Laparoscopic Urogynaecology Module
advertisement

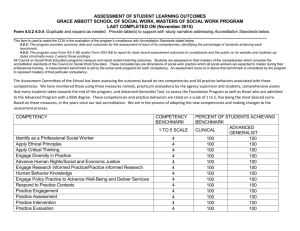
Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Optional Laparoscopic Urogynaecology Introduction: This optional module is designed to provide training in laparoscopic urogynaecology. It is intended to be completed with the subspecialty training programme in urogynaecology. Successful completion will provide a clinical foundation to offer laparoscopic urogynaecology procedures for managing women with pelvic floor dysfunction. Practitioners should demonstrate a commitment to providing laparoscopic urogynaecology care as part of a comprehensive subspecialist urogynaecology service. Learning outcomes: To be able to select patients who are suitable to be offered laparoscopic urogynaecology To have a thorough knowledge of the equipment and resources required to deliver safe laparoscopic surgical care including different energy sources To be able to counsel patients on the benefits, risks and complications of laparoscopic procedures and obtain consent To undertake laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy and sacrohysteropexy To have the opportunity to observe other laparoscopic urogynaecology procedures To understand regional referral pathways for complex and recurrent cases To be able to use evidence-based guidelines and write new guidelines when needed 1 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Section 1: Preparation for surgery Knowledge criteria Patient selection: ASA score / fitness Assessment of suitability of condition for laparoscopic surgery Knowledge of appropriate preoperative investigations Knowledge of appropriate alternative opitons Effect of previous surgery Impact of body mass Thorough counselling / consent of woman: Alternatives Risks GMP Clinical competency 1 Appropriately select suitable patients Use of synthetic mesh Properties of mesh Counsel regarding mesh complications including infection, erosion and extrusion Auditing surgical outcomes GMP Understand importance of appropriate selection of woman Have an understanding of how history, investigations and careful counselling impact on patient selection Professional skills and attitudes Able to exhibit knowledge of selection criteria Able to apply knowledge of patient selection criteria to clinical situation GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Tailored clinical experience under supervision Case logbook including complications CbD Observation of, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff MSF (TO1 and TO2) Personal study Appropriate postgraduate education courses Select appropriate mesh and counsel patient regarding benefits and risks of mesh use Able to apply up to date knowledge and guidelines to mesh selection and use Uses BSUG audit database Commitment to audit of procedures according to guidelines Appropriate guidelines and articles on mesh use Support for BSUG database Recorded outcome on BSUG database 2 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Section 2: Surgical procedures and skills Learning outcomes: To be able to perform and understand the place of the following: Appropriate laparoscopic entry techniques - Hassan - Palmer’s point - Non-standard placement of ports Safe use of appropriate energy source Suturing Knot tying - Intra-corporeal - Extra-corporeal Tests for bladder and bowel integrity Recognise and initially manage complications: - Urinary tract - Gastrointestinal tract - Haemorrhage - Late complications Knowledge criteria GMP Knowledge of relevant anatomy including anatomy of sacral promontory Clinical competency GMP Proficiency in Hassan and Palmer’s point entry techniques Ability to perform procedure GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Appropriate reading and courses MSF (TO1 and TO2) Understand the principles underlying these techniques Safe laparoscopic entry and choosing correct entry for each patients including use of veress needle, open entry, direct vision entry, palmer’s point entry Understand the principles of electrosurgery, ultrasound and other future energy sources Professional skills and attitudes Log of experience and competence CbD Be able to demonstrate ability to use bipolar effectively and have at least one energy source used for cutting i.e monopolar or ultrasound. Have an understanding of the principles underlying all the others Ability to safely perform these procedures and a thorough understanding of the safety checks required before activating the energy source Tailored clinical experience and appropriate theoretical training Trouble shooting Understand the principles of port site closure and the need to avoid port site hernia or damage underlying structures Ability to safely close port sites using appropriate needles and sutures Ability to close port sites Tailored clinical experience and practice OSATS for Palmer’s point and Hassan 3 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Knowledge criteria GMP Ability to competently suture using laparoscopic needle holders Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Proficiency in competently suturing and tying the appropriate surgical knots Ability to perform these procedures Tailored clinical experience and practice OSATS knot tying Ability to carry out visual inspection of bowel, carry out air insufflation and dye tests. Ability to check integrity of bladder using visual inspection and dye tests. Ability to perform these procedures Tailored clinical experience and practice OSATS Ability to undertake primary bladder closure when appropriate Ability to perform primary bladder repair when appropriate Tailored clinical experience and practice CbD Understand principles of ureteric anastomosis Understand the principles procedures Ability to control major haemorrhage until appropriate help available and understand the principles underlying the repair of major vessels Understand the principles underlying the repair of major vessels underlying these Recognition of delayed onset complications such as peritonitis, ileus, faecal contamination or urinary leakage Recognition of the signs and symptoms of intraabdominal trauma and the use of appropriate investigations Ability to recognise and deal with intraabdominal trauma Tailored clinical experience and practice CbD The ability to start appropriate initial management and understand the principles of subsequent management The ability to seek appropriate support e.g General Surgeon, Urologist, Intensive Care Specialist Ability to undertake intra-corporeal and extracorporeal knot tying Ability to inspect bladder, ureter, small and large bowel for perforation or damage, recognition of this and undertake appropriate special tests such as air insufflation and use of dyes Ability to visually check the ureter through its pelvic course and pass the appropriate ureteric catheter Recognition of bowel and bladder complications, assessment of these and ability if appropriate to perform primary repair, involving other surgical specialities as appropriate Understand the principles of more complex repairs such as segmental bowel resection and ureteric anastamosis and reimplantation Recognise and be able to control haemorrhage 4 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Competence level Not required Laparoscopic Urgoynaecology Logbook Level 1 Date Level 2 Signature Date Signature Level 3 Date Signature Section 1: Preparation for surgery Patient selection Surgical audit Section 2: Surgical procedures and skills Knowledge of anatomy Laparoscopic entry and closure Safe use of energy sources Suturing and knot tying Intra-operative management of complications Postoperative care and management of complications Perform laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy Perform laparoscopic sacrohysteropexy 5 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies Training Courses or sessions Date Title Signature of educational supervisor Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer 6 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust Key: Common competency framework competencies Medical leadership framework competencies Health inequality framework competencies COMPLETION OF Laparoscopic Urogynaecology Module I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of educational supervisor Signature of educational supervisor 7 GMC approved as of 15 April 2015 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, skills and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust