Directions: Match the weather conditions to the type of severe
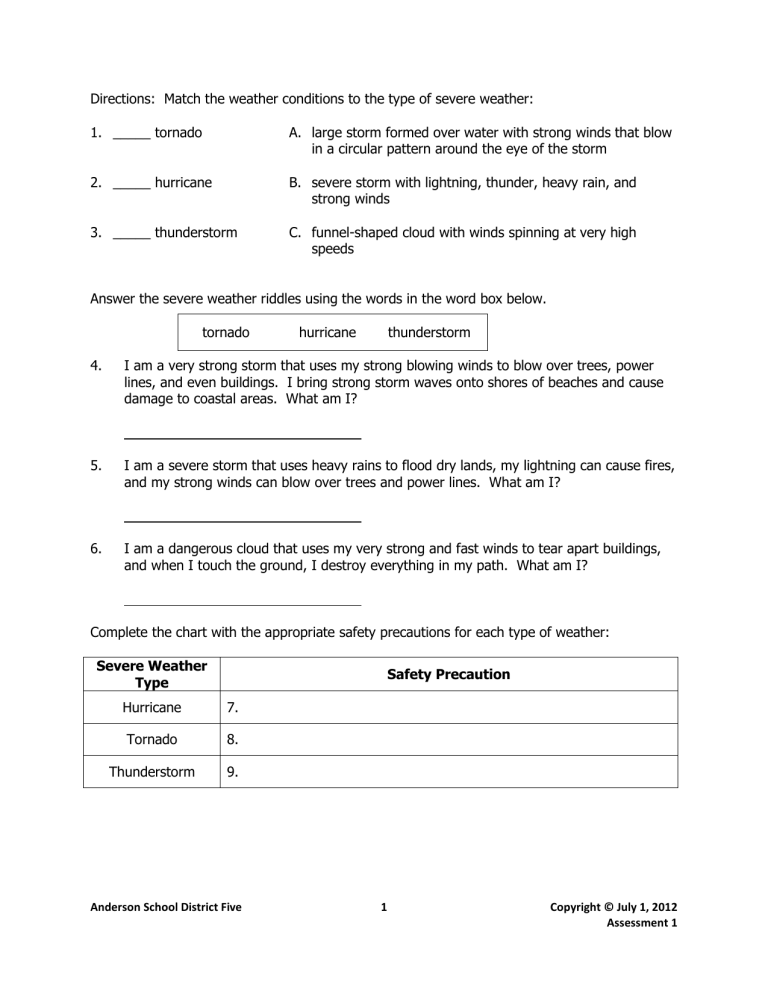
Directions: Match the weather conditions to the type of severe weather:
1.
_____ tornado
2.
_____ hurricane
3.
_____ thunderstorm
A. large storm formed over water with strong winds that blow in a circular pattern around the eye of the storm
B. severe storm with lightning, thunder, heavy rain, and strong winds
C. funnel-shaped cloud with winds spinning at very high speeds
Answer the severe weather riddles using the words in the word box below. tornado hurricane thunderstorm
4.
I am a very strong storm that uses my strong blowing winds to blow over trees, power lines, and even buildings. I bring strong storm waves onto shores of beaches and cause damage to coastal areas. What am I?
5.
I am a severe storm that uses heavy rains to flood dry lands, my lightning can cause fires, and my strong winds can blow over trees and power lines. What am I?
6.
I am a dangerous cloud that uses my very strong and fast winds to tear apart buildings, and when I touch the ground, I destroy everything in my path. What am I?
Complete the chart with the appropriate safety precautions for each type of weather:
Severe Weather
Type
Safety Precaution
Hurricane 7.
Tornado
Thunderstorm
8.
9.
Anderson School District Five 1 Copyright © July 1, 2012
Assessment 1
1.
Which of the following is an example of a translucent material?
A.
wax paper
B.
construction paper
C.
aluminum foil
D.
clear plastic wrap
2.
Lemons look yellow because _________________________.
A.
they reflect all colors of light except yellow
B.
they absorb only yellow light
C.
they absorb all sunlight
D.
they reflect only yellow light
3.
When light hits an opaque object such as a person’s body, it is blocked and a shadow in the shape of the person forms. This shows that _________________.
A.
light travels in a straight line
B.
light travels from the sun in waves
C.
light bends around solid objects
D.
light travels faster through some materials than others
4.
A transparent material is best described as one that _____________________.
A.
allows light to pass through
B.
blocks light waves
C.
allows some light to pass through
D.
is cloudy or frosted in appearance
5.
Which is an example of reflection?
A.
using eyeglasses with convex lenses to see things up close better
B.
using a magnifying lens to make small objects look larger
C.
using binoculars to see far away things better
D.
using a mirror to see your image
6.
What is the name of the object that separates white light into bands of colored light?
A.
mirror
B.
prism
C.
flashlight
D.
magnifying glass
7.
Light appears to bend when ___________________________.
A.
it moves through one material to another
B.
it passes through clear glass
C.
it strikes a mirror
D.
it moves through empty space
8.
Light energy that can be seen and that can be broken into the colors of the rainbow is
_______________________.
A.
electricity
B.
moonlight
C.
x-rays
D.
the visible spectrum
9.
Which statement does not describe how light travels?
A.
Light moves in a straight line from its source unless it is bounced off another object
B.
Light moves faster through air than through water.
C.
Light travels at different speeds through different materials.
D.
