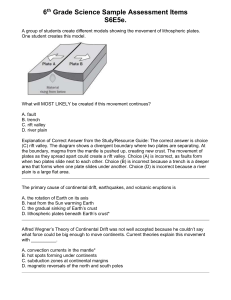
Unit 2 Topic 1: The Earth*s Layers

Unit 2 Topic 4: Theory of Plate Tectonics
Key Vocabulary:
1.
Convection current: up and down motion of heated matter
2.
Lithosphere: Earth’s crust and solid upper mantle
3.
Asthenosphere: soft layer of Earth beneath lithosphere
A.
Theory of Plate Tectonics:
1.
In 1912 Alfred Wegner theorized about the supercontinent-Pangaea
2.
Wegner found that fossils and rocks from South America were the same as fossils and rocks from Africa—this is evidence supporting Pangaea
3.
Pangaea broke apart about 200 million years ago
4.
Pieces of Pangaea slowly drifted apart—called continental drift
5.
B.
Theory of Seafloor Spreading:
1.
New ocean crust is made at tall ridges on ocean floor
2.
Heated rock rises through cracks in crust, cools, hardens & makes new ocean floor
3.
As new ocean crust forms, two side of ridge spread apart or drift
4.
Old ocean floor is pushed into Earth’s hot mantle where it melts and is destroyed
5.
When ocean floor spreads, tectonic plates move apart
C.
Movement of Tectonic Plates:
1.
Underneath the lithosphere is a soft layer of Earth called Asthenosphere.
2.
Hot matter in the Asthenosphere flows like liquid
3.
Tectonic plates sit on top of the asthenosphere
4.
When this hot liquid flows from deep within the Earth it moves toward the crust
5.
Once the liquid reaches the crust, it cools and sinks back down toward Earth’s core
6.
This up and down motion of heated matter is called convection current
7.
Convection currents in the Asthenosphere move up and down causing the tectonic plates to move slowly—a few centimeters each year
8.
Tectonic plates collide (run into each other)
9.
Tectonic plates spread apart
10.
Tectonic plates can slide past each other
11.
Movement of tectonic plates can cause earthquakes and volcanoes; can build mountains
1