WhatYourChildWillLearnPreKQ3 - Pre
advertisement
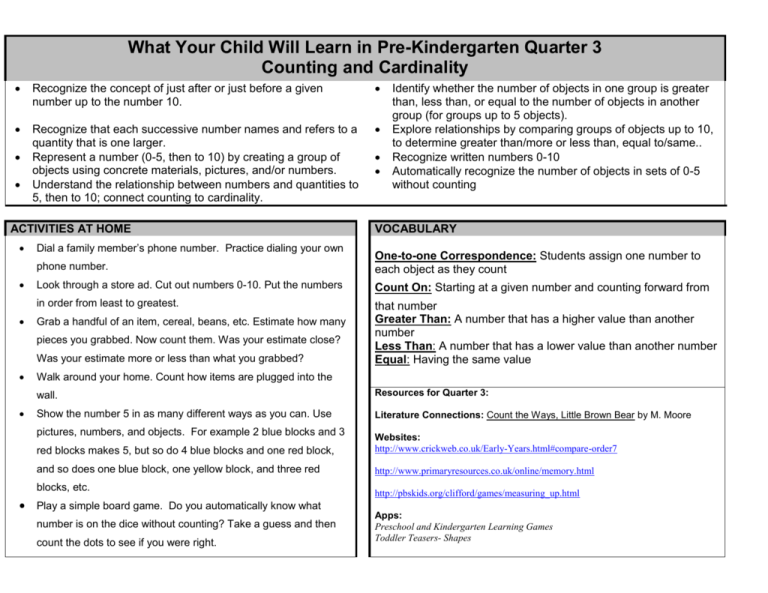
What Your Child Will Learn in Pre-Kindergarten Quarter 3 Counting and Cardinality Recognize the concept of just after or just before a given number up to the number 10. Recognize that each successive number names and refers to a quantity that is one larger. Represent a number (0-5, then to 10) by creating a group of objects using concrete materials, pictures, and/or numbers. Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities to 5, then to 10; connect counting to cardinality. ACTIVITIES AT HOME Dial a family member’s phone number. Practice dialing your own One-to-one Correspondence: Students assign one number to each object as they count Look through a store ad. Cut out numbers 0-10. Put the numbers Count On: Starting at a given number and counting forward from in order from least to greatest. that number Greater Than: A number that has a higher value than another number Less Than: A number that has a lower value than another number Equal: Having the same value Grab a handful of an item, cereal, beans, etc. Estimate how many Was your estimate more or less than what you grabbed? VOCABULARY phone number. pieces you grabbed. Now count them. Was your estimate close? Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group (for groups up to 5 objects). Explore relationships by comparing groups of objects up to 10, to determine greater than/more or less than, equal to/same.. Recognize written numbers 0-10 Automatically recognize the number of objects in sets of 0-5 without counting Walk around your home. Count how items are plugged into the wall. Resources for Quarter 3: Show the number 5 in as many different ways as you can. Use Literature Connections: Count the Ways, Little Brown Bear by M. Moore pictures, numbers, and objects. For example 2 blue blocks and 3 red blocks makes 5, but so do 4 blue blocks and one red block, Websites: http://www.crickweb.co.uk/Early-Years.html#compare-order7 and so does one blue block, one yellow block, and three red http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/memory.html blocks, etc. http://pbskids.org/clifford/games/measuring_up.html Play a simple board game. Do you automatically know what number is on the dice without counting? Take a guess and then count the dots to see if you were right. Apps: Preschool and Kindergarten Learning Games Toddler Teasers- Shapes What Your Child Will Learn in Pre-Kindergarten Quarter 3 Measurement and Data Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight. Compare two objects with common measurable attributes, to see which object has “more of”/“less of” the attribute. For example, directly compare the heights of two children and describe one child as taller/shorter. Sort objects into categories; count the numbers of objects in each category. Compares categories using words such as greater/more than, less than, and equal to/same. ACTIVITIES AT HOME VOCABULARY Trace your hand on paper. Trace a friend’s or family member’s hand too. Which hand is longer? Sort a bag of skittles or other candy by color. Count each color. What color has the most? What color has the least? Get three bowls or plates. Put them in order from biggest to smallest. Help to sort your family members laundry Find 3 objects in the home that are longer than your shoe. Grab a handful of an item, cereal, beans, etc. Estimate how many pieces you grabbed. Now count them. Was your estimate close? Was your estimate more or less than what you grabbed? Estimate how many spoonfuls it take to finish a bowl of cereal. Count each spoonful as you eat. Attribute: A characteristic of an object that students use to define the object. Example: thin, thick, small, large, 3 sides, 4 sides, etc. Length: The distance between two points or objects Weight: A measure of how heavy something is Sorting: Grouping objects based on similar attributes Non-Standard Units of measurement: Any real item that can be used to measure. Examples: paperclips, cookies, pennies, or yarn Greater Than: A number that has a higher value than another number Less Than: A number that has a lower value than another number Equal: Having the same value What Your Child Will Learn in Pre-Kindergarten Quarter 3 Geometry Match like and similar shapes. Group shapes by attributes. For example, group together all shapes with four sides. Match and sort shapes. Describe three-dimensional objects using attributes. Correctly name shapes (regardless of their orientations or overall size Compose and describe structures using three-dimensional shapes. ACTIVITIES AT HOME VOCABULARY Look around your home for solid shapes. Name at least 3 solid shapes. Look around your home for flat shapes. Name and draw at least 3 flat shapes. Look around your home for rectangle. Count them and record how many you found. Use bendy straw, toothpicks, or pipe cleaners to make as many shapes as you can. Make a picture using a square, a circle, and triangle. Describe to a friend how you made it. Find everyday solid shapes around your house that you were going to throw out or recycle. Look for empty cereal boxes, empty tissue boxes, used paper towel or toilet paper rolls, etc. Use these solid shapes like blocks to build a tower, house, city, etc. Explore position words. Use toys to model before, after, above, below, and beside. Describe using attributes. Ex. The blue car is behind the red car. Two-Dimensional (flat): The outline of a shape such as a triangle, square, or rectangle Attribute: A characteristic of an object that students use to define the object. Example: thin, thick, small, large, 3 sides, 4 sides, etc Three-Dimensional (solid): A shape having length, width, and height such as a sphere or cylinder Face: The flat surface of a solid figure Side: Line-segments of shapes Vertex: A point where to two or more straight lines meet. A corner Square: A four-sided shape with equal sides and corners Rectangle: A four-sided shape with two sets of sides that are equal and parallel, and four right angles Circle: A flat shape with no sides or corners Triangle: A three-sided figure Hexagon: A shape with six sides Sphere: A solid shape similar to a basketball Cylinder: A 3-D shape with two circular faces Cube: A 3-D shape with six square faces Cone: A 3-D shape with a curved surface and one circular face