2-1-4 Notes (blank)
advertisement

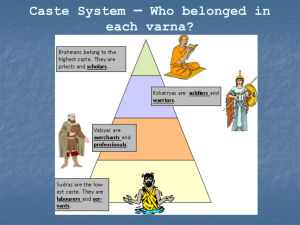
Name _______________________________ 2-1-4 2-1: The Development and Codification of Religious and Cultural Traditions (600 B.C.E. – 600 C.E.) Persistence of Older Forms of Worship Older forms of worship were still popular in many areas including: - Animism - ________________ veneration/worship (ex: In Shang China ancestor worship was practiced and from there it spread to much of East Asia.) ____________________ = The blending of practices from more than one religion (common during the classical era – ex: Christians incorporated some pagan holidays). Reformed Faiths and New Religions Judaism Judaism = First ______________________ (one-god) religion. Hebrews (the ones practicing Judaism) were conquered by a series of peoples (Assyrians, Nebuchadnezzar’s Neo-Babylonian empire, Persians, Alexander the Great, and the Romans) beginning 700s B.C.E. Jewish ________________ = When Jews were forced out of their homeland in the Middle East and had to scatter throughout the world. The Romans were the harshest and destroyed the Jewish kingdom. ______ (written 400s B.C.E) = Hebrew bible’s 1st of 5 books, it formalized the Jewish religion. Ten Commandments = Supposedly revealed by Moses and followed by the Jews. Strict restrictions (ex: Dietary constrictions (kosher) and couldn’t marry outside Jewish faith) Hebrew society patriarchal, though women respected in the home. Jews practiced slavery, but preached charity, social responsibility, and concern for the poor. ______________ = Jews believe a messiah (or “appointed one”) will return someday and free them from oppression. From Vedism to Hinduism ____________ = Religion that dominated India since 1500 B.C.E. ______________ = Priestly caste that followers are supposed to obey unconditionally ____________________ = Hundreds of essays (written 900-500 B.C.E.) questioning having to follow Brahmins unquestionably. They also raised idea of dietary restrictions, and promoted yoga to achieve liberation (this led to faith of Buddhism). ________________ (300 B.C.E) = New faith that used some aspects of Vedism (including karma and reincarnation, and caste system, which began when Indo-European invaders made the darker skin locals do menial work). __________ system = Began with 4 distinct castes: (a) Brahmins (priests); (b) kshatriyas (warriors); (c) vaishyas (farmers and artisans); shudras (servants and serfs). Over time caste system became more complex and included untouchables who performed degrading tasks. Hinduism is most polytheistic religion (thousands of gods). 3 most popular gods: (a) Brahma = masculine personification of the world soul; (b) Vishnu = the Preserver or savior; (c) Shiva = god of creation and destruction (depicted as a dancer). Law of ________ (compiled 200 B.C.E. to 200 C.E.) = Argued in favor of caste system. It was moral duty (dharma) to obey caste system and its guidelines. Women: Hindu society highly patriarchal, only men could get education and own property, and many women married in childhood). ________ = women of certain castes expected to throw themselves on fire of their deceased husbands dead bodies. Buddhism Arose in India to oppose Vedism – Buddhism agrees on reincarnation (or rebirth) but rejects the caste system. Siddhartha ______________ (563-483 B.C.E.) = Founder of Buddhism. He was a noble who appalled by suffering of common people. After much meditation, he realized moderation and peace were way to a good life. He took the name Buddha (“the awakened one”) and began to preach. ________ Noble Truths = The four main beliefs of the Buddhist religion. Eightfold _____ = Buddhists must follow the 8 aspects of this path in order to achieve nirvana. Buddhist sects - After Buddha died, Buddhism separated into two major groups (a) __________________ Buddhism = closest to Buddha’s beliefs, stresses simplicity and meditation (popular in South and Southeast Asia). (b) ________________ Buddhism = Has many rituals which developed as Buddhism combined with locals beliefs as it spread north (popular in Japan, Korea, Tibet, parts of China). Confucianism Confucius (551-479 B.C.E.) = Lived in China during Zhou dynasty. His ideas about proper relationship between society and the individual were written on paper. ________________ = Writings containing Confucius’s ideas about proper relationship b/t society and the individual (written long after his death). Confucianism focuses on ethical conduct. Rulers should