Gr. 5 FCAT 2.0 Content Focus Big Idea 7 2012-2015
advertisement
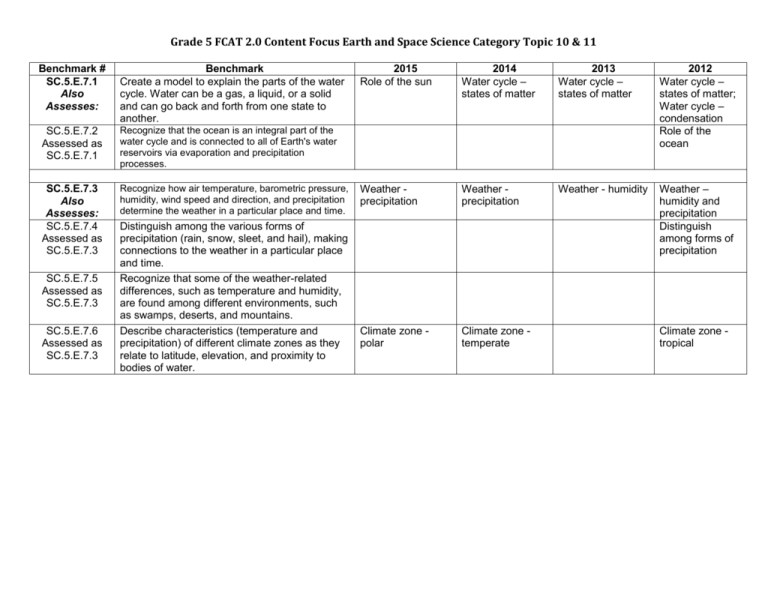
Grade 5 FCAT 2.0 Content Focus Earth and Space Science Category Topic 10 & 11 Benchmark # SC.5.E.7.1 Also Assesses: Benchmark Create a model to explain the parts of the water cycle. Water can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid and can go back and forth from one state to another. SC.5.E.7.2 Assessed as SC.5.E.7.1 Recognize that the ocean is an integral part of the water cycle and is connected to all of Earth's water reservoirs via evaporation and precipitation processes. SC.5.E.7.3 Also Assesses: SC.5.E.7.4 Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3 Recognize how air temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, wind speed and direction, and precipitation determine the weather in a particular place and time. SC.5.E.7.5 Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3 SC.5.E.7.6 Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3 Distinguish among the various forms of precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, and hail), making connections to the weather in a particular place and time. Recognize that some of the weather-related differences, such as temperature and humidity, are found among different environments, such as swamps, deserts, and mountains. Describe characteristics (temperature and precipitation) of different climate zones as they relate to latitude, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water. 2015 Role of the sun 2014 Water cycle – states of matter 2013 Water cycle – states of matter 2012 Water cycle – states of matter; Water cycle – condensation Role of the ocean Weather precipitation Weather precipitation Weather - humidity Weather – humidity and precipitation Distinguish among forms of precipitation Climate zone polar Climate zone temperate Climate zone tropical