Second Grade STEM Lesson 6 Twirlers Design Challenge
advertisement
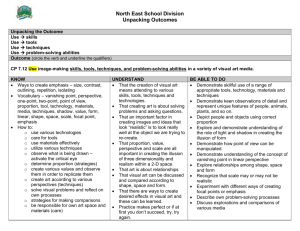
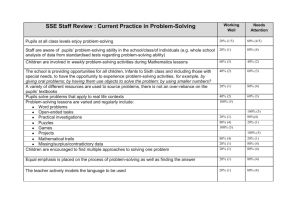
Second Grade STEM Investigation – Part 6 Twirlers Area of Focus Explanation Overview This lesson would follow Investigation 2, part 3 in FOSS Balance and Motion. Students will experience the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process using twirlers. The challenge is to build a twirler that will land safely, with the slowest descent. They will compete against other teams to design the slowest falling twirler. In the process, students will consider the limitations of the materials, gather information, make a plan, test the designs, redesign and communicate the results. Standards Science: 2-3 APPB Use science knowledge to help solve a problem. 2-3 APPD Explain why certain tools and materials were chosen to solve the problem. 2-3 APPE Evaluate how well tools and materials worked in solving the problem. CCSS ELA: 2 SL.1 Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about grade 2 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. Learning Targets I explain and describe steps of the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process in the twirlers investigation. Assessment Science Notebooks Materials Teacher: stopwatch, materials for wings including paper of various thickness (tag, cardstock, construction paper, etc.), aluminum foil, plastic (overhead projector sheets), different size paper clips, pennies (for weight), tape For each student: 1 jumbo straw 1 pair of scissors Transparent tape Vocabulary 1 Paper clip Recording Template, Twirler Challenge Twirler, wing, air resistance Area of Focus Explanation Review the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process Engage Ask students to think about and write in their notebooks about one example of the Engineering Design Process that they experienced either in the marshmallow challenge or the rolling wheel challenge. Ask students to turn to a partner and share their ideas. Introduce the Challenge Explore Explain that today they will be experiencing the design process with a partner 1 Teacher Notes Consider intentionally partnering students. Twirler Sharing Engineering Design Process Formative Assessment ASSESSING THE DESIGN PROCESS How could you design a twirler that would slowly and safely descend to the ground? Think about what you have already learned about building the twirlers and twirlers, what materials could you use to build a better twirler? How would you measure the slowest descent? How will we measure whose twirler traveled the slowest? Present the extra materials for use, including different thicknesses of paper, plastic, aluminum foil, paperclips, pennies, and tape. Remind students that they need to make a drawing of their design and a materials list before collecting materials. Ask if students have any questions, then let them begin. If students come up with different ideas for materials and you can provide them, allow it. Visit student pairs as they are working. Set up drop points in the classroom where student can drop twirlers at the same time and observe the descent. Explain Allow time for each team to share their twirler Ask each team to describe a challenging point in the process and reasons behind their choices of materials/design. Test all twirlers, measuring the descent with a stopwatch. Record results on chart paper. Discuss successes and failures. Why did some work better than others? Allow time to redesign and test again. Follow same process as above. Post the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process and discuss which steps were experienced in this challenge. Evaluate Have students return to their science notebooks and write about one part of the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process they used during this challenge. Ask them to write about any new ideas and/or redesigns they have for building a twirler in the future. 2 Create a public record and record student responses. Additional Resources and Ideas Elaborate Consider recording student teams as they are building their structures, viewing later and asking students to identify steps in the Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process. Wing Project: Overview 1 of 2 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HW7eq155QJE Engineering Problem-Solving/Design Process 1. Ask a question or define the problem 2. Gather information --research and learn 3. Imagine and Explore ideas --brainstorm ideas 4. Make a plan --draw a diagram --develop one of your ideas --consider the materials you will need 5. Create and Test --Follow your plan and test the solution. 6. Improve your design --Test it out! 3