Curriculum Overview for Year X
advertisement
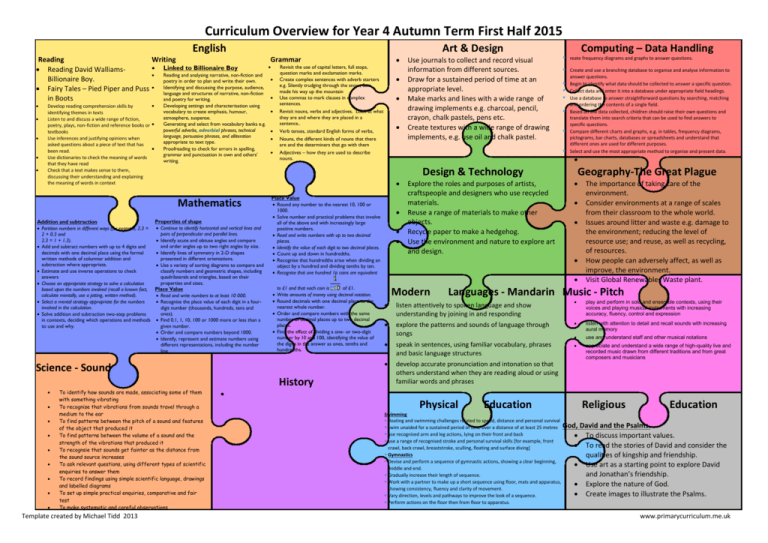
Curriculum Overview for Year 4 Autumn Term First Half 2015 English Art & Design Reading Writing Grammar Revisit the use of capital letters, full stops, Linked to Billionaire Boy Reading David Walliamsquestion marks and exclamation marks. Reading and analysing narrative, non-fiction and Create complex sentences with adverb starters Billionaire Boy. poetry in order to plan and write their own. e.g. Silently trudging through the snow, Sam Fairy Tales – Pied Piper and Puss Identifying and discussing the purpose, audience, made his way up the mountain language and structures of narrative, non-fiction Use commas to mark clauses in complex in Boots and poetry for writing. Develop reading comprehension skills by identifying themes in texts Listen to and discuss a wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks Use inferences and justifying opinions when asked questions about a piece of text that has been read. Use dictionaries to check the meaning of words that they have read Check that a text makes sense to them, discussing their understanding and explaining the meaning of words in context Developing settings and characterisation using vocabulary to create emphasis, humour, atmosphere, suspense. Generating and select from vocabulary banks e.g. powerful adverbs, adverbial phrases, technical language, persuasive phrases, and alliteration appropriate to text type. Proofreading to check for errors in spelling, grammar and punctuation in own and others’ writing. to £1 and that each coin is of £1. Write amounts of money using decimal notation. Round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number. Order and compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up to two decimal places. Find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths. History To identify how sounds are made, associating some of them with something vibrating To recognise that vibrations from sounds travel through a medium to the ear To find patterns between the pitch of a sound and features of the object that produced it To find patterns between the volume of a sound and the strength of the vibrations that produced it To recognsie that sounds get fainter as the distance from the sound source increases To ask relevant questions, using different types of scientific enquiries to answer them To record findings using simple scientific language, drawings and labelled diagrams To set up simple practical enquiries, comparative and fair test To make systematic and careful observations Template created by Michael Tidd 2013 answer questions. Begin to identify what data should be collected to answer a specific question. Collect data and enter it into a database under appropriate field headings. Use a database to answer straightforward questions by searching, matching and ordering the contents of a single field. Based on the data collected, children should raise their own questions and translate them into search criteria that can be used to find answers to specific questions. Compare different charts and graphs, e.g. in tables, frequency diagrams, pictograms, bar charts, databases or spreadsheets and understand that different ones are used for different purposes. Select and use the most appropriate method to organise and present data. Place Value Round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000. Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and with increasingly large positive numbers. Read and write numbers with up to two decimal places. Identify the value of each digit to two decimal places. Count up and down in hundredths. Recognise that hundredths arise when dividing an object by a hundred and dividing tenths by ten. Recognise that one hundred 1p coins are equivalent Science - Sound Properties of shape Addition and subtraction Partition numbers in different ways (for example, 2.3 = Continue to identify horizontal and vertical lines and pairs of perpendicular and parallel lines. 