Syllabus Earth Science
advertisement
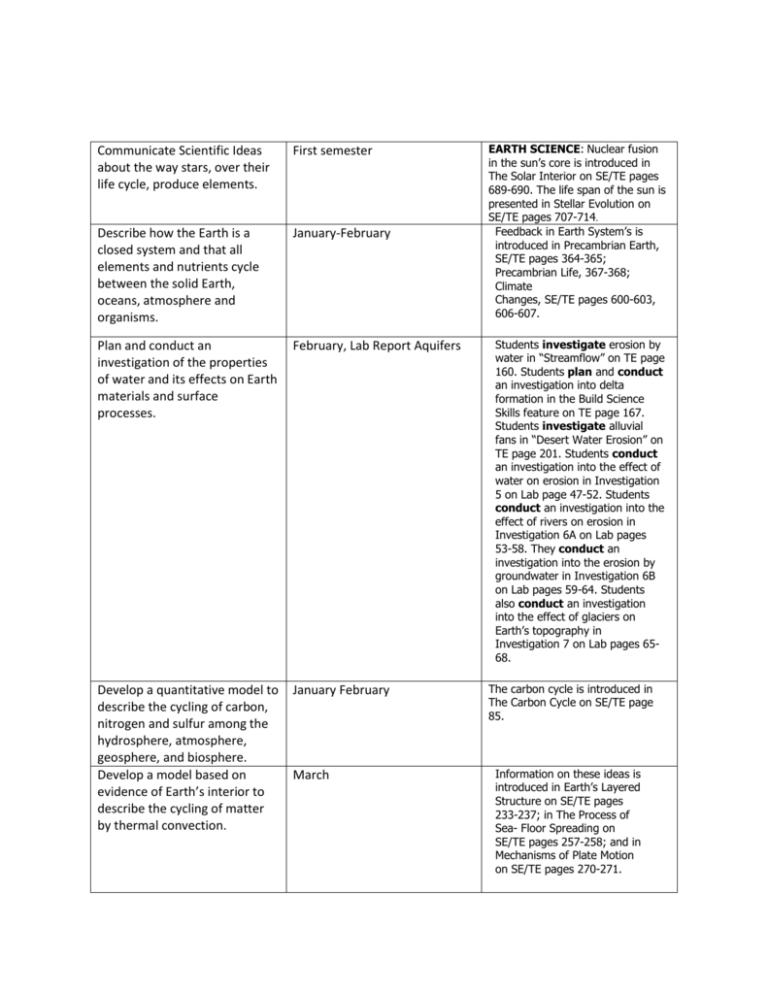
Communicate Scientific Ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. First semester Describe how the Earth is a closed system and that all elements and nutrients cycle between the solid Earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms. January-February Plan and conduct an investigation of the properties of water and its effects on Earth materials and surface processes. February, Lab Report Aquifers Develop a quantitative model to describe the cycling of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur among the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere. Develop a model based on evidence of Earth’s interior to describe the cycling of matter by thermal convection. January February March EARTH SCIENCE: Nuclear fusion in the sun’s core is introduced in The Solar Interior on SE/TE pages 689-690. The life span of the sun is presented in Stellar Evolution on SE/TE pages 707-714. Feedback in Earth System’s is introduced in Precambrian Earth, SE/TE pages 364-365; Precambrian Life, 367-368; Climate Changes, SE/TE pages 600-603, 606-607. Students investigate erosion by water in “Streamflow” on TE page 160. Students plan and conduct an investigation into delta formation in the Build Science Skills feature on TE page 167. Students investigate alluvial fans in “Desert Water Erosion” on TE page 201. Students conduct an investigation into the effect of water on erosion in Investigation 5 on Lab page 47-52. Students conduct an investigation into the effect of rivers on erosion in Investigation 6A on Lab pages 53-58. They conduct an investigation into the erosion by groundwater in Investigation 6B on Lab pages 59-64. Students also conduct an investigation into the effect of glaciers on Earth’s topography in Investigation 7 on Lab pages 6568. The carbon cycle is introduced in The Carbon Cycle on SE/TE page 85. Information on these ideas is introduced in Earth’s Layered Structure on SE/TE pages 233-237; in The Process of Sea- Floor Spreading on SE/TE pages 257-258; and in Mechanisms of Plate Motion on SE/TE pages 270-271. Assess major environmental problems caused by human actions. April-May Information about the impact of human activities on natural systems is introduced in Protecting Resources on SE/TE pages 113-117. Evaluate or refine a technological solution that reduces impacts of human activities on natural systems. April-May Information about a possible solution that could be simulated with computers is introduced in Climate Changes on SE/TE pages 600-603 and 606-607. Use a computational representation to illustrate the relationships among Earth systems and how those relationships are being modified due to human activity. April-May Information about real-world based problems relating to energy production and conservation is introduced in Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources on SE/TE pages 9495; in Fossil Fuels on SE/TE pages 95-96; in Tar Sands and Shale on SE/TE pages 97-98; and in Alternate Energy Sources on SE/TE pages 102-107. Create a computational simulation to illustrate the relationships among management of natural resources, the sustainability of human populations, and biodiversity. April-May Computational representation of the relationships among Earth systems and how these relationships are being modified due to human activity are introduced in Climate Changes on SE/TE pages 600-603 and 606-607.