The Foundations of Civil Engineering and Architecture
advertisement
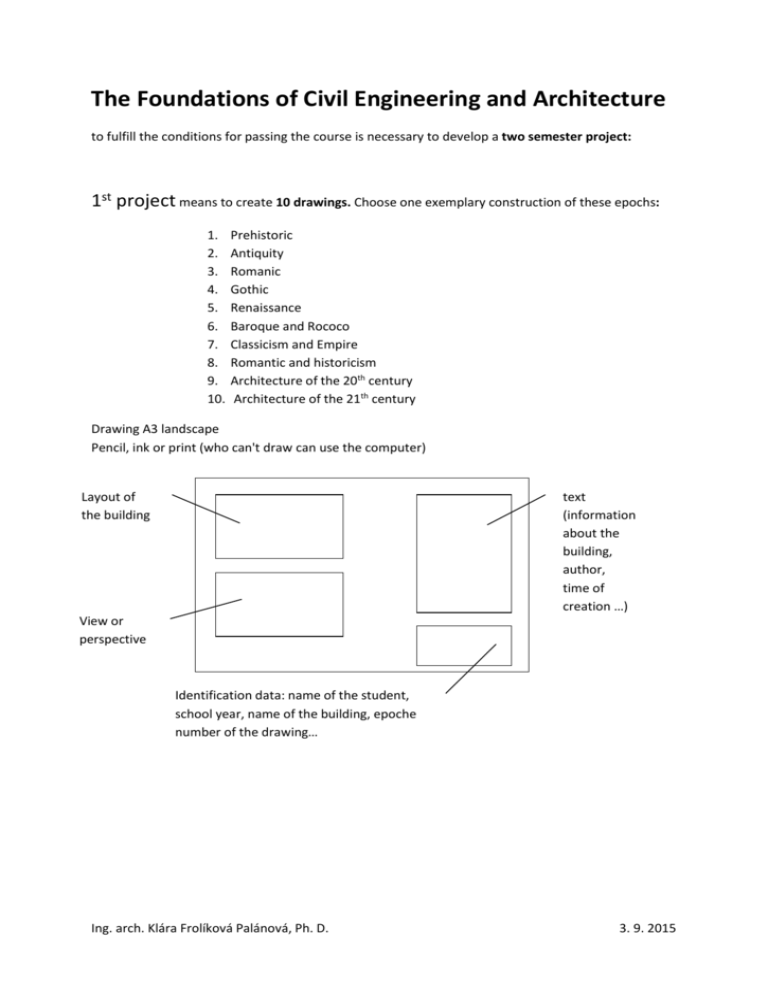
The Foundations of Civil Engineering and Architecture to fulfill the conditions for passing the course is necessary to develop a two semester project: 1st project means to create 10 drawings. Choose one exemplary construction of these epochs: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Prehistoric Antiquity Romanic Gothic Renaissance Baroque and Rococo Classicism and Empire Romantic and historicism Architecture of the 20th century Architecture of the 21th century Drawing A3 landscape Pencil, ink or print (who can't draw can use the computer) Layout of the building text (information about the building, author, time of creation …) View or perspective Identification data: name of the student, school year, name of the building, epoche number of the drawing… Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 2nd project means to write a report from the visit of the Czech town or a notable locality in the Czech Republic. It's necessary to write about the architecture. Examples of recommended sites: Towns: Ostrava, Olomouc, Opava, Zlín, Brno, Litomyšl, Praha, Karlovy Vary, Mariánské lázně, Františkovy lázně, Karlova Studánka, Velké Losiny, Plzeň, České Budějovice etc. Lednice-Valtice area etc. Drawing A4 Portrait First page has to contain identification data Use the computer Text + photo, maps, schema, layouts of the buildings etc. Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Exemplary buildings of historical epoch: 1. Prehistoric megalithic constructions (dolmen, menhir, cromlech) - STONEHENGE (Salisbury, England), dolmen PEDRA GENTIL (Barcelona, Spain), alley menhirs in CARNAC (France), cave MENGA (Malaga, Spain) corridor graves caves, huts, tents 2. Antiquity Babylon and Babylon ziggurat, Temple of Horus in Edfu, Egypt, temple in Luxor, Egypt, Pyramids of Giza, Egypt, Atre Treasury (tomb) in Greece, Lion Gate at Mycenae, Greece, Athenian acropolis in Greece, Cloaca maxima, great Roman channel in Italy, Roman pantheon in Italy, Colosseum in Rome, Italy 3. Romanic Church of Sainte-Foy in Conques (Aveyron, France), Church Notre-Dame-du-Port in ClermontFerrand, Baptisterium in Parma, Italy, Cathedral and Tower of Pisa, Italy, 4. Gothic Cathedral in Cologne, Germany, St. Stephen's Cathedral in Vienna, Austria, Milan Cathedral in Italy, Ca'd'Oro Palace in Venice, Italy, Reims Cathedral in France, St. Vitus Cathedral at Prague Castle, CZ 5. Renaissance "Hospital of the Innocents" in Florence, Italy, Dome of Santa Maria del Fiore in Florence, Italy, Medici-Riccardi Palace, Italy, Temple of St. Peter in Rome, Italy, Villa Farnese in CAPAROL, Italy, Library Marciana in Venice, Italy, Villa Rotonda, Italy, Castle in Fontainebleau, France, royal Summer Palace(Belvedere) in Prague, CZ, City Hall in Litomysl, CZ 6. Baroque and Rococo Church of St. Nicholas on the Malá Strana, Prague, CZ, Czernin Palace, Prague, CZ, Wallenstein Palace, Prague, CZ, Temple St. Paul in London, GB, St. Peter's Square in Rome, Italy, Piazza del Popolo in Rome, Italy, Zwinger in Dresden, Germany, pilgrimage church. John of Nepomuk, Žďár nad Sázavou, Cz 7. Classicism and Empire Capitol in Washington DC (USA), Boodle's club in London (England), Pantheon in Paris (France), Petit Trianon at Versailles (France), The Arc de Triomphe in Paris (France), Building of the Royal Art Society, London (England), Theater in Berlin, Germany (author K.F.Schinkel), Admiralty tower in Petersburg, Russia, chateau Kačina, CZ 8. Romantic and historicism Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Parliament, London (England), Provincial hospital, Prague (author J. Hlávka), CZ, National Theatre, Prague, CZ, National Museum in Prague, CZ 9. Architecture of the 20th century Town museum, Hradec Kralove, CZ, Villa Tugendhat, Brno, CZ, Villa Müller, Praha, CZ, Pavilion Secession in Vienna, Austria, architectural works of authors Jiří Kroha, Jan Kotěra, Josef Gočár, Le Corbusier, Erich Mendelson, Bohuslav Fuchs, Walter Gropius, F. L. Wright, Mies van der Rohe, Adolf Loos, Kenzo Tange, Niemayer, etc. 10. Architecture of the 21th century Current architectural works Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 The Foundations of Civil Engineering and Architecture Prehistory (500 000-1 000 000 years BC – 3 000-1 000 years BC) Antiquity (till 476 a. d.) o Mesopotamia o Egypt o Aegean culture o Ancient Greece o Etruscan architecture o Ancient Rome The Middle Ages (from the year 476 a. d. till 1492 a. d.) o The early Christian architecture o Byzantine architecture o Pre-Romanesque architecture o Romanesque architecture o Gothic modern period (from the year 1492 till today) o Renaissance o Baroque o Classicism, Romanticism, Empire o Historicism o building in 20. Century o the current building Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 EPOCHS... IN MORE DETAIL PREHISTORY (500 000-1 000 000 YEARS BC – 3 000-1 000 YEARS BC) ANTIQUITY (TILL 476 A. D.) o Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία "[land] between rivers"; Arabic: ( ال راف دي ن ب الدbilād al-rāfidayn); Syriac: ( ܢ ܗܪܝ ܢ ܒ ܝܬBeth Nahrain) "land of rivers") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria and to a much lesser extent southeastern Turkey and smaller parts of southwestern Iran. Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization in the West, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthians. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th-century Arab Islamic conquest of the Sassanid Empire. A number of primarily neo Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra. o o o Egypt Aegean culture Ancient Greece Classical Greek architecture, as it is known, was founded in 8th century BC following the elements of the Mycenaean and Egyptian architecture. With these influences, the Greeks have their own traditional architecture and put the base architecture that influenced European thought for a very long time. In the 7th century BC in ancient Greece gradually pushed for the construction of religious nature of certain palatial, the use of opulent materials (stone, later a marble), and finally the Greeks created several uniform styles. In the course of the 6th century BC the Greeks discovered the greater part of their Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 construction methods, which may develop, but it is still not the need for change. In this century, also completed the development of the architrave system. The Greeks built worked without any bonding material and relied purely on so the weight of the stone blocks. The construction was carried out so that individual blocks have undergone final alignment editing until after the completion of construction, as well as columns were erected up to fluted. This method to prevent unwanted damage during transport or construction. The temple stood on a pedestal, had a rectangular ground plan (usually in the aspect ratio of approximately 1: 2). The roof standing on pillars and on the sides were closer two shields. The roof covering was made of tiles of burnt clay. Building material for the construction of such a rule was a marble. In the 5th century was built the temple, what most Greeks built-the Parthenon. In the 4th century BC the Greeks began to concentrate on the profane buildings, generally believe that this shift in interest in Athens, which came needed a centralized bureaucracy. In parallel with the development of structures for bureaucratic purposes began to build the theatre and from 3th century BC developed and the architecture of the House, which led to the construction of a truly luxurious mansions. The biggest problems which accompanied the Greek architecture were the transport and economic concerns. Modern architecture historians believe that the vast majority of Greek constructions have been built without plans and detailed drawing. Just the ignorance of the plans has led to a certain fiber construction, because it was easier to experience. Perform calculations on the spot, led to frequent overcapacity buildings that caused the economic inefficiency. o o Etruscan architecture Ancient Rome The Romans took from the Greek architecture, which, however, customized to your needs and enrich it with new elements. The Etruscan arch system and joined the architrave system of ancient Greece. Thinking of the Romans has led the development of the architecture to expediency. The architecture of the so often spoken with engineering and was used for military purposes. This category includes for example. the construction of roads that allow for fast moving troops. Other buildings, which is famous for the Roman architecture, the aqueducts. These large projects have led to the development of the assessment. Since the buildings were often built from public funds, it was necessary to carry out not only planning, but also budgeting structures. These buildings need bridges, therefore, the Romans developed the original Greek and Etruscan arch and discovered the so-called "ideas. the Roman arch. For Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 these strategic buildings, the Romans found a suitable building material, which become concrete. The discovery of the concrete and the principle of boarding allowed them to build stronger walls, thanks to which they can venture into larger structures. For such construction was needed to find a suitable way of roofing and Golden scales, which enabled the discovery of the so-called the Roman arch. Another element that appeared in architecture thanks to the Romans is the urban plan of the city. Most Roman towns (excluding Rome) and military camps, was built according to a uniform model with the creation of Central forums, water distribution systems with the idea of rectangular streets. The size of such goods was subject to the standards, which have been subject to military