Law-343, Public International Law and Human Rights
advertisement
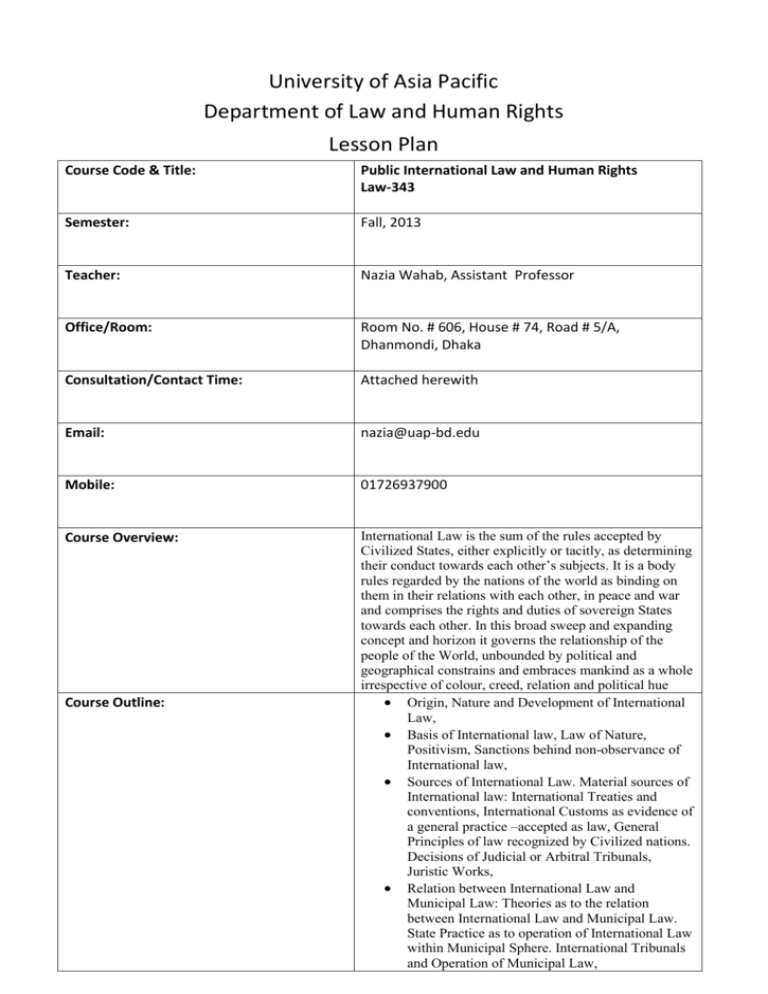
University of Asia Pacific Department of Law and Human Rights Lesson Plan Course Code & Title: Public International Law and Human Rights Law-343 Semester: Fall, 2013 Teacher: Nazia Wahab, Assistant Professor Office/Room: Room No. # 606, House # 74, Road # 5/A, Dhanmondi, Dhaka Consultation/Contact Time: Attached herewith Email: nazia@uap-bd.edu Mobile: 01726937900 Course Overview: International Law is the sum of the rules accepted by Civilized States, either explicitly or tacitly, as determining their conduct towards each other’s subjects. It is a body rules regarded by the nations of the world as binding on them in their relations with each other, in peace and war and comprises the rights and duties of sovereign States towards each other. In this broad sweep and expanding concept and horizon it governs the relationship of the people of the World, unbounded by political and geographical constrains and embraces mankind as a whole irrespective of colour, creed, relation and political hue Origin, Nature and Development of International Law, Basis of International law, Law of Nature, Positivism, Sanctions behind non-observance of International law, Sources of International Law. Material sources of International law: International Treaties and conventions, International Customs as evidence of a general practice –accepted as law, General Principles of law recognized by Civilized nations. Decisions of Judicial or Arbitral Tribunals, Juristic Works, Relation between International Law and Municipal Law: Theories as to the relation between International Law and Municipal Law. State Practice as to operation of International Law within Municipal Sphere. International Tribunals and Operation of Municipal Law, Course Outline: Course objectives: Teaching Method: Prerequisites: Basic Principles of International Law: Codification and progressive development of International Law, The Subject of International Law: States as the Principal Subjects of International Law. Different kinds of States and Non-state Entities. Associations and Grouping States-International person, Elements of State Territory: Modes of Acquisition and losing of state territory. Sovereignty and its limitation over state Territory. International Rivers and their Regions, Rights and Duties of States: Jurisdiction. State Responsibility. State Succession-Rights and Obligations of predecessor and Succession of States. Diplomatic Envoys and consuls. Special Diplomatic Missions. Diplomatic Immunities and privileges, Law and practices as to treaties. Extradition, Asylum; Air aviation law Peaceful and Forcible Settlement of International Disputes-Intervention. War and Neutrality. The United Nation Organization-its Organs. Role of the General Assembly, Security Council and the International court of justice in settling International disputes. Contribution of the United Nations in the Development of International Law. Law of nationality Law of the sea The objective of the course is to engage students in a critical reflection at a theoretical level on the system of general public international law and on fundamental developments in this area. Lecture with visual aids will be the main method of teaching; Classroom exercise, class presentation, group discussion , will be applied during the stipulated time period; Most of the assignments and case studies will be assigned to individual student or to the team(s) within the students; Presentation classes will be conducted to test the comprehensiveness of the learners; The previous day’s lecture will be reviewed in the next class List of prerequisite course(s) to be eligible to take this course Course schedule/ Class schedule Topic Reading assignment We ek Class Date 1 3-5 Nov. Origin, Nature and Development of International Law, 6-7 Nov Basis of International law, Law of Nature, Positivism, Sanctions behind non-observance of International law, 2 10, Nov 12,13 Nov. Sources of International Law. Material sources of International law: International Treaties and conventions, International Customs as evidence of a general practice – accepted as law, General Principles of law recognized by Civilized nations. Decisions of Judicial or Arbitral Tribunals, Juristic Works, 3 17,19 Nov. 4 20, 21, 24 Nov Relation between International Law and Municipal Law: Theories as to the relation between International Law and Municipal Law. State Practice as to operation of International Law within Municipal Sphere. International Tribunals and