Chapter 6
advertisement

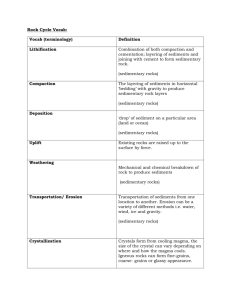
1 Chapter 6 Rocks Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Three Major Types of Rocks 1. Igneous _________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 2. Sedimentary - ________________________________________ Types of sediments 1. rock fragments 2. plant and animal remains 3. chemicals (water) 3. Metamorphic - _______________________________________ Rock Cycle - any rock can become either: Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic depending on how it is influenced by the environment. 2 Properties of Rocks Bowens Reaction Canadian geologist in 1928 proposed a hypothesis on the formation of minerals. As the magma cools different minerals can form. Chemical Stability of Minerals Physical Stability of Rocks Section 2 Igneous Rocks Formation of Magma Magma __________________________________________________ Lava _________________________________________________ 3 Textures of Igneous Rocks 1. _____________ - formed outside the earth's crust from lava. ____________ exited from the earth 2. ______________ - formed within the crust from the magma. ____________ inside the earth TEXTURE depends on the size of the rock crystals. The rate of cooling determines crystal size. a. Intrusive _________ cooling - ___________ mineral grains (plutonic after the Roman God of the underground Pluto) ex. __________ - course grained b. Extrusive cools _________ - ___________ mineral grains (volcanic) ex. __________- fine grained 4 c. intermediate cools ________________________________ ex. Obsidian Vesicular ____________________________________________________ PORPHYRY - (Por Fi Ree) - rocks with two textures a. One mineral solidifies - forms large crystals b. The other mineral solidifies later - there is less room - therefore the crystals are smaller. 5 Intrusive Igneous Rocks Batholiths and Stocks _________________________ Large igneous intrusions at least 100kms. Forms mountain bases like Sierra Nevada in Cal. _________________________ Smaller than 100kms _________________________ When magma pushed up between rock layers, if forms a dome Black Hill of South Dakota Sills and Dikes ______________ are parallel layers, small area between layers ______________ cut across rock layers Intrusive Igneous Rocks When lava hardens on the surface. 6 Composition of Igneous Rocks ___________________ High silica acid type of magma. NOT much Ca, Fe or Mg only light colored Si. Mostly intrusive magma - slow thick - does not reach the surface easily. Forms granite, quartz, orthoclase feldspar. ___________________ Low Si concentrations High in Ca, Fe and Mg Much hotter - easier to flow to the surface, extrusive Forms basalt and gabbro ___________________ Made up of mostly plagioclase feldspar, hornblende, pyroxene, and biotite mica. Diorite and andesite 7 Section 3 Sedimentary Rocks Formed from sediments bound together in some way Formation of Sedimentary Rocks Compaction ______________________________________________________. Cementation ____________________________________________________. These cements enter the pore spaces between sediments. They glue them together to make a clastic sediment rock Types of cement: 1. Silica - from weathered quartz - grey or white 2. Lime - from weathered calcite - grey or white 3. Iron - from weathered Fe containing rock - red or brown 4. Pressure can act as a cement in clay and silt. Chemical Sedimentary Rock Forming Chemically Derived Sedimentary Rocks __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Limestone tiny grains of calcite deposited in the seas or lakes. Grey or tan in color. Smooth and dense. 8 Rock Salt - table salt - made of mineral Halite. Forms when salt water dries up, the salt is left behind. Found in thick layers around the world. Gypsum Found in layers around the world. Formed from mineral gypsum. Organic Formed from remains of once living organisms (plants and animals) Coal- plant remains Fossil limestone 9 Chert Clastic Sedimentary rocks 1. Fragments must come from pre-existing rocks 2. Fragments come from weathering and erosion agents: ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 3. Fragment sizes - ______________________________________ _________________________________________________ 4. Fragments need to be cemented together to make rocks. Conglomerate - very course mixture of rounded pebbles and sand of various different sediment types (breccia is angular fragments). Sand Stone - grains of quartz cemented together. Very porous with a lot of small holes or openings. Permeable, able to absorb water. 10 Shale - tiny flakes of kaolin (clay). Held together by pressure, not cement. Very tiny holes, cannot absorb water. Smooth and easily broken. Characteristics of Clastic Sediments The characteristics of the sediments are determined by the way they are transported and deposited. 4 ways sediments are transported 1. Water 2. Ice 3. Wind 4. Gravity Sorting 11 River Deposits A river's motion causes it to carry sediment. When the river slows it cannot carry its sediments. Sediments fall to the bottom. Angularity Not rounded sediments. Broken and sharper edges. Sedimentary Rock Features 1. __________ - visible layers (beds) within rocks or rock structures. This layering is caused by changes in the rock materials. ex. a layer of Sand a layer of Clay a layer of Silt 2. _________________________________ Cross bedding - bedding layers formed near or on sand dunes or river delta's - not flat but slanted Graded Beds - different types of materials deposited within a layer 3. _____________________________ Caused when wind or water left a mark on the sandy surface and hardened. 12 4. _______________________________________ Occur when clay and silt dry, they contract and spaces form. These spaces can get buried and become rock. 5. Fossils and Concretions _______________________ Are remains, impressions or other evidence of existing plants and animals preserved in rocks. *Only Found in Sedimentary Rocks!!!! Animal dies - bone does not decay, it gets buried. Rock eventually decays but a hole is left. The hole fills in with minerals, the minerals harden, a fossil is formed. _________________ - nodules or "lumps" of fine grained silica. Chert - name of silica Flint - dark grey or black chert ______________Limestone with hollow spheres that are lined with quartz or calcite crystals. Limestone middle dissolves in water, then the water deposits quartz or calcite. 13 Section 4 METAMORPHIC ROCKS Are made from existing rocks by the action of: 1. __________________________ 2. __________________________ 3. __________________________ Formation of Metamorphic Rock _____________________________ 1. hot magma moves into rocks, heating and changing in 2. occurs in a small area 3. chemical change occurs by rearranging the minerals forming a new rock. 4. the rock does not melt, it is rearranged. _______________________________________ major source of metamorphic rock. Occurs in large areas, often associated with mountain building. Classification of Metamorphic Rock Properties of metamorphic rock depend on the parent rock or the minerals in the original rock. The parent rock’s characteristics and traits can be seen in certain metamorphic rocks. 14 Foliated Rocks 1. ___________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________ 3. Include Slate Schist Gneiss 15 Nonfoliated Rocks ____________________________________________________ Distortion or deformation: 1. ___________________________________________ 2. sedimentary rock gets laid down in horizontal layers 3. they get buried deep within the earth and are subjected to low heat and pressure; like where there is a fault line. 4. grains of rock get squeezed together and the heat rearranges minerals - a new different rock is formed. Quartzite Marble 16