purposes. Religious concept was very similar to the Greek, yet even here there was a used architectural discoveries, which allowed to draw from Greek architecture. The floor plan of the Roman temple is so classically rectangular to circular. The Romans also developed the idea of the Basilica, which became the basis of a Christian Temple. The biggest rise of Roman architecture occurred in the reign of Emperor Augustus, this development continued until 3th century, when the Roman architecture is evident in the emerging crisis. The Greek Theatre, the theatre to duplicate their skills to enable them to develop the basic ideas of the Greek Theatre. Roman funeral was not uniform, the attractions are the subterranean vaulted chambers, which were the predecessors of the catacombs. Roman architectural peculiarity are the winning arches, which are actually the ceremonial entrance gate built for returning winners. THE MIDDLE AGES (FROM THE YEAR 476 A. D. TILL 1492 A. D.) o The early Christian architecture In the 4th century to the general acceptance of Christianity, which has led to great social change. Although Christian architecture was based on the Roman Empire, was the need for a number of significant changes, since Christianity was completely different requirements for the worship of God (until 313, when came the edict of Milan, Christians gathered in private homes). For this purpose the best throw the Roman basilica, which first established itself in both parts of the Empire. For such construction was typical East-facing apse and a considerable amount of light that filtered down to the Basilica of a large number of Windows. another element which brought Christianity, was the development of the catacombs. Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 The fall of the Western Roman Empire, caused the end of centralized power, real power held a series of Kings and bishops, who, however, did not have enough resources to actually show and groundbreaking works. This architecture became the architecture of churches and in Western Europe, has been preserved from this period are very few buildings. Significantly greater importance should the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, where a series of really important buildings, which further develop the Roman experience. Here, from 5th century developed a new style. o Byzantine architecture is the summary descriptions for the architecture of the Byzantine Empire during the period from 4. till 15. century, which greatly influenced the surrounding country and, subsequently, all Orthodox countries of Europe. Under Byzantine influence was established and a number of ecclesiastical buildings in Italy, in France and elsewhere. Byzantine architecture followed the architecture of the late Roman Empire and developed her two main directions: first, took over the longitudinal type of Roman basilica, which has arches and domes, and developed a central isosceles-shaped type clubs and the central dome. Both types appear between the buildings of Emperor Constantine in Palestine (the Temple of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem and the ruined octagonal church in Antioch). The cross design was later added to a square with nine large field. The main material of Byzantine buildings were brick, the interiors of the temples were lavishly decorated with lined with marble and mosaics and frescoes. Remains of the storm in the 8. century is a general prohibition on the statues. Civil constructions differ mainly straight roofs and decorative by placing the bricks. o Pre-Romanesque architecture includes building monuments of the early middle ages (about 500-1000) from southern and Western Europe. At this time, the Germanic tribes settled, accepted Christianity and asimilated the Roman culture. In the middle of the wooden architecture in stone buildings, the majority of Christian churches. Initially very diverse building types and procedures during the reign of Charlemagne (died 814) began to align and prepare so the advent of Romanesque art. The oldest medieval stone buildings on the Czech territory are documented from the period of the Great Moravian Empire. The archaeological traces of stone churches of various types of research have uncovered in the old town, the village of Mikulčice, in blue, and other locations. Design of non-preserved structures, their origin and their relationship to the Mission of SS is the subject of scientific inquiry and hypotheses. Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 With the oldest of the Přemyslids is associated churches of St. Clement left Hradec, the Virgin Mary in Prague and is the oldest standing building, the rotunda on the Czech Budči. A few younger were Basilica. George and the rotunda sv. Vitus Cathedral at Prague Castle. Churches on the Settlements can be constructed with Boleslav i. shows well-preserved rotunda st. Petra in the old Pilsen. The stone church was built by the otonic also its Settlement Slavník dynasty at Libice, torn down was already in 995 when their massacre. o Romanesque architecture having established itself in the architecture and the Visual Arts in Western, southern and Central Europe at 11-13. century. East Europe was at that time influenced by the Byzantine style. In architecture it was gradually developed, within Europe and the epoch of the more or less uniform tradition of constructing buildings and the use of the material. The term "Romanesque" includes an attempt to express the relationship of this building style to the building style of ancient Rome, which was largely inspired by and shared with him some of the structural elements (see classical order of architecture). The relative level of style and mutual similarity of building structures in Europe was made quite a considerable mobility of the medieval people. Despite many modern ideas about life before the industrial revolution, not only the nobles and Knights, as well as merchants, artisans, monks, missionaries and traveled Europe and were thus, among others, and share the knowledge necessary to construct buildings. The development of Romanesque architecture and art was closely associated with the completion of the Christianization of Europe, since the new believers need spaces where they could collect to the liturgical ceremonies and preaching. Built with two basic types of churches, the Basilica and the Rotunda. Both had their precedent in the ancient architecture. The Basilica has a rectangular structure, whose inner space was divided lengthwise into three series of arches and more ships. Originally it served as a marketplace or courthouse. In the Christian Temple was the main ship is significantly higher and wider. On the eastern side it closed by semi-circular niche – the apse, in which was located the chancel. In the middle of the chancel stood the altar, at which the masses served. The Interior of the Basilica of the illuminated window located at the top of the wall, which delimit the Middle ship. There was a part of the construction of the tower. Also, rotunda, a simple circular building with a conical roof, was known in ancient times already. The Romans is used primarily as a tomb. Christians began to build in places where significant events commemorated the life of Saints or their martyrdom. The Rotunda was one or more apsid. A typical Romanesque building represent Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Benedictine monasteries (such as the famous abbey in Cluny), which used to be an essential part of the Basilica. In the Romanesque style also secular buildings were built, especially castles. They served primarily as a fortress to defend against the enemy, therefore, great care was given to their defense system. He formed the castle's walls, moats and towers. Part of the castle was a residential Palace. It was the monarchs or their administrators, later fortified settlements began to establish also the nobility. On the construction of the Romanesque churches and castles began to use stone, while in some countries (among them i of Bohemia and Moravia) has not yet been built primarily from wood. Irregular and unevenly sized chunks of stone joined together larger amounts of mortar. The walls used to be thorough, several metres wide. It is not surprising that a few rugged construction caused massive and cumbersome impression. Between typical characters include a semicircular Romanesque arch. We find him at the entrances and Windows, but also as a barrel vault. In addition to using flat beamed ceilings to bridge the internal space. In addition, already knew the builders of the cross Vault (based on the two arches). The weight of the vaulted ceiling was resting on massive walls and pillars, which were finished with decorative capitals. Heavy masonry applied to build a wider door or window openings. The towers and halls in the Castle palaces used to be associated two to four next to each other, separated by columns. The entrances were artistically processed portals. The Interior of the churches are mostly trimmed. The architecture of the appropriately complement the sculptures and murals. To show scenes from the Bible or from the lives of Saints, and clearly is so tilted to the faithful who couldn't read. Similar suggestions appeared also in the decoration of manuscripts. Painting decoration books and book plates, richly decorated carved wood, precious metals or gems, as well as jewelry belonging to the typical expressions of Romanesque in the field of Arts and crafts. The internal equipment was then still the castles of relatively simple. Consisted of the basic pieces of furniture. Important was the Ark, in which to store the needed items, including clothing. Served also for sitting or lying. Bed, desk, Chair and stool have simple shapes. Shining in the candlelit or torch-fixed to the candlesticks. The main source of heat was an open fire in the fireplace. o