Photosynthesis Study Guide
advertisement

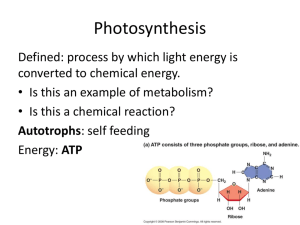
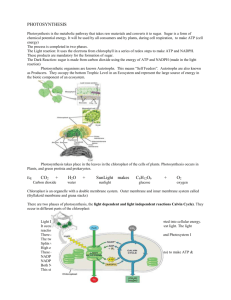
BIOLOGY / Chapter 6 Photosynthesis Study Guide **This study guide is meant as a GUIDE. It is not a substitute to studying the notes or learning the vocabulary or completing the review sheet. ** Energy flows from the sun and through all life on earth. Autotrophs use the sun to make food directly while heterotrophs must consume other organisms for food. ATP (energy) stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. Photosynthesis is the process where plants use the sun’s energy to make food. Photosynthesis: Stores energy from sunlight in glucose molecules Know the equation: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + (light) energy C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight (energy) Glucose + Oxygen Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts where plant pigments absorb light. Explain photosynthesis as a biochemical pathway. Understand light, temperature and CO2 all affect the rate of photosynthesis Review the visible light spectrum – i.e. different wavelengths produce different colors; colors are a reflection of that wavelength. Chlorophyll is the main pigment involved in photosynthesis, absorbing red and blue light and reflecting green (why plants look green). o Accessory pigments (i.e. carotenoid) are also involved in helping to capture light. o During autumn, as the chlorophyll breaks down, the other pigments become visible, changing the colors of the leaves. Identify the difference between autotrophs and hetertrophs Review the structure of the chloroplast. Pay special attention to the labeled parts. Thylakoid Remember the components of the Chromatography lab – The lab was performed to identify plant pigments by separation and isolation of the pigments using thin layer paper chromatography. The distance traveled by a particular compound can be used to identify the compound. The ratio of the distance traveled by a compound to that of the solvent front is known as the Rf value; unknown compounds may be identified by comparing their Rf's to the Rf's of known standards. **Know the Rf equation: Rf = Distance of pigment / Distance of solvent Know All the molecular “Players” in both the Light dependent reaction and the Calvin Cycle (light independent reaction) For example: Where each takes place (i.e the light reaction takes place along the thylokoid membrane. The light-dependent reactions uses solar power to generate ATP and NADPH2, which provide energy to the sugar-making reactions of the Calvin cycle. **A by-product of the light-dependent reactions is oxygen. Calvin Cycle or Dark reactions (AKA Carbon fixation) – Takes place in the stroma. The reactants are ATP, CO2, and NADPH from the Light Dependent Reactions. Product is glucose. Some intermediate molecules to knoe are PGA (3 carbon molecule), PGAL, RuBP (5- carbon) PGAL – the 3 carbon molecule that leaves the cycle and produces glucose (organic compound) Review the following vocabulary terms in detail: ATP synthase, chemiosmosis, chlorophyll, caratenoids, pigments, stomata, electron transport chain, photosystem I & II, DIAGRAM: Photosynthesis Overview 3 PGAL Overview of Diagram: An equation for light reaction is: ADP + NADP + H2O → ATP +NADPH + H ion + O2 An equation for dark reaction is: ATP + NADPH + CO2 → ADP + NADP + glucose. Know why C4, C3 and CAM plants perform photosynthesis differently.