Exercise 7 --------Additional Exercises Taking into account the
Exercise 7 --------Additional Exercises
1.
Taking into account the relationship between current account and capital account. Explain if the following phrase is correct: “A deficit in the current account of a country causes an increase in the foreign investment in this country.”
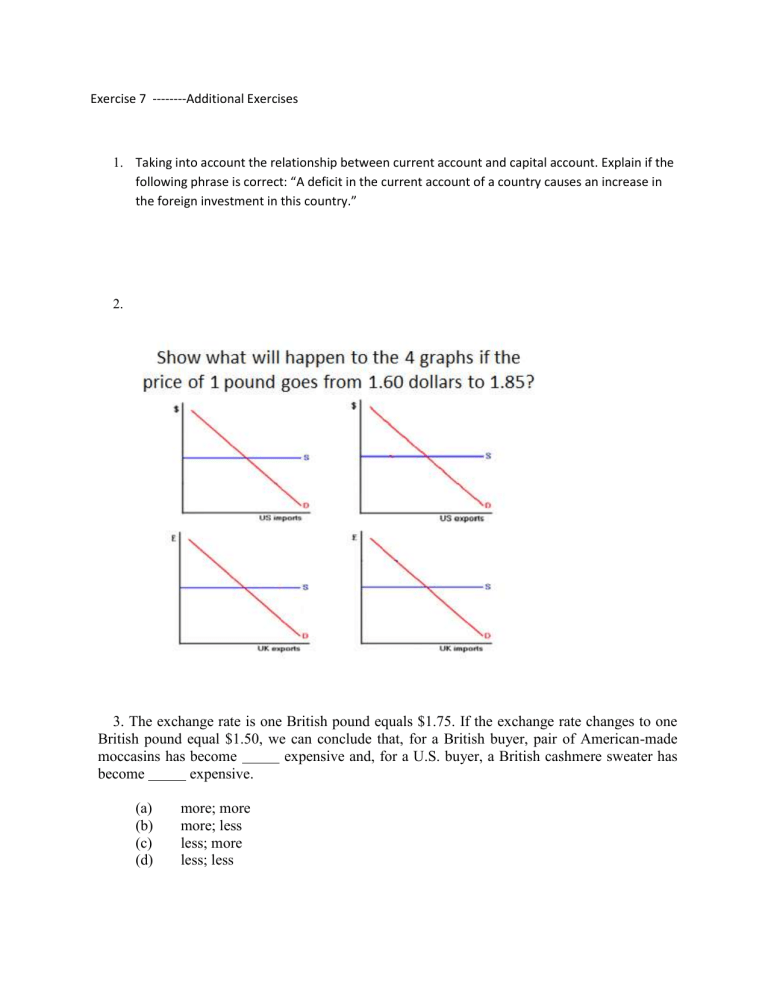
2.
3. The exchange rate is one British pound equals $1.75. If the exchange rate changes to one
British pound equal $1.50, we can conclude that, for a British buyer, pair of American-made moccasins has become expensive and, for a U.S. buyer, a British cashmere sweater has become expensive.
(a) more; more
(b) more; less
(c) less; more
(d) less; less
4. As the exchange rate changes from one British pound equals $1.50 to one British pound equals $2.00, British traders will gain from trade with the United States, and American traders will gain from trade with the United Kingdom.
(a) more; more
(b) more; less
(c) less; more
(d) less; less
5. Suppose the exchange rate between U.S. dollar and Chinese RMB is 1 dollar =6 RMB: a. A 100 RMB Chinese commodity will cost U.S. importer_________________dollars; b. If dollar depreciates by 50% (1 dollar =3 RMB), a 100 RMB Chinese commodity costs U.S. importer___________dollars. c. The demand of U.S. import from China will_____________(increase/decrease).
6. Suppose inflation rate of U.S. dollar is 2%, inflation rate of British pound is 3%, exchange rate between dollar and pound is fixed at 1 dollar=2 pound. a. Jim has 1000 U.S. dollar saving. If he converts the saving to pound, how much pound could he get? b. Suppose a U.S. bank offers interest rate at 2.5%, a British bank offers interest rate at 2.8%. Which bank should Jim choose? (Jim should save dollars in U.S. bank and save pound in British bank
7. Suppose that after a big marketing campaign, many English tourists start coming to the US. Draw in Q12. The graph below the new demand curve for US dollars, and indicate the new equilibrium price.
ANSWER:
1. This is not always true. It can be the case that the causation comes from the opposite. For instance the US is considered to be a safe place to invest money, and then other countries buy bonds or stocks from America making the demand for dollars to increase and then the price of it becomes higher in relation to other currencies. This is the same as saying that the dollar will appreciate making more attractive for Americans to import goods abroad (that all now cheaper due to the stronger dollar) and at the same time exporters will have lower demand for their products (because the dollar is now more expensive). Therefore, the trade balance will have a deficit that was caused by the foreign investments in the US.
2.
In this example there is a dollar depreciation
• Upper Left (US imports): At each price in $, British firms get less £ for their goods.
Thus, they will supply fewer goods to US: supply of US imports decreases (supply curve shifts up since the cost for British firms increased). The amount of US imports decreases in the new equilibrium.
• Upper Right (US exports): At each price in $, UK consumers will have to pay less for US goods. Thus, they will demand more US goods: demand for US exports increases (curve shifts up or right). The amount of US exports increases in the new equilibrium.
• Lower Left (UK exports): At each price in £, Americans has to pay more (in $) for
UK good. Therefore, Americans will demand fewer UK goods: demand for UK exports decreases (curve shifts down or left). UK exports a lower amount of goods to US in the new equilibrium.
• Lower Right (UK imports): At each price in £, US firms will get more $ for their products. Therefore, the supply of US goods (= UK imports) increases
(the curve shifts up because the US exporters have a higher incentive to sell). UK imports more US goods in the new equilibrium.
3.(b) Each pound is worth less U.S. currency—British buyers are becoming poorer. The opposite is true for U.S. buyers of British goods.
4.
(b) Each pound is worth more U.S. currency. British producers, selling the same amount of exports, will be able to claim more U.S. goods than before.
5. a. 100/6 = 16.67; b. 100/3 = 33.33; c. decrease
6. a. 1000*2 = 200 b. U.S. bank. Real interest rate of U.S. bank is 2.5-2 = 0.5. Real interest rate of British bank is 2.8-3 = -0.2.
7.
The dollar appreciated and the foreign currency depreciated.











