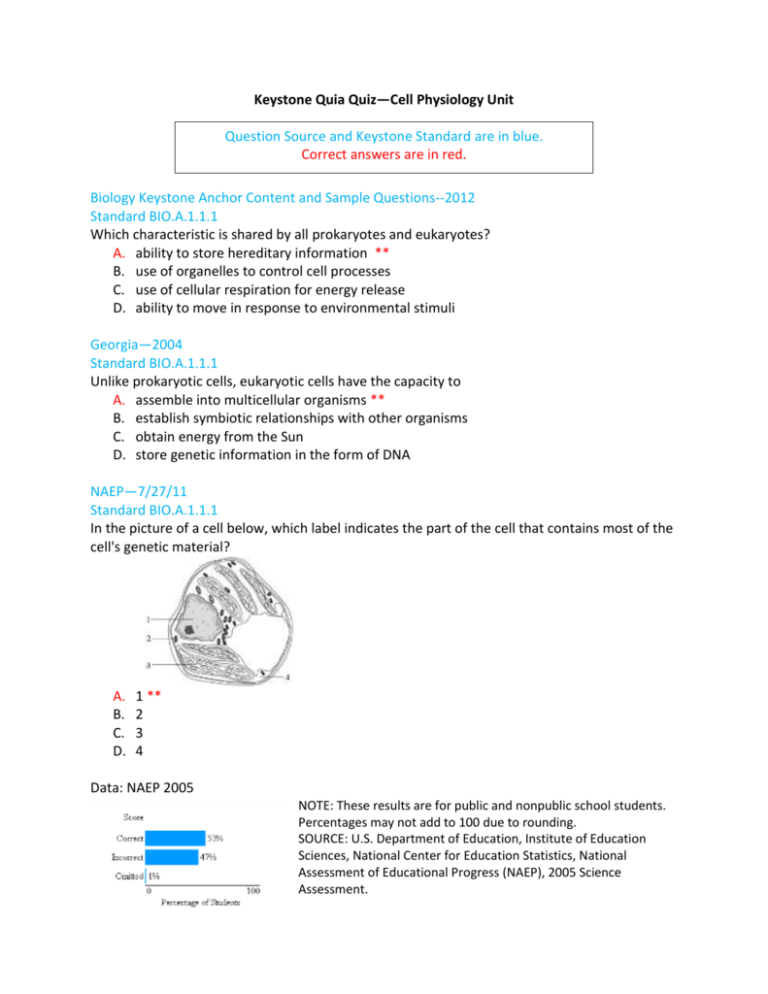
Keystone Quia Quiz—Cell Physiology Unit Question Source and Keystone Standard are in blue. Correct answers are in red. Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.1.1.1 Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? A. ability to store hereditary information ** B. use of organelles to control cell processes C. use of cellular respiration for energy release D. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli Georgia—2004 Standard BIO.A.1.1.1 Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to A. assemble into multicellular organisms ** B. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms C. obtain energy from the Sun D. store genetic information in the form of DNA NAEP—7/27/11 Standard BIO.A.1.1.1 In the picture of a cell below, which label indicates the part of the cell that contains most of the cell's genetic material? A. B. C. D. 1 ** 2 3 4 Data: NAEP 2005 NOTE: These results are for public and nonpublic school students. Percentages may not add to 100 due to rounding. SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), 2005 Science Assessment. Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? A. cell wall and nucleus B. cell wall and chloroplast C. plasma membrane and nucleus D. plasma membrane and cytoplasm ** Massachusetts—Feb 2009 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 A biologist looks at an organism through a microscope. Which of the following observations tells the biologist that the organism is eukaryotic? A. The organism is unicellular. B. The organism moves with flagella. C. The organism has a cell membrane. D. The organism has membrane-bound organelles. ** Arkansas—April 2010 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 This figure below shows an animal cell. Which number corresponds to the organelle that produces cellular energy? A. 1 ** B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Arkansas—June 2011 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Which set of organelles would be found in both human cells and plant cells? A. chloroplast, nucleus, and cell wall B. nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and cell wall C. mitochondria, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum ** D. mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, and centrioles Massachusetts—Feb 2010 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 A diagram of a plant cell is shown below. Which number identifies the organelle that functions to store water and dissolved salts? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 ** D. 4 Arkansas—June 2011 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Which process would be directly affected if all of a cell’s ribosomes were weakened? A. replicating DNA B. producing new protein ** C. metabolizing glucose to produce ATP D. transporting nutrients across the cell membrane Massachusetts—Feb 2010 Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 In a cell, which of the following organelles most likely contains digestive enzymes? A. centriole B. chloroplast C. lysosome ** D. ribosome North Carolina—2008 (2) Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Some organelles have their own DNA that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This is true of which organelle? A. cell wall B. mitochondria ** C. plasma membrane D. vacuole Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.4.1.3 The rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus work together in eukaryotic cells. What is one way that the Golgi apparatus functions? A. It assembles nucleic acids from monomers. B. It breaks down old, damaged macromolecules. C. It packages new protein molecules into vesicles. ** D. It determines which protein molecules to synthesize. Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.1.2.2 Alveoli are microscopic air sacs in the lungs of mammals. Which statement best describes how the structure of the alveoli allows the lungs to function properly? A. They increase the amount of energy transferred from the lungs to the blood. B. They increase the flexibility of the lungs as they expand during inhalation. C. They increase the volume of the lungs, allowing more oxygen to be inhaled. D. They increase the surface area of the lungs, allowing efficient gas exchange. ** California—2003 to 2008 Standard BIO.A.4.1.1 The plasma membrane of a cell consists of A. protein molecules arranged in two layers with polar areas forming the outside of the membrane. B. two layers of lipids organized with the nonpolar tails forming the interior of the membrane. ** C. lipid molecules positioned between two carbohydrate layers. D. protein molecules with polar and nonpolar tails. Missouri—2008 session I Standard BIO.A.4.1.1 What is the main function of a selectively permeable cell membrane? A. storage of water B. storage of chemicals C. breaks down molecules within the cell D. regulates what enters and leaves the cell ** Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.4.1.1 Carbon dioxide and oxygen are molecules that can move freely across a plasma membrane. What determines the direction that carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules move? A. orientation of cholesterol in the plasma membrane B. concentration gradient across the plasma membrane ** C. configuration of phospholipids in the plasma membrane D. location of receptors on the surface of the plasma membrane Biology Keystone Anchor Content and Sample Questions--2012 Standard BIO.A.4.1.2 A sodium-potassium pump within a cell membrane requires energy to move sodium and potassium ions into or out of a cell. The movement of glucose into or out of a cell does not require energy. Which statement best describes the movement of these materials across a cell membrane? A. Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B. Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. ** C. Sodium and potassium ions move by facilitated diffusion, and glucose moves by osmosis. D. Sodium and potassium ions move by facilitated diffusion, and glucose moves by active transport. Massachusetts—Feb 2009 Standard BIO.A.4.1.2 The table below lists the concentrations of water inside and outside a cell under four different conditions. Under which condition will the cell experience a net loss of water to its environment? A. Condition 1 B. Condition 2 C. Condition 3 ** D. Condition 4 North Carolina—2008 (2) Standard BIO.A.4.1.2 Placing wilted lettuce in cold water will make it crisp again. Which statement best describes what happens to restore the lettuce to its original condition? A. Water left the lettuce cells by diffusion. B. Water entered the cells of the lettuce by osmosis. ** C. Osmosis caused salts to enter the lettuce cells. D. Salts in the leaf caused water to leave the cells. NY Regents—June 2010 Standard BIO.A.4.1.2 The diagram below shows solute molecules represented by “X” both outside and inside of a cell. A process that would result in the movement of these molecules out of the cell requires the use of A. DNA B. antigens C. ATP ** D. antibodies PA Keystone—February 2011 Standard BIO.A.4.1.2 Use the image above titled “Water movement and the cell membrane” to answer the following question. The relative concentration of solute inside and outside a cell can cause water molecules to move across the membrane. Which phrase would be an alternate title to the diagram? A. Exocytosis in a Cell B. Active Transport in a Cell C. Osmosis Across a Membrane ** D. Facilitated Diffusion Across a Membrane







