Supplementary Information “What can genome
advertisement

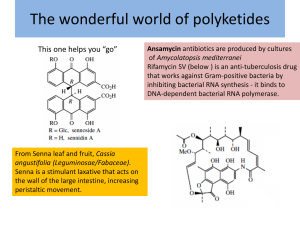
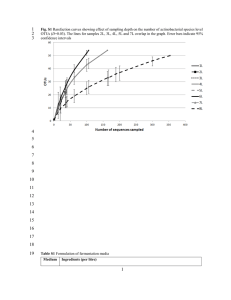
Supplementary Information “What can genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions do for prokaryotic systematics?” BISMiS Special issue, AVL Francisco Barona-Gómez*, Pablo Cruz-Morales and Lianet Noda-García Supplementary methods. RpoB-based actinobacterial species-tree (Figures 3 and 4). The sequences of genes encoding for RpoB were retrieved using BLAST (Altschul et al. 1997). The sequence alignment was performed with ClustalX (Thompson et al. 1994) using the default parameters, and then edited manually with the Jalview alignment editor (Waterhouse et al. 2009). The phylogenetic tree was constructed with MrBayes (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist 2001), using the WAG amino acid substitution model, four substitution rate categories, and estimating the topology, branch lengths, rate parameters, the proportion of invariable sites, and the Gamma distribution parameter. Two runs were performed for one million generations, the runs were sampled every 100 generations, 25 % of the trees obtained were “burned” and the rest used to obtain the final tree. Search of enzyme homologs and statistical treatment For the comparison of in silico reconstructions of the central metabolic pathways (Figure 4), amino acid sequences reported in the GSMR of S. coelicolor (Borodina et al. 2005), M. tuberculosis (Jamshidi and Palsson 2007) and C. glutamicum (Kjeldsen and Nielsen 2009) were used as queries (Supplementary Table S2). The amino acid sequences from C. glutamicum (Kjeldsen and Nielsen 2009) or S. coelicolor (Hiratsuka et al. 2008) were used as queries for the search of menaquinone biosynthetic enzymes and cardiolipin synthases homologs (Figure 3), as these were missing genes not included in the original GSMRs. For short sequences, less than 100 amino acids, a score cut-off equal or superior to 100 was used. Pathways were curated manually when necessary. These searches were done through automated BLAST searches (Altschul et al. 1997) in a actinobacterial genomes database including the 101 organisms shown in figures 3 and 4. The hits were considered as homologs of a query when the score was equal or superior to 150. For each query reaction in the metabolic reconstruction, the media (µ) and standard deviation (σ) of the number of homologs (HN) found among genomes in the database was calculated. Enzymatic expansions were defined as HN=> µ + σ. Supplementary Tables. Table S1. Central Metabolic Pathways analysed. Pathway Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate Pathway Citric acid cycle Amino acids from AKG Amino acids from THR and PYR Amino acids from Oxalacetate Amino acids from 3PGA Amino acids from R5P Amino acids from E4P and PEP Total Products Pyruvate, PhosphoenolPyruvate and ATP Fructose, E-4 Phosphate, Ribose 5-P Acetyl CoA, oxalacetate, αKetoglutarate Glu, Gln, Pro, Arg Steps Complexes Querys 10 0 49 8 0 38 8 13 3 1 94 50 Ala,Ile, Leu, Val 14 2 42 Asp, Asn, Thr, Met, Lys Gly, Ser, Cys His 18 6 10 0 0 1 64 25 37 Tyr, Phe, Trp 37 17 104 2 9 56 455 Table S2. Comparative analysis of cardiolipin and menaquinone biosynthesis in Actinobacteria. PATHWAY STEP Bifidobacterium_animalislactisADO11 Bifidobacterium_longumDJO10A Bifidobacterium_adolescentisATC15703 Tropheryma_whipplei Tropheryma_whippleiTwist Leifsonia_xyli_xyliCTCB07 Clavibacter_michiganensis Brevibacterium_linensBL2 Renibacterium_salmoninarumATCC33209 Arthrobacter_chlorophenolicusA6 Arthrobacter_aurescensTC1 Kocuria_rhizophilaDC2201 Arthrobacter_arilaitensisRe117 Micrococcus_luteusNCTC2665 Citricoccus_CH26A Kineococcus_radiotoleransSRS30216 Janibacter_HTCC2649 Propionebacterium_acnesKPA171202 Nocardioides_JS614 Catenulispora_acidiphilaDSM44928 Kitasatospora_setaeKM-6054 Streptomyces_hygroscopicusATCC53653 Streptomyces_violaceusnigerTu4113 Streptomyces_bingchenggensis Streptomyces_clavuligerusATCC27064 Streptomyces_pristinaespiralisATCC25486 Streptomyces_flavogriseusATCC33331 Streptomyces_spACTE Streptomyces_roseosporusNRRL15998 Streptomyces_roseosporusNRRL11379 Streptomyces_griseus Streptomyces_griseusXylebKG-1 Streptomyces_spACT1 Streptomyces_venezuelaeATCC10712 Streptomyces_spMG1 Streptomyces_spC Streptomyces_griseoflavusTu4000 Streptomyces_coelicolorM145 Streptomyces_lividansTK24 Streptomyces_liv1326 Streptomyces_albus