THE CHANGING EARTH OUTLINE Manav, Teresa, Edson, Parima
advertisement

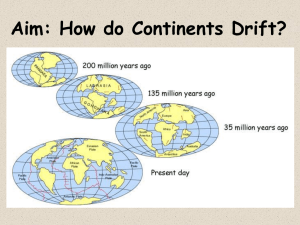
I.) II.) III.) THE CHANGING EARTH OUTLINE Manav, Teresa, Edson, Parima P2 Continental Drift Theory: The theory that states that the earth was made up of one super continent that broke apart into several smaller landmasses that make the continents we know today A.) This theory was proposed by Alfred Wegener and Frank Taylor B.) Pangaea 1.) The giant land mass from which all the continents broke apart Evidence of Theory A.) Shape of continents 1.) The coastlines of all of the continents align with each other and fit together almost like a jigsaw puzzle B.) Fossils 1.) Fossils of similar plants and animals have been found on separate continents, showing that they came from the same landmass. C.) Mountains 1.) Some mountain ranges begin on one continents and finish on another, showing that they were once connected on the same landmass. D.) Ice 1.) Glacial striations on rocks show that glaciers moved from Africa to South America, which would have been more likely if the continents were not separated by the Atlantic Ocean. E.) Positions 1.) There is evidence that ice covered the southern continents, but there is no evidence that ice covered the northern continents, showing that these northern continents once lied on/near the equator 2.) Fossils of tropical plants have been found in Antarctica showing that this frozen land was once in a more temperate climate where vegetation could grow. Plate Tectonics: A term that refers to how the Earth’s surface is built up of plates. A.) The theory of plate tectonics 1.) The outermost layer of the earth is covered in over a dozen plates, small and large, that move in relation to one another by the flow of molten rock. 2.) As these plates shift position, they may not slide past each other smoothly, and instead would move in small jolting bursts. This is the cause of earthquakes