Gothic the art style is slowly building in the Romanesque style. Starting with the show since the second half of the 12. century and continues in the high middle ages after the next three centuries. In Czech countries comes and gives way to Gothic a little later. In Germany and Central Europe lasted until the beginning of the 16. century, when in Italy and France have already pushed through following the Renaissance. It is of Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Gothic style developed, but on the contrary, it sought to deny, and when its development was based on the ancient heritage. The Gothic style was the gradual development of the Romanesque style. The beginnings of Gothic style starting in France and are associated with the building of the Abbey of Saint-Denis near Paris. In the resulting style is therefore to some extent contained in the philosophy of the direction for God, which is technically expressed verticality, compared to the romantic style was especially significant for the buildings to lighting and "dematerialization". Unlike the Gothic Romanesque already reached full extension throughout Europe, but rather in its Western and central parts. The influence of the Gothic in the territories with the influence of the Orthodox Church on the artistic sensibility was greatly limited. Massive construction such as arise. many of the Cathedral, but also the construction of minor character. The characters of architecture: 1. "Verticality"– in the construction as well as in each of its parts. Stretching to a height and narrowing. Optical impression of dematerialization and the approach to God. 2. The pointed arch, which passes through the development of a broad and less broken up to a high return sharply. This ARC is used in Windows, portals and all parts of the building, and ornate in the art craft. According to the shape of the curve can be determined as well as years of inception. 3. The internal support system, which consists of a the Vault bewildered to shaft hanging the ribs in front of the pillars. The weight of the ceiling is so transferred to the narrow lots, which allowed to gradually lighten the walls and fill the large window surfaces. The most highly developed example is the private Royal Chapel Sainte Chapelle in the Conciergerie in Paris, which is known as the Gothic greenhouse. The Vault ribs during the development of the Gothic lost the supporting function and became a decorative element. 4. External support system used in particular for Gothic cathedrals is an auxiliary agent propping up from the outer side of the pillar, which depict the pressure of the vault. It consists of supporting arches and buttressing. 5. The most common decorative elements include the pinnacles (small turrets), which adorned the roof and artistic craft. Another popular feature of the gargoyles were (fantastic head with an open mouth, which spewed water running down from the roof), the last character is called rosettes, decorated with circular window. The first Gothic Cathedral in France: Notre Dame Paris, Notre Dame Cathedral in Reims, in Chartres (the most decorated with sculpture, such as in parts of the portal are placed Saints Cathedral in Chartres – 6 and 6 of the Apostles). For each European Gothic State, at first glance, something distinctive. For Example in Germany, built the building of high quality bricks and is not trimmed in England were ceilings decorated with so called. the network vault, a very complex one, but often only ornamentally. Italian Gothic (the Doge's Palace in Venice) is a special ornament Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 on the façade reminiscent of the particular elements of the Middle East. Czech Gothic reached an excellent level in the world, especially in the field of painting (and sculpture) is valued in the foremost place. MODERN PERIOD (FROM THE YEAR 1492 TILL TODAY) o Renaissance is an artistic style and historical epoch, lasting from the 14th century till 16th century. Characterized by, inter alia, individualism, and a return to the ancient world. It is also closely linked to humanism. The concept of rebirth (rinascenza) was first used for the period of the flowering of the arts and Sciences, which began at the end of 13th century in Italy, the Italian historian Giorgio Vasarim in 1550. The term Renaissance is French translation used the French historian Jules Micheletem and further extended by the Swiss historian Jacob Burckhardtem in the 19th century. With the need for presentation of a new bourgeois nobility and the City State as a whole, has become one of the art architecture, where the most significant changes occurred. Renaissance architects once again inspired by ancient buildings (see classical order of architecture), their symmetry, simplicity and regularity proportions, it is important to also maintain the human dimension of the secular structures. Renaissance architecture is therefore different