Earth Science - WHS
advertisement

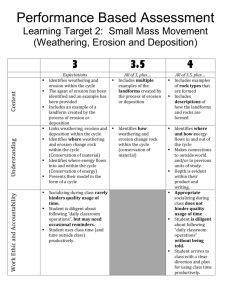
Wareham High School Science Curriculum Course Name: Earth Science Unit: 1 Introduction to Earth Science Learning Standard(s): Scientific Inquiry Skills 1-4 ES: Energy Resources in the Earth System 2.1, 2.2 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Earth is a System composed up of many layers containing many features. Essential Questions: 1. How does the earth’s interior drive/influence the features on its exterior? 2. Explain how the earth is composed up of a array of subsystems. Content: Scientific Method, Earth’s Spheres, Geosphere structures, Major/Minor Features on Earth’s Surface, Earth as a System Learning Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources and give examples. 2. Distinguish between the geosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. 3. Identify the layers of the earth’s interior. 4. Describe the features found on the continents and the ocean floor in terms of topographic units. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 2 Physical Geology: Minerals and Rocks Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.2, 3.6 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Earth is comprised up elements which form minerals and rocks Essential Questions: 1. How does the Rock Cycle work? 2. Why is the type of bond formed between elements important? 3. How can isotopes be used in radioactive dating? Content: Chemistry recap, Mineral Properties, Mineral Groups, Mineral Resources, Rock Cycle, Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks, Carbon Cycle, Metamorphic Rocks Learning Objectives: 1. Describe the Rock Cycle and the processes responsible for forming igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. 2. Compare the physical properties of rockforming minerals. 3. Compare the physical properties of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. 4. Define the criteria for a mineral. 5. Explain the difference between ionic and covalent bonding. 6. Describe what isotopes are and how they are used in radioactive decay. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 3 Sculpturing Earth’s Surface Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.1 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Weathering, Erosion and Deposition continuously alter and shape the earth’s surface Essential Questions: 1. How does mass wasting sculpt the earth’s surface? 2. Explain how chemical weathering alters materials at the earth’s surface. Content: Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, Mass Wasting, Soil Formation Learning Objectives: 1. Describe the difference between weathering, erosion, and deposition. 2. Distinguish between forces of mechanical weathering and chemical weathering. 3. Explain the process by which soil forms. 4. Identify types of mass wasting and explain how they impact the earth’s surface. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 4 Agents of Erosion: Running Water and Groundwater Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.1, 3.4, 3.5, Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Water is an active agent of erosion that constantly reshapes the earth’s surface. Essential Questions: 1. How does porosity, permeability, aquitards and aquifers influence groundwater. 2. What conditions would create karst topography? 3. What importance does deltas have? Content: Water Cycle, Running Water, Depositional features from Running water, Groundwater, Factors that influence storage/movement of groundwater, karst topography Learning Objectives: 1. Explain how running water and groundwater reshape the earth’s surface. 2. Describe how streams/rivers transport sediments. 3. Explain how oxbow lakes form. 4. Describe the importance of levees, deltas, and alluvial fans. 5. Identify ways man has tried to prevent erosion by running water. 6. Describe what karst topography is and how it forms. 7. Explain the difference between springs and wells. 8. Explain some current environmental problems involving groundwater. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 4 Agents of Erosion: Glaciers, Deserts, and Wind Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.1 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Glacial and Wind erosion alter the shape of the earth’s landscape. Essential Questions: 1. How can glaciation erode alter and reshape the surface of the earth? 2. What type of wind erosional features can be seen in the Dust Bowl of the 1930s? Content: Glacial types, Glacial erosion, Glacial features, Causes of glaciation, Arid landscapes, Wind Erosion, Wind created features, Learning Objectives: 1. Distinguish between Alpine and Continental Glaciers. 2. Explain how glaciation happens. 3. Discuss how glaciers move. 4. Identify types of glacial features caused by erosion. 5. Identify types of glacial features caused by deposition. 6. Explain how running water does the most erosional work in arid areas. 7. Contrast alluvial fans, bajada, playa, and inselbergs. 8. Identify types of wind erosional features. 9. Identify types of wind depositional features. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 5 Plate Tectonics Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Lithospheric plates continuously move reshaping the Earth’s surface. Essential Questions: 1. What is Plate Tectonics and the mechanisms for which plates move? 2. How can seismology be used to determine epicenters and to predict earthquakes? 3. How does plate tectonics relate to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building? Content: Pangea and Continental Drift Theory, Plate Tectonics, Plate Boundaries, Earthquakes, mountain building, and volcanoes Learning Objectives: 1. Explain Continental Drift Theory and the evidenced used to support it. 2. Describe the Theory of Plate Tectonics and contrast the different types of plate boundaries. 3. Discuss the forces that drive plate motion. 4. Explain seismology and its use in studying earthquakes. 5. Determine the epicenter of an earthquake. 6. Summarize the type of damage caused by earthquakes. 7. Discuss the factors that can trigger volcanic eruptions. 8. Identify the anatomy of a volcano. 9. Contrast the different types of volcanoes. 10. Distinguish between sills, laccoliths, dikes, batholiths, and monoliths. 11. Describe the Pacific Ring of Fire and it’s importance. 12. Identify the hazards of living in an earthquake/volcanic prone area. 13. Discuss the process of mountain building. 