SSE Staff Review : Current Practice in Problem-Solving
advertisement
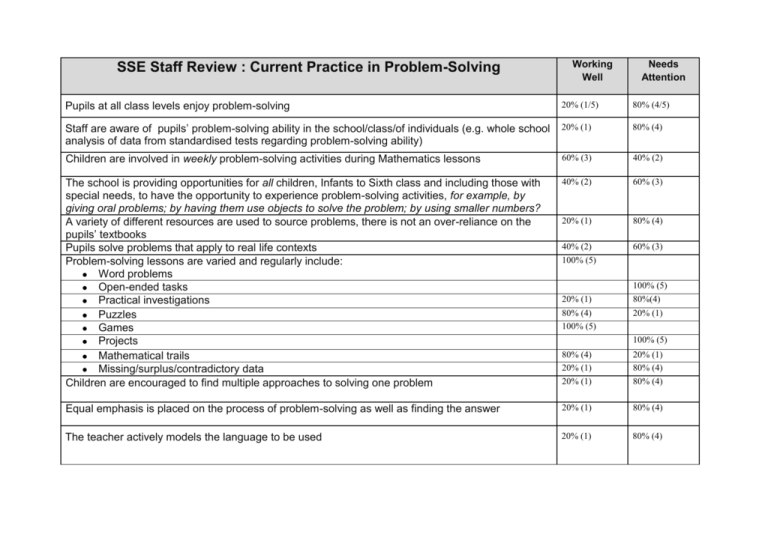
SSE Staff Review : Current Practice in Problem-Solving Working Well Needs Attention Pupils at all class levels enjoy problem-solving 20% (1/5) 80% (4/5) Staff are aware of pupils’ problem-solving ability in the school/class/of individuals (e.g. whole school analysis of data from standardised tests regarding problem-solving ability) 20% (1) 80% (4) Children are involved in weekly problem-solving activities during Mathematics lessons 60% (3) 40% (2) The school is providing opportunities for all children, Infants to Sixth class and including those with special needs, to have the opportunity to experience problem-solving activities, for example, by giving oral problems; by having them use objects to solve the problem; by using smaller numbers? A variety of different resources are used to source problems, there is not an over-reliance on the pupils’ textbooks Pupils solve problems that apply to real life contexts Problem-solving lessons are varied and regularly include: ● Word problems ● Open-ended tasks ● Practical investigations ● Puzzles ● Games ● Projects ● Mathematical trails ● Missing/surplus/contradictory data Children are encouraged to find multiple approaches to solving one problem 40% (2) 60% (3) 20% (1) 80% (4) 40% (2) 100% (5) 60% (3) 20% (1) 80% (4) 100% (5) 100% (5) 80%(4) 20% (1) 100% (5) 80% (4) 20% (1) 20% (1) 80% (4) 20% (1) 80% (4) Equal emphasis is placed on the process of problem-solving as well as finding the answer 20% (1) 80% (4) The teacher actively models the language to be used 20% (1) 80% (4) The teacher supports children in communicating/sharing their problem-solving strategies/approaches 20% (1) 80% (4) Opportunities are provided for pupils to explain how they got the answer to a problem and discuss alternative ways of approaching a problem thus giving them opportunities to practice thinking about mathematical ideas 100% Children are encouraged to listen to the views of others when solving problems and to accept the reasoning of others in order to solve problems co-operatively (constructivist approach) Opportunities to develop problem-solving in a cross curricular way are explored 100% 40% (2) 60% (3) ICT’s opportunities are used / explored as an integral part of problem-solving activities 20% (1) 80% (4) In terms of learning problem solving, do you teach problem solving strategies by moving from concrete work, to pictorial work to abstract work? 20% (1) 80% (4) *For training purposes only*