tpj12567-sup-0001-FigS1-S7
advertisement
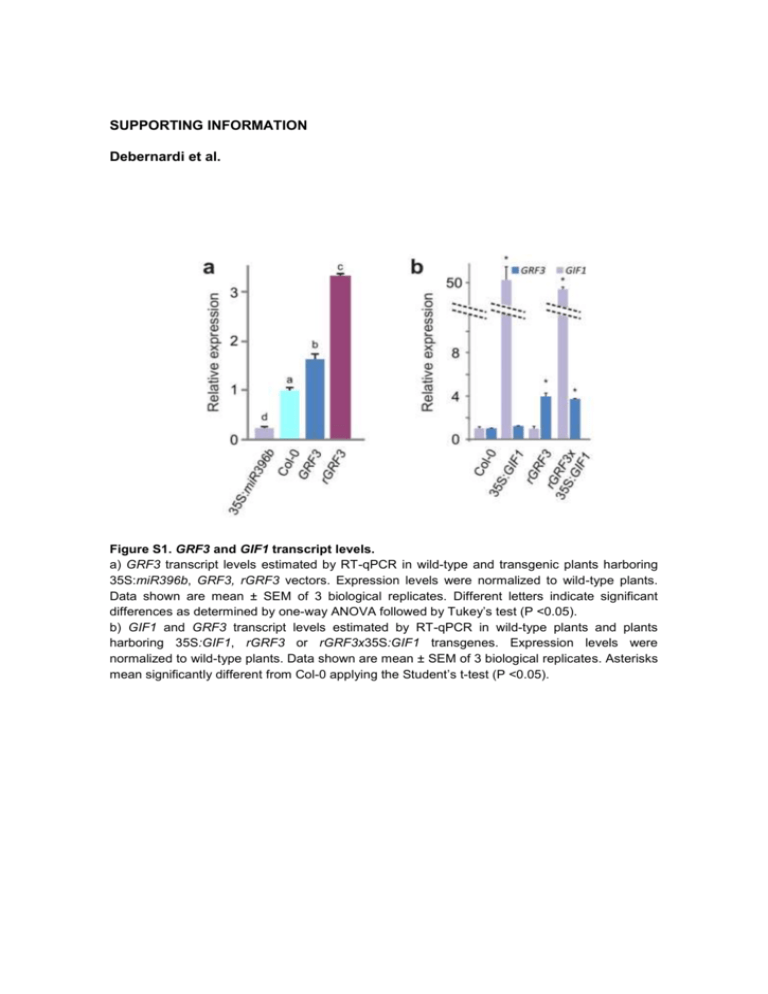
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Debernardi et al. Figure S1. GRF3 and GIF1 transcript levels. a) GRF3 transcript levels estimated by RT-qPCR in wild-type and transgenic plants harboring 35S:miR396b, GRF3, rGRF3 vectors. Expression levels were normalized to wild-type plants. Data shown are mean ± SEM of 3 biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test (P <0.05). b) GIF1 and GRF3 transcript levels estimated by RT-qPCR in wild-type plants and plants harboring 35S:GIF1, rGRF3 or rGRF3x35S:GIF1 transgenes. Expression levels were normalized to wild-type plants. Data shown are mean ± SEM of 3 biological replicates. Asterisks mean significantly different from Col-0 applying the Student’s t-test (P <0.05). Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S2. Genetic interaction between GIF1 and GRF5. a) Area of fully expanded first leaves of wild-type (Col-0), RolD:GIF1 crossed with 35S:GRF5, and heterozygous control plants. Error bars are SEM (n ≥ 14). Different letters indicate significant differences as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test (P <0.05). b) Area of fully expanded first leaves of an3-4 and Col-0 plants transformed or not with a 35S:GRF5 vector. Error bars are SEM (n ≥ 14). Different letters indicate significant differences as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test (P <0.05). c) GRF5 and GIF1 transcript levels determined by RT-qPCR in wild-type and plants transformed with 35S:GRF5, RolD:GIF1 vectors, and an3-4 mutants transformed with 35S:GRF5. Expression levels were normalized to wild-type plants. Data shown are mean ± SEM of 3 biological replicates. Asterisks mean significantly different from Col-0 applying the Student’s ttest (P <0.05). nd= non detected. 2 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S3. Functions of GRF3 in the absence of GIF1. a) Area of fully expanded first leaves of T1 S96 or an3-1 plants expressing rGRF3 from its own promoter (n= 30). b) Dark induced senescence in T1 plants (third leaves), after one and five days being in the dark. Note that an3-1/rGRF3 leaves have smaller size than the control S96, but senescence later. Scale= 1cm. c) GRF3 and GIF1 transcript levels estimated by RT-qPCR in selected T2 lines of an3-1 and S96 plants transformed with rGRF3. Expression levels were normalized to wild-type plants. Data shown are mean ± SEM of 3 biological replicates. Asterisks mean significantly different from S96 applying the Student’s t-test (P <0.05). ND= non detected. 3 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S4. Genes repressed by overexpression of GRF3 and/or GIF1. a) Genes repressed in rGRF3, 35S:GIF1 and rGRF3x35S:GIF1 plants. b) Genes repressed in (A) clustered according to their expression pattern. 4 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S5. Leaf senescence of 35S:GRF5 plants and grf3 and grf5 mutants. a) Wild-type (Col-0) and 35S:GRF5 50 day-old rosettes. b) Measurements of photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) of PSII in detached leaves of wild-type, 35S:miR396b, and grf5-1 and grf3-1 mutant lines. 5 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S6. Response of hormone regulated genes in 35S:GIF1, rGRF3 and rGRF3x35S:GIF1 microarrays a) Average log2 expression of hormone responsive gene lists in 35S:GIF1, rGRF3, rGRF3x35S:GIF1 microarrays. A number at the top-left of the boxes indicates the number of genes in each list. ACC, ethylene; CK, cytokinin; IAA, auxin, GA, gibberellin; BL, brassinolide; 6 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network ABA, abscisic acid; Up genes up-regulated by the hormone; Down, genes down-regulated by the hormone. See Nemhauser et al. (Cell 2006) for details 7 Debernardi et al. Functions of the miR396-GRF-GIF network Figure S7. Missexpression of GRF3. a) GRF3 transcript levels estimated by RT-qPCR in apices of wild-type and selected T2 plants transformed with rGRF3 (GRF3:rGRF3), AS1:rGRF3 and ANT:rGRF3 vectors. Expression levels were normalized to wild-type plants. Data shown are mean ± SEM of 3 biological replicates. Asterisks mean significantly different from Col-0 applying the Student’s t-test (P <0.05). b) Leaf area at different days after sowing (DAS) of the first leaves. c) Cell area of mature first leaves. 8