Name_______________________________ HW

Name_______________________________ HW-2b Due Date____________ Period______
1. What is the speed of all forms of electromagnetic radiation? 3.00 x 10 8 m/s
2. List all forms of electromagnetic radiation according to increasing frequency:_________________________________
Radio / microwaves / infrared / visible light / ultraviolet / x-rays / gamma rays_________________________________
3. List the colors of light in the visible spectrum according to increasing energy:__________________________________
Red / orange / yellow / green / blue / violet______________________________________________________________
4. Which theory of light, the wave or particle theory, best explains the following phenomena? a. the interference of light?________wave_______ b. the photoelectric effect?_______particle________ c. The emission of electromagnetic radiation by an excited atom?_________particle________
5. Distinguish between the ground state and an excited state of an atom: The ground state of an atom is the atom’s
lowest energy state. An excited state of an atom is any energy state that is higher in
energy than the atom’s ground state.
6. According to Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, how is hydrogen’s emission spectrum produced?According to Bohr,
a line-emission spectrum is produced when an electron drops from a higher-energy orbit
to a lower-energy orbit, emitting a photon. The photon’s energy is equal to the difference
in energy between the two levels.
7. Solve for the frequency of light whose wave length is 4.257 x 10 -7 cm._________7.05 x 10 16 Hz__________________
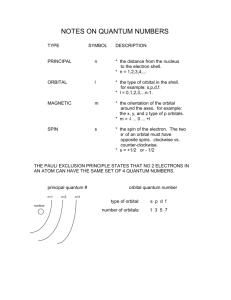
8-9. a. What is the principle quantum number?_# used to specify the main energy level of an atom b. How is it symbolized?___n______ c. What are shells?_all orbitals within the same main energy level_____________________________________ d. How does n relate to the number of electrons allowed per main energy level?______2n 2 ______________
10. a. What information is given by the angular momentum quantum number?___orbital shape_____________ b. What are sublevels, or subshells?___all orbitals associated with a value of l___________________________
11. a. What information is given by the magnetic quantum?_____orientation of orbital around the nucleus_______ b. What many orbital orientations are possible in each of the sublevels? s_1_ p__3_ d__5_ f__7_
12. a. What information is given by the spin quantum number?___spin state of an electron in an orbital
b. What are the possible values for this quantum number?_____+1/2 -1/2
s = p =
13. a. Sketch the shape of an s orbital and a p orbital. b. How does a 2s orbital differ from a 1s orbital? It is higher in energy and extends further from the nucleus. c. How do a 2p x
and a 2p y
orbital differ?__They have a different orientation in space around the nucleus____________
14-15. a. In your own words, state the Aufbau principle. electrons fill orbitals starting at the lowest available (possible) energy states before filling higher states b. State Hund’s rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electrons. c. State the Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can have the same four quantum numbers.
Therefore two electrons in the same orbital with have opposite spins. d. What is the significance of the spin quantum number? It allows two electrons with opposite spin values to occupy the same orbital.
16. Determine the highest occupied energy level in the following elements.
He__1__ Be__2___ Al__3___ Ca___4__ Sn___5___
17. Write the orbital notation for the following elements:
F Na
18-19. Write both the complete electron-configuration notation and the noble-gas notation for each of the elements: a. Na 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 [Ne] 3s 1 b. Sr 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 5s 2 [Kr] 5s 2 c. Cu 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 3d 10 [Ar] 4s 1 3d 10
20-21. Identify each of the following atoms on the basis of its electron configuration: a. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5 F c. [Ne] 3s 2 3p 5 Cl b. [Ar] 4s 1 K d. [Ar] 4s 2 3d 6 Fe
22. Draw a chart showing the electron orbital filling order.
23-24. Write the short-hand (noble gas) notation for the electron configurations of each of the following elements: a. As [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 3 b. Pb [Xe] 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2 c. La [Xe] 6s 2 4f 1 d. Lr [Rn] 7s 2 5f 14 6d 1
25. How do the electron configurations of chromium and copper contradict the Aufbau principle?In chromium, each 3d orbital gets 1 electron before 4s gets two & in copper, each 3d orbital gets two electrons before 4s gets two.
26-28. a. Write the electron configuration for phosphorus: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3 b. How many electrons are in each atom? 15 c. What is the atomic number of this element? 15 d. Write the orbital notation for this element: e. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of phosphorus have? 3 f. What is its highest occupied energy level? 3 g. How many inner-shell electrons does the atom contain? 10 h. In which orbital(s) are these inner-shell electrons located? 1s 2s 2p x
2p y
2p z
_c._3__29. What is the maximum number of unpaired electrons that can be placed in a 3p sublevel? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
30. (Refer to the “photoelectric effect” in you book [p.99]) When blue light shines on potassium metal in a photocell, electrons are emitted. But when yellow light shines on the metal, no current is observed. Explain:
Photons of blue light are higher in energy than photons of yellow light. Electrons can be emitted only when a photon of sufficient energy strikes the surface of the metal. Therefore, the energy of blue light is greater than the threshold energy, but the energy of yellow light is not.