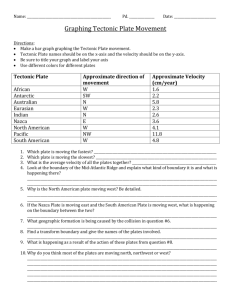
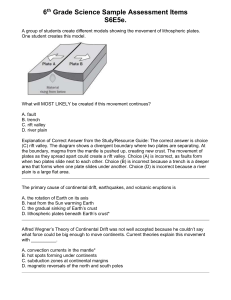
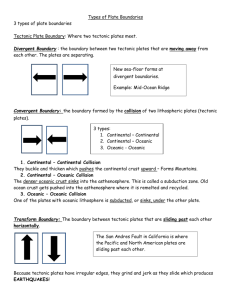
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics: the theory that Earth`s
advertisement

Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics: the theory that Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere. Plate Boundaries: o a place where tectonic plates touch o can collide, separate, or slide past each other o earthquakes can occur at each type of plate boundary Types of plate boundaries: o Convergent boundary: two tectonic plates collide Continental-continental collisions: both plates buckle and thicken, which pushes the continental crust upward Continental-oceanic collisions: denser oceanic crust sinks into the asthenosphere---subduction zone; old ocean crust gets pushed into the ashtenosphere, where it is remelted an recycled Oceanic-oceanic collisions: one plate is subducted/sinks under the other plate o Divergent boundary: two tectonic plates separate; new seafloor forms here; mid-ocean ridges are most common type of divergent boundary Plates separate from each other, as they move apart, new magma rises to fill the gap, cools and forms new sea floor o Transform boundary: two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally (San Andreas Fault in California—where Pacific and North American plates are sliding past each other) Because tectonic plates have irregular edges, they grind and jerk as they slide—produces earthquakes Possible Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion: Changes in density within the asthenosphere; density changes are caused by the outward flow of thermal energy from deep within the Earth; rock is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and tends to rise to the surface of Earth; as rock gets near the surface, rock cools, becomes more dense, tends to sink o Ridge Push: mid-ocean ridges, oceanic lithosphere is higher than where it sinks into the asthenosphere; oceanic lithosphere slides downhill under the force of gravity o Convection: hot rock from deep within the Earth rises, cooler rock near surface sinks; convection causes the oceanic lithosphere to move sideways and away from mid-ocean ridge o Slab Pull: oceanic lithosphere is denser than asthenopshere, the edge of the tectonic plate that contains oceanic lithpshere sinks and pulls the rest of the tectonic plate with it Tracking Tectonic Plate Motion: Very slow; can’t feel or see the movement; measured in centimeters per year Global Positioning Systems: system of satellites; radio signals are continuously beamed from satellites to GPS ground stations—record the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station; over time, distances change slightly; recording the time it takes the GPS to move a given distance, can measure the speed at which each tectonic plate moves