Cell Growth and Reproduction
advertisement

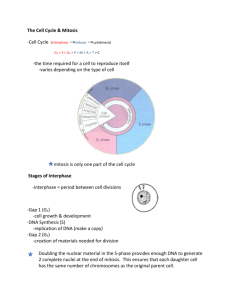
Cell Growth and Reproduction Keystone Eligible Content: Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division (i.e. mitosis or meiosis), cytokinesis Compare the processes and outcomes of mitotic and meiotic nuclear divisions Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information Explain the functional, relationships between DNA, genes, alleles, and chromosomes and their roles in inheritance Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division (i.e. mitosis or meiosis), cytokinesis. 1. Name and describe the three parts of the cell cycle. 2. Identify mitotic phases: A ____________________ C ____________________ B ____________________ D ____________________ 3.List the above phases of mitosis in order (use letters) _____, _____, _____, _____ Compare the processes and outcomes of mitotic and meiotic nuclear divisions. 4. Compare mitosis and meiosis: Mitosis Meiosis Number of cell divisions Number of daughter cells Number of chromosomes in daughter cells (2N/N) Daughter cells are genetically (identical/different) than parent cell Occurs in what type of cell 5. Distinguish between the terms diploid and haploid and give an example of each type of cell. 6. Identify the diploid and haploid chromosome number for humans. Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information. 7. What do we call the monomers of nucleic acids? 8. What three things make up the monomer? 9. What do we call the process where DNA makes a copy of itself? 10. Identify the four nitrogen bases are present in a molecule of DNA. 11. Which of the nitrogen bases mentioned above is only found in DNA? 12. Which nitrogen base replaces it in a molecule of RNA? 13. Identify the base pairing rules found in DNA. What type and how many bonds are between each base pair? 14. Circle the DNA strands below that would represent the new DNA molecules that would result from replication. Original DNA A B Replicated DNA C Explain the functional relationships between DNA, genes, alleles, & chromosomes and their roles in inheritance. 15. Describe the relationship between DNA, gene, allele, chromosome, and nuclei. Assessment Anchor – Cell Growth and Reproduction: Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division (i.e. mitosis or meiosis), cytokinesis. Use the illustration below to answer question 1. 1.Which statement best describes the phase of the cell cycle shown? a. The cell is in prophase of mitosis because the number of chromosomes has doubled. b. The cell is in prophase I of meiosis because the number of chromosomes has doubled. c. The cell is in teolphase of mitosis because the cell is separating and contains two copies of each chromosome. d. The cell is in telophase of meiosis because the cell is separating and contains two copies of each chromosome. Use the diagram below to answer question 2. 2. Which event most likely occurs next in mitosis? a. The chromatin condenses. c. The chromosomes double in number. b. The nuclear envelope dissolves. d. The cell membrane pinches inward to divide the cytoplasm Compare the processes and outcomes of mitotic and meiotic nuclear divisions. 3. Mitosis and meiosis are processes by which animal and plant cells divide. Which statement best describes a difference between mitosis and meiosis? a. Meiosis is a multi-step process. b. Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells. c. Meiosis is used in the repair of an organism. d. Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells. 4. Patau syndrome can be a lethal genetic disorder in mammals, resulting from chromosomes failing to separate during meiosis. A. Identify the step during the process of meiosis when chromosomes would most likely fail to separate. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ B. Describe how chromosome separation in meiosis is different from chromosome separation in mitosis. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ C. Compare the effects of a disorder caused by chromosomes failing to separate during meiosis, such as Patau syndrome, to the effects of chromosomes failing to separate during mitosis. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information. 5. Which process helps preserve the genetic information stored in DNA during DNA replication? a. the replacement of nitrogen base thymine with uracil b. enzymes quickly linking nitrogen bases with hydrogen bonds c. the synthesis of unique sugar and phosphate molecules for each nucleotide d. nucleotides lining up along the template strand according to base pairing rules Explain the functional, relationships between DNA, genes, alleles, and chromosomes and their roles in inheritance. 6. In a flowering plant species, red flower color is dominant over white flower color. What is the genotype of any red-flowering plant resulting from this species? a. red and white alleles present on one chromosome b. red and white alleles present on two chromosomes c. a red allele present on both homologous chromosomes d. a red allele present on at least one of two homologous chromosomes