2 + 0.3 and 2.3 = 1 + 1.3). Identify acute and obtuse angles and compare and order angles up to two right angles by size. Add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits and decimals with one decimal place using the formal Identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes written methods of columnar addition and presented in different orientations. subtraction where appropriate. Use a variety of sorting diagrams to compare and Estimate and use inverse operations to check classify numbers and geometric shapes, including answers quadrilaterals and triangles, based on their properties and sizes. Choose an appropriate strategy to solve a calculation based upon the numbers involved (recall a known fact, Place Value calculate mentally, use a jotting, written method). Read and write numbers to at least 10 000. Select a mental strategy appropriate for the numbers Recognise the place value of each digit in a fourinvolved in the calculation. digit number (thousands, hundreds, tens and ones). Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods Find 0.1, 1, 10, 100 or 1000 more or less than a to use and why. given number. Order and compare numbers beyond 1000. Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations, including the number line. sentences. Revisit nouns, verbs and adjectives. Look at what they are and where they are placed in a sentence.. Verb tenses, standard English forms of verbs, Nouns, the different kinds of nouns that there are and the determiners that go with them Adjectives – how they are used to describe nouns. Create and use a branching database to organise and analyse information to Design & Technology Mathematics Use journals to collect and record visual information from different sources. Draw for a sustained period of time at an appropriate level. Make marks and lines with a wide range of drawing implements e.g. charcoal, pencil, crayon, chalk pastels, pens etc. Create textures with a wide range of drawing implements, e.g. use oil and chalk pastel. Computing – Data Handling reate frequency diagrams and graphs to answer questions. Explore the roles and purposes of artists, craftspeople and designers who use recycled materials. Reuse a range of materials to make other objects. Recycle paper to make a hedgehog. Use the environment and nature to explore art and design. Geography-The Great Plague Modern The importance of taking care of the environment. Consider environments at a range of scales from their classroom to the whole world. Issues around litter and waste e.g. damage to the environment; reducing the level of resource use; and reuse, as well as recycling, of resources. How people can adversely affect, as well as improve, the environment. Visit Global Renewables Waste plant. Languages - Mandarin Music - Pitch play and perform in solo and ensemble contexts, using their voices and playing musical instruments with increasing accuracy, fluency, control and expression explore the patterns and sounds of language through songs listen with attention to detail and recall sounds with increasing aural memory use and understand staff and other musical notations speak in sentences, using familiar vocabulary, phrases and basic language structures appreciate and understand a wide range of high-quality live and recorded music drawn from different traditions and from great composers and musicians develop accurate pronunciation and intonation so that others understand when they are reading aloud or using familiar words and phrases listen attentively to spoken language and show understanding by joining in and responding Physical Education Swimming floating and swimming challenges related to speed, distance and personal survival swim unaided for a sustained period of time over a distance of at least 25 metres God, use recognised arm and leg actions, lying on their front and back use a range of recognised stroke and personal survival skills [for example, front crawl, back crawl, breaststroke, sculling, floating and surface diving] Gymnastics Devise and perform a sequence of gymnastic actions, showing a clear beginning, middle and end. Gradually increase their length of sequence. Work with a partner to make up a short sequence using floor, mats and apparatus, showing consistency, fluency and clarity of movement. Vary direction, levels and pathways to improve the look of a sequence. Perform actions on the floor then from floor to apparatus. Religious Education David and the Psalms. To discuss important values. To read the stories of David and consider the qualities of kingship and friendship. Use art as a starting point to explore David and Jonathan’s friendship. Explore the nature of God. Create images to illustrate the Psalms. www.primarycurriculum.me.uk To use results to draw simple conclusions Template created by Michael Tidd 2013 www.primarycurriculum.me.uk