Lesson 1.2: Learning the Key Terms 1. organ system 2. tissues 3
advertisement
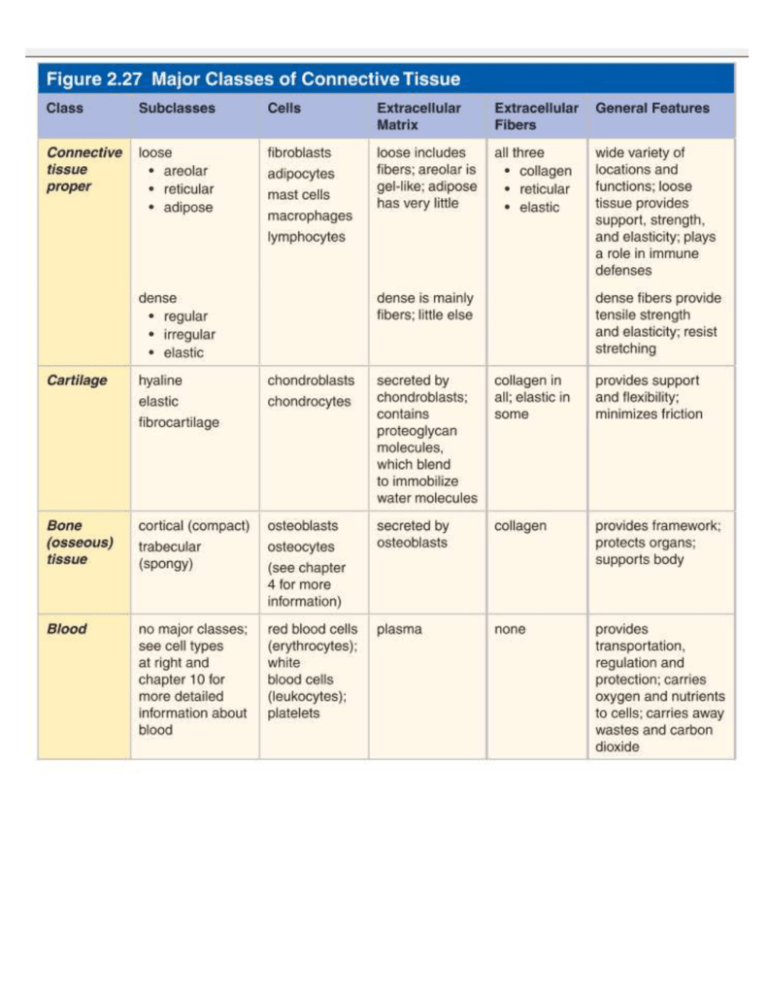
Lesson 1.2: Learning the Key Terms Lesson 1.4: Learning the Key Terms 1. organ system 1. D 2. tissues 2. G 3. cells 3. F 4. molecules 4. B 5. organ 5. A 6. homeostasis 6. C 7. homeostatic mechanisms 7. H 8. Negative feedback 8. E 9. Positive feedback 10. Homeostatic imbalance 11. metabolism 12. receptor 13. effector 14. Atoms 15. metabolic rate 16. control center Chapter 1 Practice Test 25. F 1. Homeostasis 26. F 2. physiology 27. I 3. Net force 28. B 4. statistical inference 29. D 5. metabolic rate 30. C 6. F 31. E 7. T 32. J 8. T 33. H 9. F 34. G 10. F 35. A 11. C 36. Answers may vary. Organ systems work together 12. D 13. B 14. D 15. A 16. H 17. G 18. D 19. J 20. I 21. C 22. A to maintain homeostasis through processes called homeostatic mechanisms. To maintain homeostasis, all systems must work together and adjust when the body’s external and internal environments change. 37. Answers may vary. Among these are the size and direction of the force, the area over which the force is 23. B distributed, and the material properties of the loaded 24. E body tissues. Lesson 2.1: Learning the Key Terms Lesson 2.3: Learning the Key Terms 1. A 1. F 2. E 2. M 3. L 3. P 4. C 4. H 5. J 5. E 6. S 6. N 7. Q 7. O 8. B 8. I 9. R 9. R 10. G 10. C 11. F 11. D 12. D 12. T 13. N 13. L 14. H 14. G 15. M 15. A 16. O 16. K 17. I 17. S 18. K 18. B 19. P 19. Q 20. J Lesson 2.3: Study Questions elasticity, to tissues. 1. protect the body from physical damage; control 9. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and substances entering and leaving the body; provide carries away wastes and carbon dioxide. It also sensory information; and secrete various substances 2. simple epithelia, stratifi ed epithelia, squamous epithelia, cubodial epithelia, and columnar epithelia 3. the skin provides transportation, regulation, and protection. 10. Cartilage provides support and fl exibility, while bone provides a stronger framework that protects organs and supports the body. 4. both face deep inside the body’s cells 11. The fi bers are not all parallel and run in all directions. 5. An exocrine gland secretes its product to the outside As a result, irregular dense connective tissue is good at world. An endocrine gland secretes its product into resisting stretching forces from a variety of directions. the interstitial space. 12. the study of cells 6. Glandular organs are large, complex glands, with blood 13. Answers may vary. Hyaline cartilage forms the ends vessels and connective tissue instead of only cells. of the ribs where they connect to the sternum, or 7. connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood breastbone. It is also found in the nose, trachea 8. Collagen fi bers are strong and resistant to stretch. They give tensile strength to tissue. Reticular fi bers (windpipe), and larynx (voicebox). Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear and the epiglottis. Fibrocartilage is found in the discs between vertebrae help to provide a structural framework that keeps and in the discs in the knee joint. cells in place. Elastic fi bers give springiness, or 14. skeletal 15. Both skeletal and cardiac muscle is striated, which means it has striations, or stripes. 16. smooth muscle 17. glial cells and neurons; Glial cells are supporting Lesson 2.3: Complete the Chart 1. connective tissue proper 2. cartilage 3. bone (osseous) tissue 4. blood cells and neurons carry electrical signals to muscles, 5. regular glands, or other neurons, and also receive same 7. adipo input from other neurons. 8. lympho 6. fi bro 9. chondro 10. chondro 11. osteo 12. osteo 13. erythrocytes 14. leukocytes 15. matrix 16. fi bers 17. collagen 18. elastic 19. collagen Chapter 2 Practice Test 25. F 1. nucleic acids 26. G 2. neurons 27. J 3. cytokinesis 28. E 4. chondroblasts 29. I 5. Golgi apparatus 30. H 6. F 31. F 7. F 32. A 8. T 33. C 9. F 34. B 10. T 35. D 11. D 36. Answers may vary. Understanding how cells 12. D work, and how they work together, is important 13. A for understanding anatomy and physiology. 14. C Understanding cells and the tissues made from them 15. A 16. E 17. D 18. J is also necessary for understanding diseases and their treatment. This is especially so now because 19. I modern medicine so greatly depends on therapies 20. C targeted at cellular processes. 21. B 37. Answers may vary. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, 22. H 23. A 24. G telophase Prophase: chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Metaphase: some spindle fi bers lock on to the centromeres of the chromosomes and pull the chromosomes until they are all positioned along the midline of the cell. Anaphase: the enzyme separase cuts each centromere in half and each chromatid pulls itself along the spindle fi ber toward the centriole; 46 chromatids go to one side and 46 chromatids move to the opposite side. Telophase: the chromosomes gather around each centriole, where they decondense, or spread out; new nuclear membrane forms around the DNA