from the Gothic to its installation environment; the work is no longer a defensive function, but rather representative. There are new types of buildings: the Palace and the city's urban and suburban villas. Next to the stone began to take on a much larger quantities of materials such as marble and bricks. Widely applies to the colonnades, arches and domes and the staircase becomes a separate architectural element. There is a new kind of decoration of the facades called Sgraffito. o Baroque is art-cultural direction, who ruled in Europe between the years 1600 and 1750. Originated in Italy and spread throughout Europe and its colonies. The word Baroque then indicates this period. The early Baroque architecture represent Giacomo della Porta, Jacopo Barozzi da Vignola and Carlo Maderno. The most important baroque architects is a trio of Italians: Architect (also a painter and sculptor) Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Francesco Borromini and Guarino Guarini. These Italian architects of the Summit follows a series of other important Italian and other architects. Especially Pietro da Cortona, Filippo Juvarra, Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach, Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt, Balthasar Neumann, and also branched family Dientzenhoferů, whose two members, a father and a son, Christopher Kilian Ignác, operated mainly in the Czech lands. Another significant architect, active in the Czech lands is Jan Santini. Three in the Czech Republic working architects can then be supplemented by Giovanni Battistu Alliprandiho, which Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 was undoubtedly the ones by the architect than recently wrongly acclaimed František Maxmilián Kaňka. Baroque-the manifestation of monumentality: the effort to impress the man, the emphasis on emotionalism and exaltovanost, internal tension, pathos, exaggeration the churches should act as the image of heaven carried over on the ground, palaces and castles are representative of wealth and power the shape of the ellipse or intersections were ellipses (infinity) a common architectural element: the dome expensive materials: gold, rare wood, colored marbles o Classicism, Romanticism, Empire is art direction, which is inspired mainly by the ancient patterns and stresses a sober reason, moderation and clear, regular order. Originated in France 17. century during the reign of the "Sun King" Louis XIV. as a reaction to an emotional and passionate Baroque and from there it spread to the whole of Europe. This first phase of classicism is sometimes also called the baroque classicism, because here the Baroque elements mixed with elements of the neoclassical. Historically, this term still ranks into the culture of the Baroque. The following is from the Rococo era largely veered away. New onset of classicism (also louis-seize or style of Louis XVI.) brought the Protestant Academy (1419–1622) (josefinismus), when classicism became the style of the Royal courts of enlightenment and the French Revolution, when classicism style became a wealthy burghers. For the next wave of classicism, which brought Napoleon Bonaparte and the Napoleonic wars, the designation of the Empire style is used (from the French empire, the Empire). In the second half of the 19th century neoclassical architecture style became common in the 20th century, and urban construction. She returned several times in the 19th century as an expression of strength and power as well as style dictatorial and totalitarian regimes. For this period from the mid-19th century in the US usually uses the name of neoclassicism, which, of course, in English and French literature often means the same thing as classicism. Most strikingly, the classicism in architecture where the Renaissance architecture and the Palladium. Big impact should be "history of ancient art" j. j. Winckelmann from year 1764, that the ancient art of assorted and theoretically described. Buildings are regular, have direct and clean lines, often a huge portico and triangular Gables and a relatively modest decoration, so austere grandeur and partook of the Act. Builds mainly Palace (e.g. the Louvre or the Černín Palace in Prague) and public buildings (the estates Theatre in Prague), the entire district and the town of damaging environmental impacts (Terezin, Saint Petersburg), but in all of Austria and Emperor Joseph II's churches (e.g. St. Nicholas Church. Cross in Prague Na Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 příkopě), barracks and the first factories and apartment buildings. From the second half of the 19th century in neoclassical style puts the entire schematic residential area of big cities (a big part of Paris, Vienna, Budapest, Prague, Smíchov, Vinohrady, Karlin, Žižkov, the centre of Brno and most Czech cities), a number of schools, town halls, Court and other public buildings (the National Theatre in Prague). Another typical example