“Know – Understand – Do” Organizer Name: Date(s): Course
advertisement
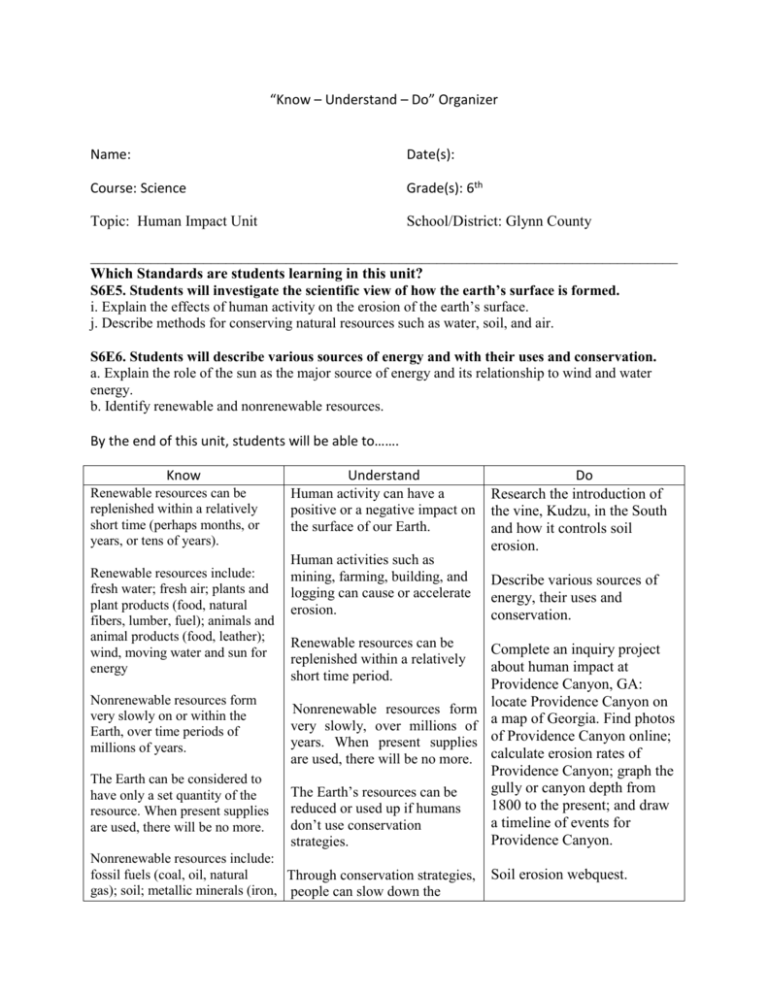
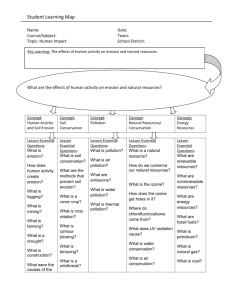
“Know – Understand – Do” Organizer Name: Date(s): Course: Science Grade(s): 6th Topic: Human Impact Unit School/District: Glynn County ______________________________________________________________________________ Which Standards are students learning in this unit? S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. i. Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the earth’s surface. j. Describe methods for conserving natural resources such as water, soil, and air. S6E6. Students will describe various sources of energy and with their uses and conservation. a. Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy. b. Identify renewable and nonrenewable resources. By the end of this unit, students will be able to……. Know Renewable resources can be replenished within a relatively short time (perhaps months, or years, or tens of years). Renewable resources include: fresh water; fresh air; plants and plant products (food, natural fibers, lumber, fuel); animals and animal products (food, leather); wind, moving water and sun for energy Understand Human activity can have a positive or a negative impact on the surface of our Earth. • Human activities such as mining, farming, building, and logging can cause or accelerate erosion. Do Research the introduction of the vine, Kudzu, in the South and how it controls soil erosion. Describe various sources of energy, their uses and conservation. Renewable resources can be replenished within a relatively short time period. Complete an inquiry project about human impact at Providence Canyon, GA: Nonrenewable resources form locate Providence Canyon on • Nonrenewable resources form very slowly on or within the very slowly, over millions of a map of Georgia. Find photos Earth, over time periods of years. When present supplies of Providence Canyon online; millions of years. are used, there will be no more. calculate erosion rates of Providence Canyon; graph the The Earth can be considered to gully or canyon depth from The Earth’s resources can be have only a set quantity of the 1800 to the present; and draw reduced or used up if humans resource. When present supplies a timeline of events for don’t use conservation are used, there will be no more. Providence Canyon. strategies. Nonrenewable resources include: fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural • Through conservation strategies, gas); soil; metallic minerals (iron, people can slow down the Soil erosion webquest. copper, gold, silver, lead, mercury, zinc, uranium); nonmetallic minerals (kaolin, salt, lime, sulfur, and diamonds, sand). degradation of the environment and the depletion of nonrenewable resources. The atmosphere and the oceans have a limited capacity to Oil and gas are formed from the absorb wastes and recycle remains of marine plants, animals materials naturally. and microorganisms that lived in seas millions of years ago. Cleaning up polluted air, water, The ultimate source of the energy in fossil fuels is from the sun. Photosynthetic plants and marine algae lock this energy into organic matter. When we burn plants, coal, oil, or gas, we release the sun's trapped energy. When hydrocarbons are burned as fuel, they release a greenhouse gas (CO2) that is linked with global warming. Burning hydrocarbons also releases pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and unburned hydrocarbons that contribute to air pollution. Nuclear power is generated from the heat released when uranium atoms split (undergo fission). That heat boils water to make the steam that turns the turbines to generate electricity. Wind electricity is produced by turbines which can be grouped together on a "wind farm." It is cost-competitive with other forms of electricity, but only certain parts of the country such as the Great Plains states