Operation of Municipal Law The Subject of International Law: States as the Principal Subjects of International Law. Different kinds of States and Non-state Entities. Associations and Grouping StatesInternational person Reading Assignment on assignment sources of to read UN international law charter for sources of international law 26 Nov 5 6 7 27, 28, Nov 1,3Dec Elements of State Territory: Modes of Acquisition and losing of state territory. Sovereignty and its limitation over state Territory. International Rivers and their Regions Previous class task Rights and Duties of States: Jurisdiction. State Responsibility. State Succession-Rights and Obligations of predecessor and Succession of States. Diplomatic Envoys and consuls. Special Diplomatic Missions. Diplomatic Immunities and privileges, Discussion on Sources of Law Previous class task Previous class task Previous class task Previous class task Field trip/plant visit (if any) N/A 4, 5, 8, 10, 11,12 Dec Work assignment Previous class task Class Test 13-21 Dec Review Class Previous class lecture MID TERM EXAM 8 29, 31 Dec 1, 2 Jan Law and practices as to treaties. Previous class task 9 5, 7,8,9 Jan Extradition 10 12, 15, 16 Jan Reading assignment on Extradition Act, 1974 Reading assignment to read the case Colombia vs Peru 11 19, 21 Jan 12 22,23,26 Jan Asylum Air aviation law Peaceful and Forcible Settlement of International Disputes-Intervention. War and Neutrality. The United Nation Organization-its Organs. Role of the General Assembly, Security Council and the International court of justice in settling International disputes. Contribution of the United Nations in the Development of International Law Previous class task Previous class task 28 Jan 13 29,31 Jan-2 Feb 14 4-5 Jan 6-13 Class Test Law of the sea Law of nationality Draw picture of different part of the sea Reading assignment on read the statutory law on nationality of Bangladesh Assignment on Law of the sea Review Class FINAL EXAM (23 Feb-8 March) Basic text(s): 1. Public International Law: M.P Tandon & Rajesh Tandon 2. International Law-Arif Khan 3. International Law and Human Rights-Dr. S.K kapoor 4. International Law: Dr. Mizanur Rahman 5. Others: as prescribed in the prospectus. Reference text(s): Additional reading material: Assessment / Assignment Methods: Marks for assessment will be given by the course teacher through class tests, quizzes, assignments, presentation, class performance, class attendance etc. There should be at least (n+1) where ‘n’ is the number of class tests for a course. The course teacher must submit a copy of marks of Assessment (mentioning the fractions in class tests, quizzes etc.) of his course to the Head of the respective departments. Grading Systems: Introduction to international Law, J.G Starke, Thenth Edition 1. Charter of the United Nations and statute of the International court of Justice 2. Others necessary statue of Bangladesh. Assessment: 30 %(Assessment Marks 30 includes: Class test/ Assignment 10+ Class attendance 10 + Class performance & Viva voce 10.) Mid-Semester Examination: 20% Semester Final Examination: 50% Total:100% Each course has a letter grade equivalent to a certain number of grade points. Letter grades and their corresponding grade points are as follows: Letter Grade Grade Point 80% and above A+ 4.00 75% to less than 80% A 3.75 70% to less than 75% A+ 3.50 65% to less than 70% B+ 3.25 60% to less than 65% B 3.00 55% to less than 60% B- 2.75 50% to less than 55% C+ 2.50 45% to less than 50% C 2.25 40% to less than 45% D 2.00 Less than 40% F 0.00 Exemption E -- Incomplete I -- Satisfactory S -- Numerical Grade Students’ responsibilities: Course content: Course Teacher reserves the right to make necessary changes in the course content depending on the process of the class. Class Makeup: In case of unavoidable circumstances student should attend lecture or exam. In addition student will be offered a makeup. All make up classes will be held as per rescheduling (Nazia Wahab) Asst. Professor Department of Law and Human Rights The University of Asia pacific suggested by the course Teacher with assistance of Department Office. Exam Make Up: There will be no makeup of any exam. Under special circumstance with consultation of the concerned faculty member student will get a chance for sit for a repeat exam. Academic code of conduct: Any academic misconduct will be dealt according to the provision of Students’ Code of Conduct. Consultation Hour: Students are most welcome to make appointment at the time convenient to both the teacher and students.









