LEGAL MED TRANS p. 312-320
b. Nose- suicide: muzzle of gun may be placed in the
nostril and there would be no visible wound of
entrance
-injuries are dangerous due to infection to
the brain
c. Ear- rupture of the tympanic membrane
-hemorrhage suggests fracture of the base
of the middle cranial fossa
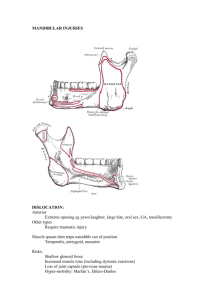
d. Mouth- fracture of lower jaw is due to direct
violence and is the most common in the insertion of
the canine and region of the condyle
-spread of infection is to the respiratory
system
Injuries to the Lungs
-hemorrhage cause compression and collapse of the
lungs
-contusion may be caused by blunt instrument or
compression of the chest
-death is due to shock and hemorrhage
Complications of Lung Injuries
a. Hemorrhage- 1500cc may be recovered sa pleura
b. Compression of lungs –death by asphyxia
c. Severe pneumothorax- laceration of bronchi
d. cerebral air embolism- laceration of pulmo veins
e. Hemoptysis –
f. Subcutaneous emphysema- laceration of parietal
pleura and lung
Neck-ligature marks: death by hanging or
strangulation
-cut throat wounds: diagonal
-homicidal wounds: horizontal
-asphyxia, pneumonia, hemorrhage, shock: cause of
death
-wounds of the esophagus are not common
-reflex by the vagus nerve can cause loss of
consciousness or even death
Injuries to the Heart (aawwwww....)
-sharp instruments, bullets, sharp fractured ribs
-contusion is easily produced in slight trauma
-wounds in the ventricle less dangerous because of
thick muscle layer
-right vent: most common wounds with external
violence
-rupture of aorta: may be due to aneurysm
-cause of death: hemorrhage or cardiac tamponade
Vertebral Column and Spinal Cord:
a. Fracture of the Vertebrae- Fracture of C1-4 can
cause paralysis of the phrenic nerve
*causes of the fracture of the spine:
(1) direct violence –blow from back, fall, collision
(2) Indirect violence – fall on feet, buttocks, forcible
bending of the body, twist of the body
b. Concussion of the spine
-occur even without external injuries
-Sx: headache, restlessness, pain in spine, loss of
sexual power, irritability of the bladder
Injuries of Diaphragm
-penetrating wounds cause herniation of organs
2. Injuries in the Chest
Injuries to the chest wall
-easily contused because ribs are superficial
-stab wounds are common
-rib fracture: pain in respiration
Causes of rib fracture:
a. direct violence – blow, stab, bullet
b. indirect violence- fracture is not at the site of
application of force
-crush injuries, pressure on the chest
-usually mid-axillary
-usual site of fracture of sternum is the junction of
the manubrium and gladiolus, usually transverse
-sternum fracture is associated with laceration of the
pericardium and heart injury
3. Abdominal Injuries
Abdominal Wall
-most vulnerable: point of attachment of organs,
source of blood supply, point where vessels change
direction
-triangle in the middle superior half of the abdomen:
bounded by the ribs on both sides and horizontal
line through the umbilicus is prone to trauma
Stomach-gastric ulcer or new growth causes rupture
-rupture most frequent in pyloric end and greater
curvature
Intestine-cause of death: peritonitis and hemorrhage
Liver –one of the most vulnerable
-right lobe more frequently involved
-rupture is usually transversely or AP
Spleen –superficial and fragile so involved in trauma
-laceration is common in the hilus
Kidney –right is more vulnerable
-“crush syndrome”:secondary kidney changes in
crush injuries; edema and anuria after crush
Pancreas-fat necrosis after trauma if not death
4. Pelvic injuries
-fracture of pubis is the most common
-urinary bladder may be injured
Urinary Bladder- Sx of rupture include pain in lower
abdomen, bloody urine, muscle rigidity
Uterus-gravid uterus is likely to rupture in trauma
Vagina-laceration is due to sexual act or faulty
instrumentation in criminal abortion