Streptomyces_spSPB74 Streptomyces_spSA3actG Streptomyces_spTU6071 Streptomyces_spSPB78 Streptomyces_avermitilis Streptomyces_sviceusATCC29083 Streptomyces_scabiei Streptomyces_viridochromogenesDSM40736 Streptomyces_ghanaensis Streptomyces_spE14 Streptomyces_griseoauratiacus Streptosporangium_roseumDSM43021 Acydothermus_cellulolyticus11B Thermomonospora_curvataDSM43183 Frankia_alniACN14a Frankia_EAN1pec Frankia_SPCcI3 Salinispora_tropica Salinispora_arenicola Verrucosispora_marisAB1803 Micromonospora_carbonacea Micromonospora_aurantiacaATCC27029 Micromonospora_spM42 Micromonospora_spL5 Saccharopolyspora_erythraea Saccharomonospora_viridisDSM43017 Streptomyces_spAA4 Amycolatopsis_mediterraneiU32 Corynebacterium_amycolatum_SK46 Corynebacterium_kroppenstedtiiDSM44385 Corynebacterium_urealyticumDSM7109 Corynebacterium_jeikeniumK411 Corynebacterium_jeikeiumATCC43734 Corynebacterium_glucuronolyticumATCC51867 Corynebacterium_diphteriae Corynebacterium_striatumATCC6940 Corynebacterium_accolensATCC49725 Corynebacterium_efficiensYS314 Corynebacterium_glutamicumR Corynebacterium_glutamicumATCC13032 Nocardia_farcinicaIFM10152 Rhodococcus_equiATCC33707 Rhodococcus_opacusB4 Rhodococcus_jostiiRHA1 Rhodococcus_erythropolisSK121 Rhodococcus_erythropolisPR4 Mycobacterium_vanbaaleniiPYR1 Mycobacterium_gilvumPYRGCK Mycobacterium_smegmatisMC2155 Mycobacterium_spJLS Mycobacterium_spMCS Mycobacterium_spKMS Mycobacterium_ulceransAgy99 Mycobacterium_marinumM Mycobacterium_kansasii12478 Mycobacterium_parascrofulaceumATCCBAA614 Mycobacterium_avium104 Mycobacterium_leprae Mycobacterium_tuberculosisCDC1551 Mycobacterium_bovisAF212297 Chorismate biosynthetic pathway Futalosine biosynthetic pathway MenA MenB MenC MenD MenE MenF MenG MenH MqnA 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 MqnB 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 MqnC 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 MqnD 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 CL Synthase MK Type 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H6 and H8) (1) MK-9 (H4) (a) (1) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) MK-8 (H2) (2) Eukaryotic 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Prokaryotic 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 2 1 1 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 The colours are indicative of: yellow, one ortholog was detected; orange, two or more orthologs were detected; white or cero, not detected. The MK type data was obteined from (Collins et al. 1977; Collins et al. 1985). Supplementary References Altschul, S. F., T. L. Madden, A. A. Schaffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller and D. J. Lipman (1997). "Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs." Nucleic Acids Res 25(17): 3389-3402. Borodina, I., P. Krabben and J. Nielsen (2005). "Genome-scale analysis of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) metabolism." Genome Res 15(6): 820-829. Collins, M. D., M. Goodfellow, D. E. Minnikin and G. Alderson (1985). "Menaquinone composition of mycolic acid-containing actinomycetes and some sporoactinomycetes." J Appl Bacteriol 58(1): 77-86. Collins, M. D., T. Pirouz, M. Goodfellow and D. E. Minnikin (1977). "Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria." J Gen Microbiol 100(2): 221230. Hiratsuka, T., K. Furihata, J. Ishikawa, H. Yamashita, N. Itoh, H. Seto and T. Dairi (2008). "An alternative menaquinone biosynthetic pathway operating in microorganisms." Science 321(5896): 1670-1673. Huelsenbeck, J. P. and F. Ronquist (2001). "MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees." Bioinformatics 17(8): 754-755. Jamshidi, N. and B. O. Palsson (2007). "Investigating the metabolic capabilities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv using the in silico strain iNJ661 and proposing alternative drug targets." BMC Syst Biol 1: 26. Kjeldsen, K. R. and J. Nielsen (2009). "In silico genome-scale reconstruction and validation of the Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolic network." Biotechnol Bioeng 102(2): 583-597. Thompson, J. D., D. G. Higgins and T. J. Gibson (1994). "CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice." Nucleic Acids Res 22(22): 4673-4680. Waterhouse, A. M., J. B. Procter, D. M. Martin, M. Clamp and G. J. Barton (2009). "Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench." Bioinformatics 25(9): 1189-1191.