14. Identify the types of folds and faults by using USGS maps and aerial footage. 15. Contrast mountain building in subduction zones. 16. Define isostasy and its role in mountain building. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 6 Deciphering Earth’s History Learning Standard(s): ES: Earth Processes and Cycles 3.7 ES: Matter and Energy 1.1, 1.8 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Earth’s landscapes have been altered many times over many years. Essential Questions: 1. How is relative dating used to date the age of the earth? 2. What is radioactive dating and how does it help with aging the earth? Content: History of Geology, Relative Dating, Fossils, Radioactivity, Geological Time Scale Learning Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between relative dating and radioactive dating. 2. Determine the course of events by using principles of relative dating. 3. Contrast the different types of fossils and explain how fossils are used in correlation. 4. Discuss radioactive dating in terms of radioactive decay (half-lives) and its importance. 5. Identify the blocks of time can organized in large chunks of time called eons all the way to smaller portions of time called epochs. 6. Apply information from the geological time scale in regards to major events in Earth’s history. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 7 Introduction To Oceanography Learning Standard(s): ES: Matter and Energy 1.3, 1.5, 1.7, 1.8 ES: Origin and Evolution of Universe 4.2 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Oceans play a large role in shaping the earth’s surface. Essential Questions: 1. How does wave erosion alter the shape of the coastlines? 2. What adaptations are seen in marine life found in various marine environments? 3. How has human altered the shape of the coastlines? 4. What challenges are encountered when harvesting resources from the seafloor? Content: Features of the oceanfloor, Seafloor sediments, Resources from the Ocean, Seawater composition/properties, Marine Life Zones and Environments, Surface Circulation, Wave Erosion and Depositional features, Human influences on coastlines, Tides Learning Objectives: 1. Identify the types of features found on the seafloor. 2. Describe the difference between an emergent coastline and a submergent coastline. 3. Discuss how wave erosion alters the coastline. 4. Evaluate how humans have changed the coastlines. 5. Articulate the adaptations found in marine life based upon their marine environment. 6. Describe composition of seawater and how this can alter the diversity of life in all depths of the ocean. 7. Discuss ocean productivity and its relationship to marine food webs. 8. Explain ocean circulation and the forces that drive currents and waves. 9. Identify the anatomy of a wave. 10. Explain how tides form and contrast the different types of tidal patterns seen around the world. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 8 Introduction to Meteorology Learning Standard(s): ES: Matter and Energy 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.8 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Atmosphere plays a part in shaping the Earth’s surface. Essential Questions: 1. Content: Atmospheric composition, Earth-Sun relationships, Heat Transfer, Solar Radiation, Humidity, Stability of Air, Cloud formation, Air Pressure, Wind, Local/Global Wind patterns, Weather Patterns and Storms, Climate Change Learning Objectives: 1. Describe the composition of the atmosphere and how this plays a part in weather. 2. Discuss the difference between rotation and revolution and how season vary. 3. Contrast the mechanisms for heat transfer and how this relates to weather. 4. Discuss Solar radiation and its effect on climate. 5. Describe how changes in humidity can alter the pressure and or temperature of the air. 6. Explain how fog and clouds form. 7. Describe how air pressure creates wind. 8. Contrast local winds to global wind patterns. 9. Describe air masses and explain the type of weather associated with certain air masses. 10. Discuss how thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes form and their impact on the earth’s surface. 11. Describe how the world’s climate is classified and identify different types of biomes. 12. Explain how climate change is altering the surface of the earth. 13. Discuss the roles humans have in climate change. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials Unit: 9 Introduction to Astronomy Learning Standard(s): ES: Origin and Evolution of Universe 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Entire universe is driven by energy: gravity and electromagnetism. Essential Questions: 1. How does mass wasting sculpt the earth’s surface? 2. Explain how chemical weathering alters materials at the earth’s surface. Content: History of Astronomy, Earth-Moon Relationship, Eclipses, Phases of the Moon, Formation of the Planets, Doppler Effect, Red/Blue Shifts, EMS, Anatomy of the Sun, Stellar Evolution Learning Objectives: 1. Compare and contrast the different types of models used in early astronomy. 2. Discuss the importance of Kepler, Copernicus, Galileo, and Newton to modern astronomy. 3. Describe the how day/night and seasons are created. 4. Identify the phases of the moon and relate this to tides. 5. Explain the nebular theory and the Big Bang theory in regards to the formation of the universe. 6. Identify features of the solar system. 7. Describe the Doppler Effect and how this is used to identify whether an open or closed universe exists. 8. Describe the EMS and how equipment used in astronomy uses the EMS. 9. Identify the anatomy of the sun and solar storms and relate this to incidents on Earth. 10. Describe how a stellar parallax is used and explain why it isn’t used on extremely faraway stars. 11. Contrast absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude and relate this to stars. 12. Apply information from the H-R diagram and relate this to star size, shape, color, temperature, and brightness. 13. Discuss stellar evolution and explain the difference between the different types of galaxies. Instructional Practices/Differentiated Learning: Lecture, Group work, Labs, Studentcentered learning Assessment: Lab Conclusions, Informal/Formal assessment, Questions of the Day, Visuals/Models Resources: Text, Websites, Colleagues, Supplemental Materials