have enough strong, steady wind for widespread wind power development. Solar electricity can be produced or soil or restoring depleted soil, forests, or fishing grounds can be very difficult and costly. Heat, electricity, and transportation energy is generated through energy resources. Learning to conserve natural resources are not just important for the local population but for the entire world population. Pollution does not just affect people near the pollution site; pollution, waste, and erosion can affect people in surrounding areas and can be harmful to entire communities and countries. Create a pie chart for energy resources. Make a flow chart for the role of the Sun as the ultimate energy source. Make a cause and effect chart for human impact and soil erosion. Create a sequence thinking map for fossil fuels and burning hydrocarbons and their contribution to air pollution. Make a flow chart for electricity generated from nuclear power. Compare and contrast the pros and cons between renewable and nonrenewable energy resources. Identify conservation methods for Earth’s natural resources. Recognize the impacts of human beings on air, water, and soil pollution. Discuss examples of human impacts on the topography in Georgia. Discover how much water is wasted if water is left on while brushing teeth-extension activity at home. Inquiry project about personal responsibility for recycling. Identify things that are being done wrong to the environment after looking at a in photovoltaic cells that can be placed on rooftops and other sunny places. The cost of photovoltaic systems continues to drop dramatically, but they are still several times as expensive as the cheapest electricity. The sun's energy can be used economically without conversion to electricity. Some uses are to heat water for home use, and to heat and light buildings designed to take advantage of the sun's path through the sky. Hydroelectricity is produced by turbines below dams. It is inexpensive and is the most widely used form of renewable energy, but the best sites for hydro in the U.S. already have been dammed, and further dams would have to displace valuable urban and farm land. Of the total energy used in the U.S., most comes from petroleum, followed by natural gas and coal. Burning coal contributes to air pollution and acid rain. Burning low sulfur coal produces less acid rain. Certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat in the lower atmosphere (troposphere). This phenomenon has been referred to as the greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), ozone (O3), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and chlorofluorocarbons. Ozone protects life on earth by absorbing most incoming solar ultraviolet radiation. Release of picture that has examples of nonpoint pollution and nonconservative soil practices. List some ways humans affect our environment on each- soil, air, and water. List activities humans can engage in to change or decrease our natural resource use. Using Internet or other resources, compare United States’ use of land, air, and water with other major countries. Determine major environmental issues that are impacting countries around the world such as deforestation. Reveal and write about why conservation is such an important issue in our school, community, state, and nation as the world’s population continues to increase. chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's) from aerosol cans, cooling systems and refrigerator equipment removes some of the ozone, causing "holes" to open up in this layer allowing the UV radiation to reach the earth. Ultraviolet radiation is known to cause skin cancer and has damaging effects on plants and wildlife. Good soil conservation techniques include: contour plowing; strip planting - different crops in strips; cover crops; crop rotation; terraces; planting groundcovers - roots hold the soil; windbreaks; tree planting; mulching.