be benevolent and citizens should have good behavior. Confucius believed humans were good and would remain good if treated well. Order and hierarchy are very important (including importance of elders and ancestor worship), and well-being of group more important than the individual. VERY patriarchal = Men ruled, got education, fought wars, could have multiple wives, and could divorce a woman who failed to produce an heir. Women were homemakers and mothers and were allowed only a limited education. __________________ = A competing belief system in China which viewed people as immoral and wanted harsh punishments to keep people in line. Daoism Laozi = Founder of Daoism (500 B.C.E.), later viewed as a god in Daoism. Tao-te Ching =- Main text of Daoism. Daoists believe the universe is governed by the ________ (or the “way”). It preached seeing the world in non-logical ways and stresses compassion, moderation and humility. Daoists seek harmony with universe and not concerned about politics and material possessions. Blended easily with Chinese beliefs: Stressed ancestor veneration and fortune-telling (I-Ching = Daoist used to read the future). _______________ = Most famous symbol of Daoism, shows nothing is absolute and opposites flow into each other. Christianity Jesus of ________________ = A wandering teacher from a Jewish family who became founder of Christianity (called himself the “Son of God”). Jesus questioned Jewish traditions, angering conservative Jews. The Romans, who controlled the Jews at the time, viewed Jesus as a threat and arrested and crucified him in Jerusalem. Despite Romans making Christianity illegal, it grew over next 300 years (1st in Middle East, then in Roman Empire) b/c it was very appealing to the poor (gave them hope for a happy afterlife.) Women: Early on Christianity appealing b/c it gave women more influence, but over time women lost those powers (ex: could not have positions of leadership in the church.) ___________________________ = Roman emperor who legalized Christianity through the Edict of Milan (313 C.E.), and in 380 C.E. Christianity became the empire’s official religion. A formalized hierarchy began (pope – priests – bishops) and a dogma (official list of beliefs) was formed. __________ = Church fathers met to write this book which consisted of the Old Testament (parts of the Hebrew Bible) and the New Testament. After the fall of the Roman Empire in the 400s C.E., the Christian church drifted apart. Thought and Culture Science: _______________ learning = Learning through observation (popular during this time period). Most attributed the workings of the world to the will of the gods. Greeks (600-200 B.C.E.) began studying the principles of science and math (Pythagoras, Euclid, Archimedes). ______________ Method = Created by Greeks, it combined observation with experimentation. Philosophy: Philosophy = Systematic mode of rational thought, pioneered by Greeks and followed by Romans. (Socrates, Plato, Aristotle). _______________________ = Written by Plato, it pondered the best way to govern society. Literature: IN INDIA: Mahabharata = Indian epic with section called Bhagavad-Gita, a poetic dialogue discussing concept of dharma. IN CHINA: Not much fiction, but instead Confucian and Daoist classics (as mentioned earlier, the Analects, the Tao-te Ching, and the I-Ching). Also, The Art of ______ by Sun Tzu, is one of oldest works on diplomacy and strategy. IN GREECE: Greeks had strong literary tradition (ex: Iliad, Odyssey). Greek dramas became popular (ex: Aeschylus’s Oresteia trilogy). IN ROME: Aeneid = Epic poem by Virgil serves as foundation myth for Rome. Architecture: Mostly for religious or political purposes, though military defense important also. IN MIDDLE EAST: Large building projects continued (ex: Great Library of Alexandria (Egypt), ____________________________________________ (created by Nebuchadnezzar). IN EUROPE: Greco-Roman architecture = Used distinctive columns, and Romans used archways and domes (ex: __________________ in Athens, and the Pantheon and the Colosseum in Rome). IN MESOAMERICA: Continued building pyramids (used for sacrifices, not as tombs). IN INDIA: Cave ____________ (to honor Buddhist and Hindu deities), and Pillars of Ashoka (inscribed with Buddhist teachings) IN ASIA: Greco-Buddhist architecture and sculpture = Result of Alexander the Great’s conquests into Central Asia, combined Greco-Roman and Buddhist architecture, giving first statue of Buddha in human form.