of neoclassical architecture are the French parks and gardens with a strictly geometrical plan, a symmetric system of roads, houses and alleys where there are cut out shrubs and trees into geometric shapes. The examples in the Czech Republic are the flower garden in Kroměříž, fridge, Dobříš Chateau, Veltrusy or the beautiful courtyard. Romanticism is an artistic and philosophical direction and the position of the Euro-American culture of the end of the 18. century and the beginning of the 19th century. of the century. The basic rocks of romanticism are feeling, individuality (and individual experience) and soul (in particular the torment of the soul). Romanticism was formed as a response to the monopoly of reason in the philosophy of the Enlightenment, the starkness of the antiquity inspired classicism. The default suggestions looking for in the past (mainly in the middle ages) and in exotic countries. Against the enlightenment sense puts the romanticism often irrational feelings, against the desire to know and to recognize the desire to relive and experience against a known and clear the mystery and secrets against the rationality of the imagination. Protestant optimism gave way to despair, helplessness and progress commitment to (also in vain) of the victim. These characteristics are typical especially for romantic art (art, music), but also the position. The term romanticism was derived from the words of the novel, therefore, from the literary genre, which in the 18th century began to frequently include psychological (a sentimental novel) or the mystical (gothic novel) elements. Definition of romanticism: "who says the romanticism, modern art, says, it is intimacy, spirituality, color, longing for infinity, expressed by all means by which art reigns"-Charles Baudelaire The romantic architecture is fundamentally influenced by this period focus on the nostalgic past. Architects in his work inspired by the architecture of other historical eras, or other cultures. Romantic architecture as the original style, there is virtually no specific form is then given to the style, from which the structure is based on. The most common style, which used to be the first and the most imitated the Gothic, such construction or building modifications refer to as neo-Gothic. Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Empire [em] or empir [ampír] [1] [2] (from the French empire, Empire), also called the Imperial style, means the period of classicism (neoclassicism, respectively), which has spread from France at the beginning of the 19. century, during the reign of Napoleon Bonaparte. Style especially in architecture and in the design of clothing, furniture and various objects of art and in Central Europe, there was throughout the first half of the 19th century. of the century. It plays in the architecture of the romanticism (historical styles of the period), and in the town of households including furniture biedermaier. Castle Fryštát (Karviná) Castle Kostelec nad Orlicí Castle Hnojník Castle Starý Rybník Castle Kačina church the Holy Cross (Praha) Rental homes in Prague: Platýz (Národní třída), homes in Karlin, in the Smichov district, etc. Masaryk station Chain bridge at Stádlce o Historicism the art, in particular the architectural direction 2. mid-19th century in imitation of the older styles o building in 20th Century The architecture of the 20th century does not have a consistent style of individual styles and styles often do not respond and are so different that there are between the architectural currents points. For the entire 20th century is typical of the work with new materials (steel, glass), which due to its characteristics allow you to search for new solutions. Very popular was constructivism, modernism and then Postmodernism later. In the Socialist bloc, the so-called developed. socialist realism, manifested in the architecture. The specific type of architecture is the Nazi architecture developed in particular in the 1930 's. and 40. years in the Third Reich and Italy [source?]. For 20th century is typical of the use of right angles that allow you to more efficiently use the space. o the current building The Source Of The www.wikipedie.cz, www.wikipedia.org Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015 Recommended literature: Galindo, Michelle. European architecture. Praha: Slovart, 2009. 512 pgs. Wilfried Koch. A Handbook of European Architectural Styles. 1980. 159 pgs. Emily Cole. The Grammar of Architecture. Bulfinch Press, 2002. 352 pgs. Emily Cole. A Concise History of Architectural Styles. A. & C. Black, 2003. 352 pgs. Kenneth Frampton. Modern Architecture: A Critical History. Thames & Hudson, 2007. 424 pgs. Harry Francis Mallgrave. Architectural Theory: An Anthology from Vitruvius to 1870. Wiley, 2006. 590 pgs. Meiss, Pierre von. Elements of architecture. Abingdon: E & FN Spon, 1990. www.wikipedia.org Ing. arch. Klára Frolíková Palánová, Ph. D. 3. 9. 2015