Study Guide
advertisement

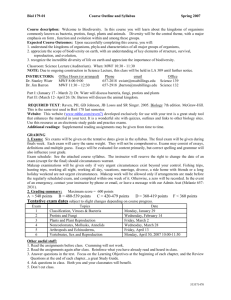
Classification Study Guide 1. Amphibian means ‘double life’. Explain this: Amphibians live the first part of their life in water, the 2nd half they live on land. 2. Are most animals vertebrates or invertebrates? Most animals are invertebrates 3. Explain bilateral symmetry: organisms with bilateral symmetry have one line of symmetry that runs down their body- each side is a mirror image of the other. Examples: humans & butterflies 4. Explain radial symmetry. List organisms that have this type of symmetry and their characteristics: radial symmetry is being symmetrical among many lines (like a circle) that go through the center of the organism. Many cnidarians and echinoderms have this type of symmetry which includes having their mouth located in the center of their body with no head or tail. Examples: sea star & jellyfish 5. How and what do fish breathe? Most use gills to breathe oxygen (dissolved). 6. How are protists similar to animals? They are both Eukaryotes. Some protists are also consumers and heterotrophs. 7. How does bacteria reproduce? Asexually and sexually (binary fission and conjugation) 8. How is a reptile egg different from an amphibian egg? Reptile eggs have a soft leathery shell (must be covered with soil or compost). Amphibian eggs lack a shell (must develop in water). 9. In what type of habitat would you most likely find fungi? Wet and warm and often shade 10. In what ways do fish reproduce? Many use external fertilization and lay eggs. Some use internal fertilization Some have live birth. 11. List characteristics common to all arthropods. Jointed segments, bilateral symmetry, most have exoskeleton, ectotherms 12. List phyla of animals that are invertebrates. Invertebrates: Sponges, cnidarians, worms, mollusks, echinoderms, arthropods 13. List phyla of animals that are vertebrates. Vertebrates: Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish 14. List the 3 domains. Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya 15. List the 6 kingdoms. Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals 16. List the 8 levels of classification from largest to smallest. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 17. Some protists have pseudopods or cilia. How are pseudopods and cilia used? For movement (locomotion) 18. To which phylum do vertebrates belong? Chordata (chordates) which have a spinal cord or nerve cord 19. Why are bacteria considered to be prokaryotes? Their cell (unicellular) lacks a nucleus 20. What are bacteria that break down dead organisms called? Decomposers 21. What are the 2 major groups of vascular plants? 1. Angiosperms (flowering) Ex. Oak tree, maple tree, daisy, orchid, apple tree (any plant with fruit/flowers) 2. Gymnosperm (seed-producing plants that do not produce flowers ex. conifers, cycads, Ginkgo) 22. What are fruiting bodies in fungi? Used in reproduction ex. mushroom 23. What are the characteristics (traits) of all protists? mostly unicellular, some multicellular (algae), can be heterotrophic or autotrophic, most live in water (some live in moist soil or human body), ALL are eukaryotic 24. What are the characteristics of fungi? Eukaryotes, most multicellular, some unicellular, all heterotrophs, most reproduce by spores 25. What are the major functions of animals? obtaining food and oxygen, keeping internal conditions stable, movement, and reproduction 26. What are the only animals with feathers? What are other characteristics of this group? Birds, scales on feet, endothermic, 4- chambered heart 27. What characteristics are shared by all animals? Heterotrophs, multicellular, eukaryotes 28. What is a flagella? What does it look like (may draw a picture) and how is it used? Whiplike tail; used for movement 29. What is an arthropod’s tough outer covering called? exoskeleton 30. What is fertilization? What type of reproduction is this part of and how does it differ from other forms of reproduction? Joining of egg and sperm; sexual reproduction; offspring have traits from both parents 31. What is budding? In which type of reproduction does it occur? A form of asexual reproduction in which a small part of the parent's body separates and develops into a new individual 32. What is the difference between a heterotroph an autotroph? Autotroph make their own food. Heterotroph have to get their food by eating other organisms. 33. What is the main function of a leaf? To photosynthesize (make food for plant) 34. What makes archaebacteria different from eubacteria? It has a different chemical makeup, archaebacteria lives in more harsh environments and is an older organism 35. What is regeneration? It is when an organism grows back a body part (such as a tail). 36. What is binomial nomenclature? Who first suggested it? Provide an example. What classification level of each part? The two part naming system created by Carolus Linnaeus. Ex. Homo sapien (Genus and species) 37. Where do most invertebrates live? -In the water Most of the Earth’s surface is covered in water. Water helps support many invertebrates who could not survive on land. 38. Why do mammals have fur? They are endotherms. Fur helps to hold in their body heat and adds protection. Which mammal(s) can fly? bats 39. Why are amphibians sensitive to changes in the environment? -because they have thin, moist, and porous skin 40. Why do some organisms have a backbone and what are they called? To protect the notochord (spinal cord), are called vertebrates 41. What is homeostasis? -a property of an organism that helps it maintain its systems within a normal range ex. maintaining temperature, sugar levels, or water levels 42. What is spontaneous generation? Why was it discredited (found to be wrong)? It was the idea that living things could come from non-living things. We now know that is untrue because of Redi’s and Pastuer’s experiments. Living things must come from over living things through reproduction.