Light travels at a slow speed.
10.
You place a flower in a clear vase of water. As you view the stem from the side, it appears broken. This is an example of __________________.
A.
reflection
B.
translucence
C.
refraction
D.
magnification
11.
Explain why a black object looks black.
12.
Each piece of cardboard in this experiment has one hole. The student wants to be able to see the flashlight bulb. Without moving her head, what can the girl do to see the light? Why is this necessary?
13.
The picture shows a pencil in a container of water. Why does the pencil look as if it is broken?
A.
because the shiny glass reflects light
B.
because the water separates the light into many colors
C.
because the part of the pencil outside the water casts a shadow by the water
D.
because light rays appear to bend when they pass from air into water and from water into air
14.
Jenny wants to buy new window shades for her bedroom. She likes to sleep late into the day.
What would be the best material for her to purchase to make the shades?
A.
an opaque material
B.
a transparent material
C.
a translucent material
D.
a reflective material
15.
Which of the following are the three basic properties of light?
A.
reflection, refraction, and absorption
B.
red, blue, and green
C.
transparent, translucent, and opaque
D.
colors, brightness, and visibility
16.
At what distance would the light on an object be the brightest?
A.
5 feet
B.
10 feet
C.
15 feet
D.
20 feet
1.
The study of the earth’s weather is called ____________________.
A.
geology
B.
astronomy
C.
meteorology
D.
biology
2.
Which of the following is a qualitative observation about the weather?
A.
The wind is blowing 15 mph.
B.
It is raining.
C.
The temperature is 76°F.
D.
It rained more on Monday night than Wednesday night.
3.
Look at the partial thermometer below. What is the temperature?
A.
B.
76°F
90°F
C.
18°F
D.
70°F
° F
120
°C
50
100
80
60
50
40
30
4.
A thermometer is used to measure _______________________.
A.
air pressure
B.
air temperature
C.
water pressure
D.
wind speed
5.
A wind vane is used to measure ____________________.
A.
wind direction
B.
wind speed
C.
air pressure
D.
temperature
6.
Charles noticed that the current wind speed was 35 km/hr on the Beaufort Scale.
Which weather instrument did he use to determine this?
A.
thermometer
B.
wind vane
C.
anemometer
D.
rain gauge
7.
Using the data table below, forecast the temperature for April.
Month
March
Precipitation
2 inches
Wind
Direction
North
Temperature
51°F
April
May
June
2 inches
3 inches
1 inch
A.
34°F
B.
62°F
C.
78°F
D.
101°F
NW
West
SW
?
74°F
83°F
Use the words in the box to identify the weather instrument described below. wind vane anemometer thermometer rain gauge
8.
The faster the air moves, the faster it will turn this instrument.
9.
Most liquids expand when they are heated and contract when they are cooled in this instrument.
10.
This instrument always points into the wind.
11.
This instrument is used to measure rainfall in inches.
12.
Sally walked outside one day before school. She noticed that she needed to wear long pants, tennis shoes, and a light jacket. The wind was stirring the brightly colored leaves that had fallen off the tree. What is the season?
A.
fall
B.
winter
C.
spring
D.
summer
13.
14.
15.
16.
Anderson School District Five 8 Copyright © July 1, 2012
Assessment 2
1.
Water vapor occurs during which stage of the water cycle?
A.
condensation
B.
evaporation
C.
precipitation
D.
run-off
2.
Clouds are formed during the _________________ stage of the water cycle.
A.
condensation
B.
evaporation
C.
precipitation
D.
run-off
3.
Snow, sleet, and hail are caused by _______________.
A.
above freezing temperatures in the air
B.
liquid water on Earth becoming a gas
C.
freezing temperatures in the air
D.
water evaporating from Earth
4.
Small droplets of water began to form on the outside of a soda can on a summer day. This is an example of ___________________.
A.
condensation
B.
evaporation
C.
precipitation
D.
run-off
5.
Which of these best describes the water cycle?
A.
The climate of our region is warm and wet.
B.
Water changes form as it cycles between the Earth and the air.
C.
Water is made of hydrogen and oxygen.
D.
Thunderstorms are most common during the summer months.
Anderson School District Five 9 Copyright © July 1, 2012
Assessment 2
6.
Puffy, lumpy-looking clouds often with a flat bottom are classified as
_______________.
A.
cirrus
B.
cumulus
C.
stratus
D.
fog
7.
Layers of clouds that spread out covering a large area are classified as
________________.
A.
cirrus
B.
cumulus
C.
stratus
8.
You observe a dark cumulus cloud in the sky. What weather condition is likely to occur?
A.
sunny and mild
B.
slow, steady rain
C.
thunderstorms
9.
A rain gauge is used to measure __________________________.
A.
temperature
B.
air pressure
C.
wind direction
D.
rainfall
10.
Circle the forms of precipitation that result from freezing temperatures in the air? snow hail rain sleet
Anderson School District Five 10 Copyright © July 1, 2012
Assessment 2
Match each water cycle process to its component.
11.
Evaporation
12.
Run off
13.
Condensation
14.
Precipitation
A.
Water vapor changes back to droplets of water, forming clouds.
B.
A form of water falls from clouds to Earth’s surface.
C.
Precipitation from land surfaces flows back into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
D.
The Sun’s heat energy causes liquid water to become water vapor as it rises.
Anderson School District Five 11 Copyright © July 1, 2012
Assessment 2










