Unit 3 Vocabulary - Reading Community Schools
advertisement

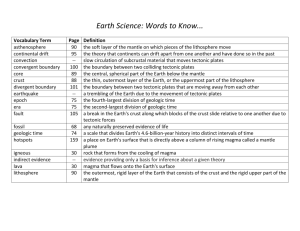
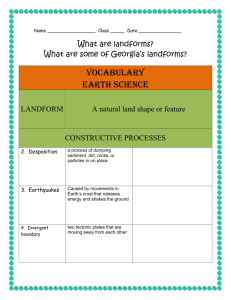
Unit 3 Vocabulary Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals and organic matter Rock Cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Weathering – the process in which water, wind, ice, and heat break down rock Erosion – the process by which sediment is removed from its source Deposition – the process in which sediment moved by erosion is dropped and comes to rest Uplift – the movement within the Earth that causes rocks inside the Earth to be moved to the Earth’s surface Tectonic Plates – a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continental Drift – the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations Sea-Floor Spreading – the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies Convergent Boundary – the boundary formed by the collision of two tectonic plates Divergent Boundary – the boundary between two tectonic plates that is moving away from each other Transform Boundary – the boundary between tectonic plates sliding past each other Ridge Push – a force in which oceanic lithosphere slides downhill from the midocean ridge due to gravity Convection – the circulation of hot rock to the surface and cooler rock sinking that causes movement of the oceanic lithosphere Slab Pull – a process in which the denser oceanic lithosphere edge of the tectonic plate sinks into the asthenosphere and pulls the rest of the plate with it